NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 54
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
I
n recent years, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have
attracted significant attention in medicinal, biomedical and
pharmaceutical research owing to their valuable physicochemical
and antibacterial properties. The objective of this study was
to prepare, characterize and evaluate the potential of green
synthesized silver nanoparticles (G-AgNPs) against human
pathogenic bacteria and evaluate their cellular responses in WS1
wounded cells in combination with laser irradiation (830 nm,
fluence of 5 J/cm
2
). When themixture of silver nitrate solution and
leaf sap extract (LSE) was exposed to direct sunlight, it yielded a
rapid color change fromcolorless to reddish-brown, indicating the
formation of G-AgNPs. Physicochemical characterization such
as single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry,
high resolution transmission electron microscopy and surface
chemistry studies (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and
x-ray diffraction) revealeda small sizeof 38±2nm, smoothsurface
and existence of LSE on the G-AgNPs. G-AgNPs possessed good
antibacterial activity against both
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
and
Staphylococcus aureus
.
In vitro
wound healing studies such as
cell morphology, cell migration, cell proliferation, cell apoptosis
and nuclear morphology studies were investigated in WS1 cells.
Overall, these results suggest that the use of G-AgNPs and in
combination with laser shows great potential to heal wounds in
in vitro, and this combined therapy did not show any toxicity to
the cells. Thus, the present study reveals that the novel G-AgNPs
demonstrated effective antibacterial properties against both
gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial strains, and G-AgNPs
in combinationwith photobiomodulation showed excellent wound
healing properties in WS1 cells.
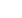
Figure 1:
[a] HRTEM image of G-AgNPs, [b] and [c]
confocal image of G-Ag-
NPs treated Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.
Recent Publications
1. D Sathish Sundar, N N Houreld, E M Kroukamp and H
Abrahamse (2017) Cellular imaging and bactericidal
mechanism of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles
against human pathogenic bacteria. Journal of
Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology DOI:
10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.11.001.
2. Sathish Sundar Dhilip Kumar, Gover Antoniraj, Senthil
Kumar, Shyam Mohapatra, Nicolette Houreld and
Ruckmani Kandasamy (2016) Recent trends of
biocompatible and biodegradable nanoparticles in
drug delivery: A review. Current Medicinal Chemistry
23:3730-3751.
3. C Senthil Kumar, M D Raja, D Sathish Sundar, M Gover
Antoniraj and K Ruckmani (2015) Hyaluronic acid
co-functionalized gold nanoparticle complex for the
targeted delivery of metformin in the treatment of liver
cancer (HepG2 cells). Carbohydrate Polymers 128:63-
74.
4. D Sathish Sundar, M Surianarayanan, R Vijayaraghavan,
ABMandal andDRMacFarlane (2014)Curcumin loaded
poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) nanoparticles from
gelled ionic liquid – In vitro cytotoxicity and anti-cancer
in SKOV-3 cells. European Journal of Pharmaceutical
Sciences 51:34-44.
5. D Sathish Sundar, A Mahesh, M Surianarayanan and
A B Mandal (2014) Synthesis and characterization of
curcumin loaded polymer/lipid based nanoparticles
and evaluation of their antitumor effects on MCF-7
cells. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta 1840(6):1913-
1922.
Combined effect of 830 nm laser irradiation and silver
nanoparticles in WS1 wounded cells
Sathish Sundar Dhilip Kumar, Nicolette Nadene Houreld
and
Heidi Abrahamse
University of Johannesburg, South Africa
Sathish Sundar Dhilip Kumar et al., Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008