Page 106
May 24-25, 2018
London, UK
Vascular Surgery 2018
3
rd
Edition of World Congress & Exhibition on
Vascular Surgery
Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Therapy
ISSN: 2573-4482
T
etralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the most common congenital heart
diseasewith>80%ofchildrenexpectedtolivebeyondtheageof
40. However, due to gradual loss of pulmonary valve function after
initial surgical repair, resulting in severe pulmonary regurgitation
(PR), TOF patients require frequent surgical revisions. To delay
open heart surgery, a non-invasive percutaneous pulmonary valve
implantation(PPVI)devicewasfirstintroducedbyBonhoefferetal.
showing satisfactory clinical performance. However, morphology
still limits PPVI eligibility. We focus on automatically defining
the shape of the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) in TOF
patients with PR late after surgical repair to assess the variations
of anatomy and guide the design of new PPVI devices. TOF
patients (n=59, age 25±15 years) referred to our centre for follow-
up cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) between
August 2007 and April 2017 were retrospectively selected for
this study with inclusion criteria: i) steady-state free precession
cardiac-gated 3D whole-heart images; ii) moderate to severe PR
(regurgitant fraction (RF) 39±10%); and iii) no metal artefacts. A
statistical shape analysis (SSA) framework was used to calculate
the principal component (PC) modes of shape variation in the
population from unsupervised statistical learning. The first three
PC modes accounted for 36% of the variance. Mode 1 was most
correlated to BSA (r=0.66, p≤0.001) describing size differences,
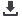
together with mode 2 (r=0.47, Figure 1 - representation of the
principal modes of shape p≤0.001). Mode 2 revealed presence of
a highly variation in the population enlarged pulmonary trunk
whilst mode 3 described elongation of the vessel and correlated
with vessel
centerline length (r=0.57, p≤0.001). Mode 3
was inversely correlated with pulmonary RF (r=-0.43, p≤0.001).
Advanced image processing and statistical shape analysis of the
RVOT in TOF identifies features important to guide the design and
optimization of new PPVI devices, benefitting the largest number
of patients requiring a new valve.
stephane.couvreur.13@ucl.ac.ukStatistical shape analysis of the right ventricular outflow
tract in patients with tetralogy of Fallot
Stephane Couvreur
1, 2
, Agnieszka Nowacka
2
, Benedetta Biffi
1, 2
, Jan Bruse
3
, Gaeta-
no Burriesci
1, 4
, Andrew Taylor
1, 2
, Claudio Capelli
1, 2
and
Silvia Schievano
1, 2
1
UCL Institute of Cardiovascular Science, UK
2
Great Ormond Street Hospital, UK
3
Vicomtech‐IK4, Spain
4
Fondazione Ri.MED, Italy
J Vasc Endovasc Therapy 2018, Volume 3
DOI: 10.21767/2471-8084-C1-003