Notes:
Volume 3, Issue 2
Insights in Analytical Electrochemistry
ISSN: 2470-9867
Analytical Chemistry-Formulation 2017
August 28-30, 2017
Page 27
8
th
Annual Congress on
&
14
th
International Conference and Exhibition on
August 28-30, 2017 Brussels, Belgium
Analytical and Bioanalytical Techniques
Pharmaceutical Formulations
Rapid determination of U-236 in the soil contaminated by the fukushima daiichi nuclear power
plant accident using single extraction chromatography combined with triple-quadrupole inductively
coupled plasma-mass spectrometry
G S Yang, H Tazoe
and
M Yamada
Hirosaki University, Japan
Institute of High Energy Physics, CAS, China
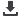
Method Development for 236U in Soil
Based on use of the new generation of triple-quadrupole ICP-MS (ICP-MS/MS), a novel technique for measuring
236U
activities
and
236
U/
238
U ratios in soil has been developed. This simple method incoporated two procedures: a total dissolution with HF
+ HNO
3
+ HClO4 followed by single DGA chromatographic separation (Figure 1). The analytical accuracy and precision of
236
U/
238U
ratios, measured as
236
U
16
O+/
238
U
16
O+, were validated by using the reference materials IAEA-135, IAEA-385, IAEA-
447, and JSAC 0471[1].
U Isotope in the Soil Contaminated by the FDNPP Accident
For 46 soil samples lightly and heavily contaminated as
134
Cs by the FDNPP accident, the
236
U/
238
U isotopic ratio ((0.99−13.5)×10-
8) was comparable with those of global fallout values found in surface soil in Japan [2, 3], indicating the release of radioactive
U from the FDNPP accident was a trace amount.
References
[1]Yang
et al
. (2016)
Anal. Chim. Acta
944, 44-50.
[2]Sakaguchi
et al
.
(2009) Sci. Total Environ.
407, 4238–4242.
[3] Sakaguchi
et al
.
(2010) Sci. Total Environ.
408, 5392–5398.
Biography
Guosheng Yang obtained his PhD from Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in 2012. After working in the National Institutes for Quantum and
Radiological Science and Technology, Japan (2012-2014) and CAS, China (2014-2015), he is working in the Institute of Radiation Emergency Medicine, Hirosaki
University, Japan mainly to develop novel mass-spectrometric methods to measure trace radioisotopes (
135
Cs,
236
U,
129
I,
90
Sr, Pu isotopes).
yanggs@hirosaki-u.ac.jpG S Yang et al., Insights in Analytical Electrochemistry, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2470-9867-C1-002