Pharmacognosy 2018
American Journal of Ethnomedicine
ISSN: 2348-9502
Page 48
April 16-17, 2018
Amsterdam, Netherlands
6
th
Edition of International Conference on
Pharmacognosy and
Medicinal Plants
Statement of the Problem:
Diabetes is now one of the major
health problems prevailing in the world. Diabetic people have
been treated with conventional synthetic drugs for a long time
result in many side effects. Therefore, the search for more
effective and safer anti-diabetic agents derived from plants has
become an interest area of active research. Today millions of
people use herbs either with prescription and non-prescription
medications; the increasing use means that there is potential
for more interactions between herbal products and conventional
medicines; causing either potentially dangerous side effects
and/or reduced benefits from the medication. As the incidence
and severity of herb-drug interactions is increasing due to a
worldwide rise in the use of herbal preparations, more research
regarding herb-drug interactions are needed. The purpose of this
study is to investigate the hypoglycemic effect of
Allium sativum
bulbs growing in Sudan, and to determine their interaction with
metformin drug used in diabetes treatment.
Methodology:
The Soxhlet apparatus was utilized during
extractions. The hypoglycemic effects were evaluated
in vitro
and
in vivo
by glucose reuptake using isolated rats hemi-diaphgrams
tissue and by estimate glucose tolerance in glucose-loaded
Wistar rats. GC-MS was used for chemical analysis.
Findings:
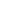
The
A. sativum
extracts in this study have
in vitro
hypoglycemic effect on rat’s hemi-diaphgrams tissue. Petroleum
ether extract has the highest effect, even more than metformin
due to the presence of well-known anti-diabetic compounds; its
effect was reduced followingmetformin combination. Chloroform
extract has activity less than petroleum ether, but still more than
metformin; its combination also showed an antagonistic action.
The ethyl acetate extract effect is less than chloroform and was
reduced with combination. Methanolic extract has less activity
than ethyl acetate and was not affected with combination. The
lowest effect was obtainedwhen ethanoic crude extract was used;
combination potentiates its effect but is still less than metformin.
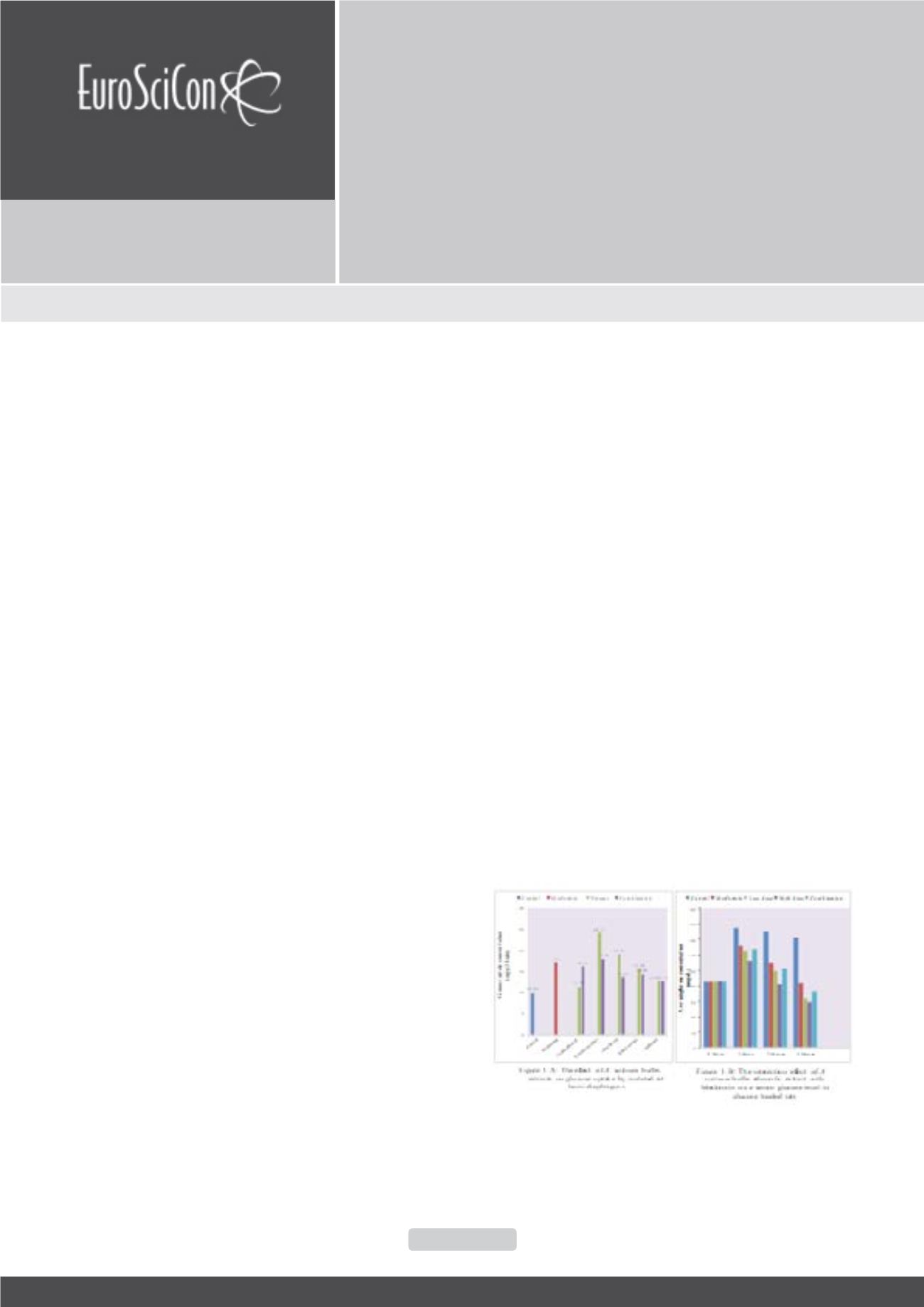
Petroleum ether extract has
in vivo
hypoglysimic effect greater
than metformin drug; decreased with metformin combination.
Conclusion & Significance:
The extract alone was significantly
anti- diabetic agent; the effectiveness was decreased with
Metformin combination.
Recommendations:
Further studies are required to elucidate the
mechanisms of interactions.
Anti-hyperglycemic effect of the extracts of Allium sativum
bulbs growing in Sudan: with and without metformin drug in
diabetes treatment
Ikram Mohamed Eltayeb
and
Amina Djamila Yacouba
University of Medical Sciences and Technology, Sudan
Ikram Mohamed Eltayeb et al., Am J Ethnomed 2018, Volume 5
DOI: 10.21767/2348-9502-C1-005