NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 63
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
F
ibre reinforced polymeric (FRP) are used in different
components of aerospace, space, marine, automobile and
civil infrastructure. These materials are becoming prime choice
of materials in the field of structural components. During their
in-service period different structural components experience a
wide range of loadings. The current investigation was focused
on the assessment of mechanical and thermal behavior of
glass FRP composite on the addition of nano-TiO
2
particles. The
control glass/epoxy(GE) composites and nano-TiO
2
modified
GE composites were tested at different crosshead speeds viz.
1, 10, 100, 500 and 1000 mm/min. nano-TiO
2
was used as filler
material and the epoxy matrix was processed with different nano-
TiO
2
contents (0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 wt. %). Addition of 0.1 wt. % nano-
TiO
2
particles exhibited an improvement in strength of nano-
TiO
2
/GE composites at all crosshead speeds. Different failure
patterns of nano-TiO
2
enhanced GE composite tested at 1, 10,
100, 500 and 1000 mm/min crosshead speeds were identified.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was carried out to know
the main cause of failure that induced different morphologies.
Furthermore, the viscoelastic behavior of the material was carried
out using dynamic mechanical thermal analyzer which correlated
the mechanical and thermo-mechanical behavior of the FRP
composites.
Recent Publications
1. Mahato K K, Dutta K, Ray B C (2018) Loading rate
sensitivity of liquid nitrogen conditioned glass fiber
reinforced polymeric composites: An emphasis on
tensile and thermal responses, Journal of Applied
Polymer Science, 135:9.
2. Mahato K K, Dutta K, Ray B C (2017) High-temperature
tensile behavior at different crosshead speeds during
loading of glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites,
Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 134: 16.
3. Mahato K K, Rathore D K, Dutta K, Ray B C (2017)
Effect of loading rates of severely thermal-shocked
glass
fiber/epoxy
composites,
Composites
Communications, 3: 7-10.
4. Mahato K K, Dutta K, Ray B C (2017) Static and Dynamic
Behavior of Fibrous Polymeric Composite Materials
at Different Environmental Conditions Journal of
Polymers and the Environment, 1-27.
5. NayakRK,MahatoKK, RayBC, (2016)Water absorption
behavior, mechanical and thermal properties of
nano TiO
2
enhanced glass fiber reinforced polymer
composites, Composites Part A: Applied Science and
Manufacturing 90:736-747.
Biography
Kishore Kumar Mahato is pursuing PhD at National Institute of Technology,
Rourkela, India. He has published around 15 research articles in different SCI
and Scopus indexed journals. The research work is focused on failure and
fracture behavior of fibre reinforced polymeric Composite in different harsh
environments. Investigations are focused on the assessment of mechanical
behavior of environmentally conditioned FRP composites through experi-
mental and numerical analysis. Primarily, the polymer matrix and the exist-
ing fibre/polymer interface are susceptible to harsh and hostile in-service
environments which can alter the durability and integrity of fibrous polymer-
ic composites. The mechanical response of polymeric materials is loading
rate sensitive and the precise mode of failure depends on the in-service en-
vironment. The environmental parameters which may influence the perfor-
mance of the composites includes but not limited to temperature, moisture,
UV and other high energy radiations.
kishorepce@gmail.comMechanical and thermal behavior of nano-TiO
2
enhanced glass
fibre reinforced polymeric composites at various crosshead speeds
Kishore Kumar Mahato
1
, Krishna Dutta
2
and
Bankim Chandra Ray
3
1
Ph D Scholar, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, NIT Rourkela, India
2
Ph D, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, NIT Rourkela, India
3
Ph D, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, NIT Rourkela, India
Kishore Kumar Mahato et al., Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008
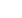
Figure 1:
Scanning electron micrographs showing (a) matrix
cracking (b) fibre imprints.