Medchem & Toxicology 2018
Page 85
Journal of Organic & Inorganic Chemistry
ISSN: 2472-1123
A n n u a l C o n g r e s s o n
Medicinal Chemistry,
Pharmacology and toxicology
J u l y 3 0 - 3 1 , 2 0 1 8
Am s t e r d a m , N e t h e r l a n d s
I
n the past decade, a problem of increasing number of bacterial pathogens presenting multidrug resistance to antibiotics has
been observed. According to the World Health Organization multidrug-resistant bacteria are responsible for an estimated
25,000 deaths in Europe each year. The accumulation of antimicrobial agents in the environment and the exposure to these
drugs provides the pressure for the diffuse of resistant pathogens. That is why the joint programming initiative on antimicrobial
resistance supported by 18 European countries plus Canada recommended a promotion of research and development of novel
antimicrobial strategies and antibacterial agents as the one of the key measures that should be adopted to fight the emergence
and spread of antibiotic resistance worldwide. Regarding development of novel antimicrobial drugs, naphthoquinone derivatives
are of wide interest because of their diverse functions and clinical applications. This system moiety is present in many natural
compounds of wide biological action. The major objective of the present study was the synthesis and biological evaluation of
a new series of 1, 4-naphthoquinone derivatives. The obtained compounds were tested against a panel of Gram-positive and
Gram-negative bacteria strains as well as Candida strain. Additionally, we have verified the haemolytic properties of selected
compounds against human erythrocytes. Each of examined naphthoquinone derivatives presented certain antimicrobial activity
with predominant MIC values of 125-250 µg/mL. The most promising bacterial target of naphthoquinone derivatives presented
the highest and selective potency towards
S.aureus
with MIC values between 7.8 and 62.5 µg/mL. The details of our studies,
which describe the synthesis, antimicrobial activity, and proposition for the mechanism of an action of studied compounds, will
be presented
.
Oleh.Demchuk@UMCS.Lublin.plNew 1, 4-naphthoquinones: antimicrobial agents
Oleg M. Demchuk
1
, M Janeczko
2
K Kubinski
2
and M Maslyk
2
1
Maria Curie-Skłodowska University, Lublin, Poland
2
The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland
J Org Inorg Chem 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2472-1123-C3-009
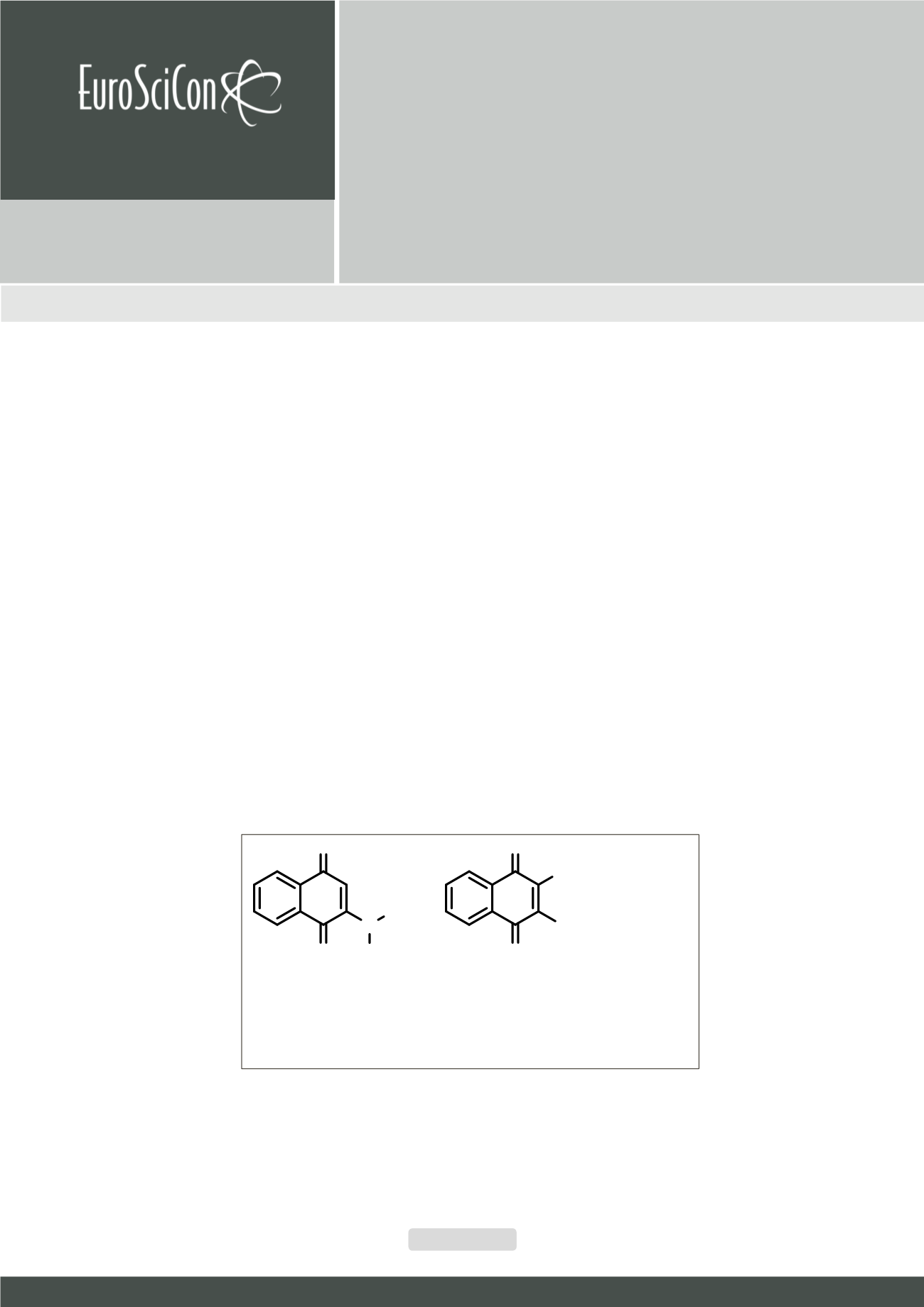
Figure.
New 1, 4-naphthoquinone derivatives
A r =
Ph ,
3 , 4 - Me
2
- C
6
H
3
,
2 , 4 , 6 - Me
3
- C
6
H
2
,
2 , 4 - Me O
2
- C
6
H
3
,
2 , 4 , 6 - Me O
3
- C
6
H
2
, 6 , 7 - Me O
2
- na phth - 2 - yl ,
4 - NMe
2
- C
6
H
4
,
2 - Me , 4 - NMe
2
- C
6
H
3
,
4 - NB n
2
- C
6
H
4
,
2 - Me O , 4 - NH ( A c )
- C
6
H
3
...
R
2
=
H ,
Ph
R
=
Ph ,
CH ( iP r ) CO
2
H ,
CH ( i n d o l - 3 - yl ) CO
2
H ,
CH ( Me ) CO
2
Me ...
O
O
A r
R
2
O
O
N
H
R