NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 61
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
A
fter trauma, fast hemostasis is an essential strategy in
extensive bleeding, in this decade, much effort has been
made to develop the hemostatic agents, but the existent options
have ample restrictions, including failure tomaintain the structure
of the styptic in the face severe bleeding and rapid changes in pH.
Since the changes in pH of injury site is an important factor in the
failure of styptic and their structural damage, in this study gelatin-
silica nanohybrid behavior in severe bleeding was evaluated
under different pH. Experiments including blood absorption, zeta
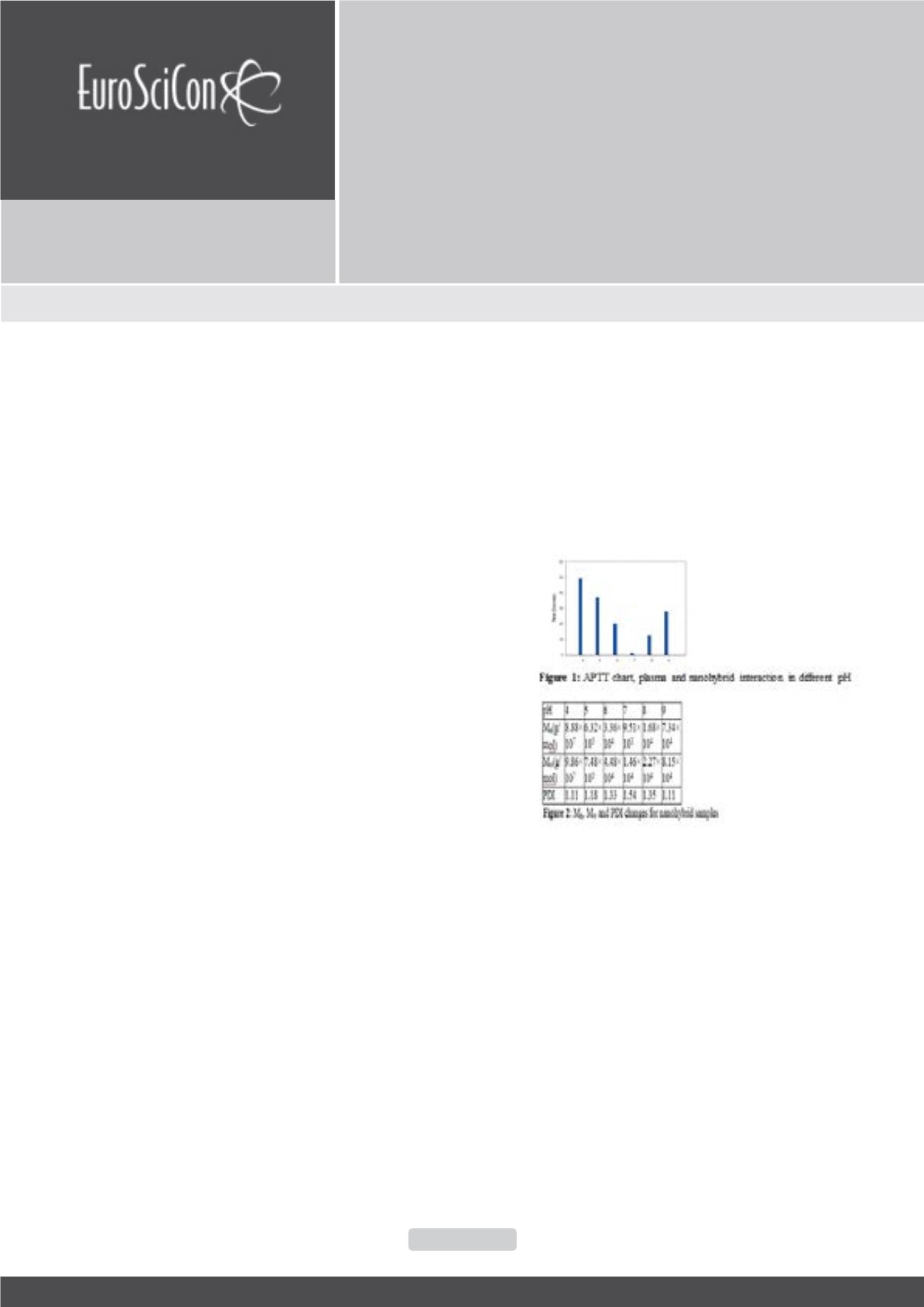
potential measurements, and poly disparity index by GPC tests
were studied. By changing the pH of environment, structural
integrity and there upon nanohybrid hemostatic behavior
changed dramatically. So that nanohybrid showed the most
blood absorption (440%) and acceded to a coherent structure
with tendentious to alpha helix and beta-sheets (the secondary
structure of a protein), that also provide ability to maintain
integrity of structure in severe bleeding. These results obtained,
in alkaline or acidic environment nanohybrid hemostatic behavior
was limited, so that in the acidic pH, the blood absorption was
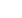
reduced to 110% and 1.6 times the normal clotting time delayed.
Based on the results of this study, it was found that changes in
nanohybrid behavior in acidic pHwere much more than in alkaline
pH and nanohybrid can also maintain the structural integrity
with rapid hemostasis. According to the desire of injury site to
change the pH to alkaline side, the resulting nanohybrid has an
ideal ability to control excessive bleeding and can be proposed for
further studies
in vivo
as a novel styptic.
Recent Publications
1. Chenani M and Ahmadinejad M (2016) Preparation
and characterization of novel gelatin/silica nano-
hybrid as a styptic for massive bleeding. Journal of
Nanomaterials and Biostructures 4:1277- 1288.
soodehmoradi@gmail.comEvaluation of hemostatic behavior of gelatin-silica nanohybrid
by changing the pH of injury in severe bleeding
S Moradi
1
, M Chenani
1
and
S A Ahmaditabatabaei
2
1
Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
2
Imperial College London, UK
S Moradi et al., Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008