Pharmacognosy 2018
American Journal of Ethnomedicine
ISSN: 2348-9502
Page 73
April 16-17, 2018
Amsterdam, Netherlands
6
th
Edition of International Conference on
Pharmacognosy and
Medicinal Plants
Development of a herbal formulation containing extracts of
Camellia sinensis and Limonium algarvense and assessment of
its in vitro bioactivities
Maria J Rodrigues
1
, Marta M Oliveira
1
, Vanessa F Neves
1
, Andreia Ovelheiro
1
, Catarina A
Pereira
1
, Nuno R Neng
1
, José M F Nogueira
2
, Luísa A Barreira
1
and
Luísa M Custódio
1
1
Centre of Marine Sciences, Portugal
2
University of Lisbon, Portugal
T
he growing interest of stakeholders and consumers in herbal
products urges the need for research aiming to unravel
innovative products with health improvement potential. Green
tea (
Camellia sinensis
(L.) Kuntze, CS) is commonly sold in
mixtures combining different herbs, fruits or spices in order to
improve or add beneficial properties to such beverages. Having
this in mind, and following previous promising results obtained
with the halophyte sea lavender (
Limonium algarvense
Erben. LA)
this work prepared and evaluated herbal beverages containing
mixtures of CS and LA flowers in terms of antioxidant capacity
and inhibition of enzymes related with Alzheimer’s (acetyl- and
butyrylcholinesterase) and Type 2 diabetes
mellitus
(α-amylase
and α-glucosidase). The phenolic profile was determined by
HPLC. Both synergistic and antagonistic interactions were
observed. LA and CS samples had strong antioxidant activity,
whereas LA and CS mixtures exhibited higher OH radical-
scavenging and anti-lipid peroxidation capacity. LA samples had
higher cholinesterase inhibition than CS and mixtures resulted in
stronger enzymatic inhibition. CS had the highest α-glucosidase
inhibition, which decreased when combined with LA. CS had
higher phenolic contents, and its combination with LA increased
the phenolic diversity of themixtures. Results showed that LA and
CS infusions and decoctions and their combinations have relevant
in vitro
antioxidant, neuroprotective and antidiabetic properties.
Infusions and decoctions of LA and CS mixtures should thus be
further explored as potential innovative functional beverages able
to prevent oxidative stress and lipid oxidation related diseases,
and to reduce the progression of neurodegenerative diseases and
diabetic complications.
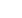
Figure 1:
Limonium algarvense flowers.
Recent Publications
1. Rodrigues M J, Custódio L, Lopes A, Oliveira M, Neng
N R, et al. (2017) Unlocking the
in vitro
anti-inflamatory
and antidiabetic potential of
Polygonum maritimum
.
Pharmaceutical Biology 55:1348–1357.
2. Rodrigues M J, Katkam G N, Zengin G, Mollica A,
Varela J, et al. (2017) Juncaceae species as sources of
innovative bioactive compounds for the food industry:
In vitro
antioxidant activity, neuroprotective properties
and in silico studies. Food and Chemical Toxicology
107:590–596.
Maria J Rodrigues et al., Am J Ethnomed 2018, Volume 5
DOI: 10.21767/2348-9502-C1-006