Notes:
Volume 3, Issue 2
Insights in Analytical Electrochemistry
ISSN: 2470-9867
Analytical Chemistry-Formulation 2017
August 28-30, 2017
Page 25
8
th
Annual Congress on
&
14
th
International Conference and Exhibition on
August 28-30, 2017 Brussels, Belgium
Analytical and Bioanalytical Techniques
Pharmaceutical Formulations
Properties of bacterial cellulose wound dressing containing sericin and polyhexamethylene biguanide
Supamas Napavichayanun
and
Pornanong Aramwit
Chulalongkorn University, Thailand
T
he ideal wound dressing should be a moist and oxygen-permeated environment, exudate adsorption, enhanced wound
closure, and infection protection. The bacterial cellulose wound dressing containing sericin and polyhexamethylene
biguanide (PHMB) is a natural wound dressing that is easily produced from bacterial cellulose (
A. xylinum
strain in coconut
water medium), silk sericin (protein from silk cocoon), and antiseptic (PHMB). Components of this dressing contain many
benefits closely to the ideal wound dressing properties. For the dressing production, the bacterial cellulose dressing was loaded
with 1% w/v silk sericin followed by 0.3% w/v PHMB loading. All processes were carried out in sterile conditions. After
preparation, the dressings were sterilized with gamma radiation at 25 kGy. The properties of the dressing were tested in term
of sericin and antimicrobial releasing, antimicrobial property, and collagen type I production test comparing with commercial
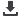
product. The results showed that the sufficient concentration for elimination of all bacteria (
S. aureus,
MRSA
, B. subtilis, E.
coli, P.aeruginosa, A. baumannii
) of PHMB was released from the dressing within 30 minutes and optimal concentration
for collagen type I production of sericin was released within 4 hours. The dressing was superior in terms of antimicrobial
activity against all bacterial strains than Bactigras®. In comparison with silver-loaded Acticoat®, the antimicrobial activity of the
dressing was better against Gram-positive bacteria often found in chronic wounds (
S. aureus
and MRSA). The antimicrobial
difference between the dressing and Suprasorb®X + PHMB was only noticed for
B. subtilis
. Moreover, the cells cultured from
the released solution of our novel dressing produced significantly higher amount of collagen type 1 than those cultured with
the bacterial cellulose wound dressing without silk sericin. Therefore, the bacterial cellulose wound dressing containing sericin
and PHMB contains many advantages to be the ideal wound dressing.
Biography
Supamas Napavichayanun is a PhD student at the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, Thailand. She earned a BSc from Faculty of
Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University in 2010. Her research experience has ranged from protein including silk proteins and biomaterials. She also
did clinical researches in the area of dermatology especially materials for wound healing application.
snsupamas@gmail.comSupamas Napavichayanun et al., Insights in Analytical Electrochemistry, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2470-9867-C1-002