Notes:
Volume 3, Issue 2
Insights in Analytical Electrochemistry
ISSN: 2470-9867
Analytical Chemistry-Formulation 2017
August 28-30, 2017
Page 23
8
th
Annual Congress on
&
14
th
International Conference and Exhibition on
August 28-30, 2017 Brussels, Belgium
Analytical and Bioanalytical Techniques
Pharmaceutical Formulations
Cyclodextrin-based formulations: The present and the future
Tamas Sohajda
and
Lajos Szente
Cyclolab Ltd., Hungary
C
yclodextrins (CDs) are “cone-shaped” cyclic oligosaccharides, with a hydrophobic cavity and hydrophilic outer surface.
These nanoscale substances have long been used as functional excipients in different pharmaceuticals due to their ability to
encapsulate drugs and alter their disadvantageous features, e.g. increase the aqueous solubility, improve bioavailability, enhance
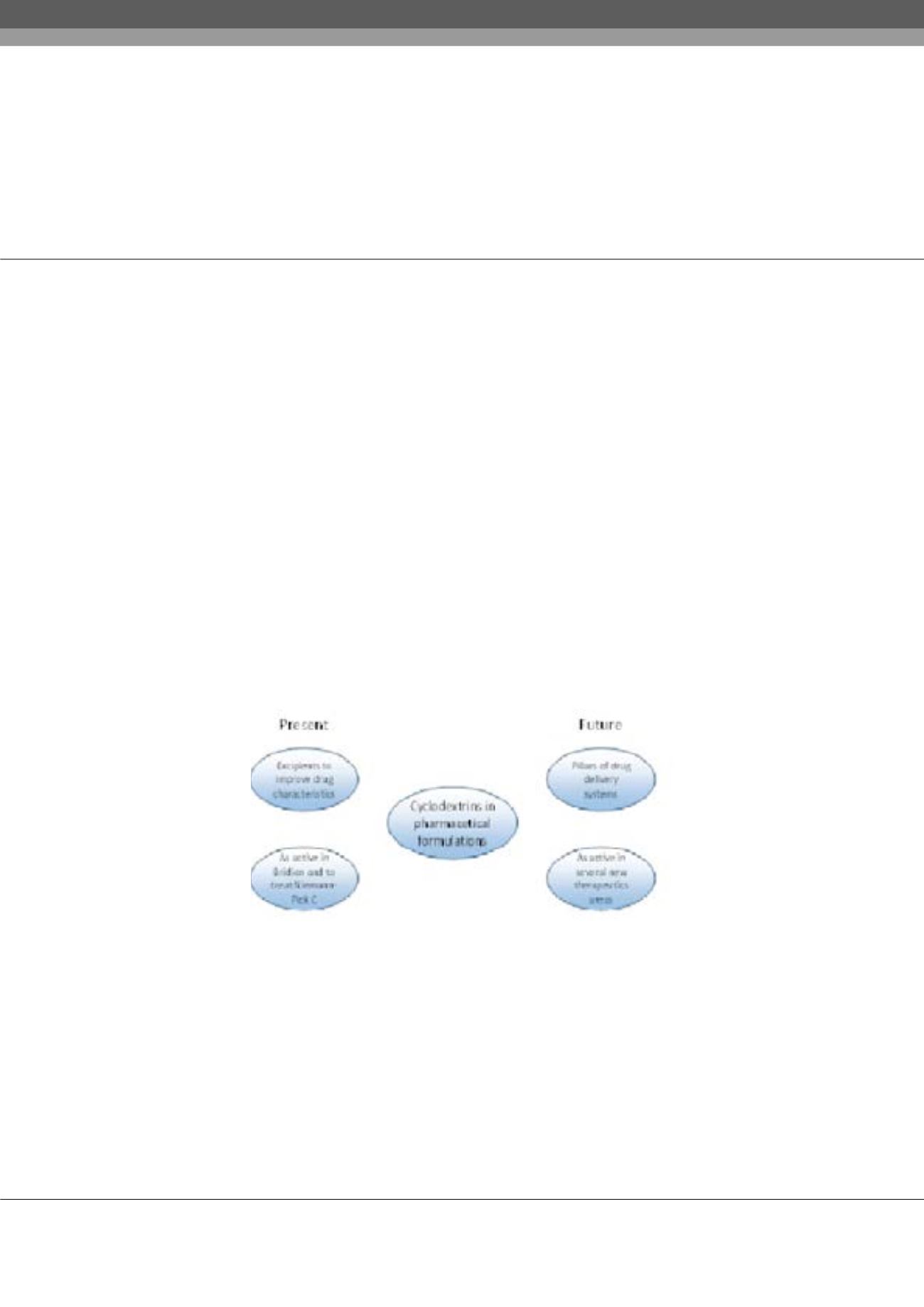
chemical stability or simply to mask their taste. At present more than 40, CD-enabled human pharmaceutical products are
on the market. The present of CDs is thus dominantly being used as excipients. The most favored are 2-hydroxypropyl-β-
CD (HPBCD) and sulfobutylether-β-CD, applied in dozens of parenteral formulations, while other derivatives are used for
oral, topical, nasal or ocular administration. The marvel of CDs lies in their flexibility: you can optimize the excipient for
the active ingredient and for the purpose simultaneously. In the present lecture illustrative drug products will be highlighted
demonstrating the applicability of derivatized oligosaccharides in the development of drug formulations. Outlook to the future
potential related to drug delivery use of CDs will also be provided. CDs tagged with biological recognition-based labeling were
prepared in order to deliver specific drugs to the site of action. Also, combinations with the application of colloidal structures
(dispersions, liquid crystals and macromolecules) will be discussed. Yet the future of CDs is not limited to being used as
excipients. We can harvest from their complex forming ability
in vivo
as well, in products, containing CDs as APIs. While the
initial idea was to use CDs as detoxification agents or to selectively remove chemicals from the system (e.g. Sugammadex –
Bridion), this concept has grown into clinical trials and studies using CDs as API alone (HPBCD as an orphan drug against
Niemann-Pick C, Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis or Alport Syndrome). A number of further therapeutic applications of
CDs themselves are expected to come, some potential areas will be reviewed.
Biography
Tamás Sohajda has been working at CycloLab Ltd., for six years. Currently he is the Director of Research and Development. After graduating as a Pharmacist, he
obtained degrees in Pharmaceutical Economy and Quality Assurance. He wrote his PhD thesis on the investigation and understanding of cyclodextrin complexes
on a molecular level studying a great number of biological activities and CD derivatives. At CycloLab Ltd. he has been coordinating all development and research
works aimed at various and diverse fields such as developing new, cyclodextrin-aided formulations (solid and semi-solid dosage forms, parenterals, etc.), preparing
generic formulations or improvements of current products by introducing CDs, designing new industrially important CD derivatives ideal as next generation
excipients, drug delivery systems or as biologically active compounds.
sohajda@cyclolab.huTamas Sohajda et al., Insights in Analytical Electrochemistry, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2470-9867-C1-002