NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 62
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
A
s the expression level of proteins in human body is closely
related to the occurrence and progression of cancers, the
development of highly sensitive, high-throughput, rapid and low-
cost optical technology for multiplex protein detection is of great
significance to the fundamental research in oncology and the
clinicalapplicationsinearlycancerdiagnosisandtherapeutics.Wefocus on the development of a novel multiplex protein detection
platformwhich combines surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
(SERS) technique with the microfluidic chip. This study aims to
improve the detection sensitivity, multiplexing ability, efficiency as
well as to reduce the overall costs. Here, the spectral-spatial joint
encodingmethod has been proposed to develop a novel analytical
platform for high-throughput protein detection, which is further
employed for the detection of tumor markers and the study on
the interaction mechanism of anti-cancer drugs. This platform
provides a new technological route for the early cancer diagnosis
and therapeutics. The main content of this presentation are
listed as follows: gold@silver core-shell nanorods were adapted
to develop a SERS-based immunoassay with highly increased
sensitivity; SERS spectral encoding technique was employed for
multiplex detection of cancer biomarkers; SERS spectral-spatial
joint encoding method was proposed to develop a SERS-assisted
3D barcode chip for multiplex protein detection; and a versatile
microfluidic platform for the detection of tumor secretions was
presented, in which the mechanism of anti-cancer drugs and the
process of intercellular communication were studied..
Recent Publications
1. Wu L, Wang Z Y, Zhang Y Z, Fei J Y, Chen H, Zong
S F and Cui Y P (2017)
In situ
probing of cell–cell
communications with surface-enhanced Raman
scattering (SERS) nanoprobes and microfluidic
networks for screening of immunotherapeutic drugs.
Nano Research 10:584-594.
2. Wu L, Wang Z Y, Fan K Q, Zong S F and Cui Y P (2015)
A SERS-assisted 3D barcode chip for high-throughput
biosensing. Small 11:2798-2806.
3. Wu L, Wang Z Y, Zong S F and Cui Y P (2014) Rapid
reproducible analysis of thiocyanate in real human
serum and saliva using a droplet SERS-microfluidic
chip. Biosensors & Bioelectronics 62:13-18.
4. Wu L, Wang Z Y, Zong S F, Chen H, Wang C L, Xu S
H and Cui Y P (2013) Simultaneous evaluation of p53
and p21 expression level for early cancer diagnosis
using SERS technique. Analyst 138:3450-3456.
5. Wu L, Wang Z Y, Zong S F, Huang Z, Zhang, P Y and Cui
Y P (2012) A SERS-based immunoassay with highly
increased sensitivity using gold/silver core-shell
nanorods. Biosensors & Bioelectronics 38:94-99.
Biography
Lei Wu is currently a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in International Iberi-
an Nanotechnology Laboratory (INL). He obtained his Bachelor’s and PhD
degree from School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Southeast Uni-
versity, China in 2012 and 2017, respectively. His research interests include
Biophotonics, Nanophotonics and Optofluidic Systems. He has published
14 research papers with total citations over 200 times, and has delivered five
oral presentations on international conferences.
lei.wu@inl.intMultiplex detection of protein biomarkers with surface
enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Lei Wu
International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory, Portugal
Lei Wu, Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008
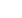
Figure 1:
(up) SERS spectra of nanoparticles labeled with differ-
ent Raman reporters (4MBA, DTNB and 2NAT); (down) Multiplex
detection of protein biomarkers with encoded Raman probes.