NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 64
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
L
ongitudinal creep behavior of nanocomposite for
nanocrystalline (NC) Ni-NiZr glass has been studied at various
temperatures (from 1200 to 1400 K) at 1 GPa stress using
molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. A simulation box of the
specimen 15.85 × 15.85 × 15.85 nmdimension (contains 312,924
atoms) is taken for performingMD simulation. Common neighbor
analysis (CNA), Centro-symmetry parameter (CSP) analysis,
Wigner–Seitz defect analysis and radial distribution function
(RDF) have been carried out to investigate the structural evolution
and deformation mechanism of nanocomposite specimen
during creep process. Self-diffusion of nanocomposite specimen
has been performed using MD simulation for interface region
and whole specimen at different temperature. Average atomic
displacement and local stress in the regions (2Å, 4Å, and 6Å)
adjacent to the NC Ni-NiZr glass interface is evaluated during
creep deformation process to investigate the atomic movement
near the interface of NC Ni-NiZr glass. It is found from creep
curves that primary and secondary creep regime is reduced with
increasing creep temperature. Creep rate for nanocomposite
specimen is observed to be shifted downward with increasing
creep temperature after 180 ps time period. Creep rate for creep
process occurring at 1400 K temperatures are observed to be
increased more from starting of tertiary creep regime to 180 ps
time period and then decreased to 300 ps.
Recent Publications
1. Meraj, M., Yedla, N., & Pal, S. 2016. The effect of
porosity and void on creep behavior of ultra-fine
grained nano crystalline nickel. Materials Letters, 169,
265-268
2. Pal, S., & Meraj, M. 2016. Structural evaluation and
deformation features of interface of joint between
nano-crystalline Fe–Ni–Cr alloy and nano-crystalline
Ni during creep process. Materials & Design, 108, 168-
182.
3. Pal, S., Meraj, M., & Deng, C. 2017. Effect of Zr
addition on creep properties of ultra-fine grained
nanocrystalline Ni studied by molecular dynamics
simulations. Computational Materials Science, 126,
382-392.
4. Meraj, M., & Pal, S. 2017. Nano-scale simulation based
study of creep behavior of bimodal nanocrystalline
face centered cubic metal. Journal of Molecular
Modeling, 23: 309.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3481-y
5. Meraj, M., & Pal, S. 2017. Effect of temperature
and stress on creep behavior of ultrafine grained
nanocrystalline Ni-3 at% Zr alloy. Metals and Materials
International, 23(2), 272-282.
6. Meraj, M., & Pal, S. 2017. Healing mechanism of
nanocrack in nanocrystalline metals during creep
process. Applied Physics A, 123(2), 138.
7. Meraj, M., & Pal, S. 2017. Comparative creep behaviour
study between single crystal Nickel and ultra-fine
grained nano crystalline Nickel in presence of porosity
at 1120 K temperature. Metallurgical Research &
Technology, 114(1), 107.
Longitudinal creep behavior of nanocrystalline Ni-NiZr glass
nanocomposite
Md. Meraj
1
and
Snehanshu Pal
2
1
Ph. D scholar, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology
Rourkela, Rourkela-769008, INDIA.
2
Ph. D, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology Rourke-
la, Rourkela-769008, INDIA
Md. Meraj et al., Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008
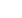
Figure 1:
Three dimensional sectional view of nanocomposite for NC Ni-NiZr
glass specimen (a) particle type, (b) CSP, (c) creep and (d) creep rate curves of
nanocomposite of NC Ni-NiZr glass for different temperatures at 1 GPa stress.