Page 56
Journal of Medical Physics and Applied Sciences
ISSN: 2574-285X
I n t e r n a t i o n a l C o n f e r e n c e o n
Nuclear Medicine &
Radiation Therapy
Nuclear Medicine & Radiation Therapy 2018
O c t o b e r 0 1 - 0 2 , 2 0 1 8
S t o c k h o l m , S w e d e n
Introduction:
Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) is a rare medical condition following obstruction of the hepatic venous outflow by either
thrombotic or non-thrombotic occlusions. Performing liver scintigraphy for patients with possible BCS is usually uncommon due
to the ability of other diagnostic modalities such as U/S, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and CT.
Case presentation:
Patient A, a 23 year old female, presented with severe abdominal pain and swelling. The patient is a known HIV
patient and is on active ARV treatment as well as oral contraceptives. Initial examinations of the patient confirmed jaundice as
well as ascites. Blood tests concluded liver failure and an ultrasound of the abdomen showed decreased liver size, the remaining
abdominal organs were normal. The patient then treated with antibiotics and a combination of furosemide and spironolactone. As
there was no improvement in patient’s condition and no obvious abnormalities were detected by ultrasound scan, the attending
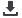
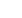
physician requested a nuclear medicine liver scan. The scan images demonstrated increased uptake in the caudate lobe of the
liver. These findings were suggestive of BCS and a CT scan was advised to confirm the diagnosis. Contrast CT scans performed,
which demonstrated a thrombus of the infrahepatic inferior vena cava, confirming a diagnosis of BCS. The patient was then
treated with anticoagulation medication.
Discussion:
Patient A was on oral contraceptives, which is known to increase the chances of blood clotting. Physicians believed
this to be the cause of BCS in patient A. BCS usually presents with hepatomegaly; however patient A had a shrunken liver. The
BCS in this patient might have been an unconfirmed diagnosis without the help of NM liver scintigraphy.
Conclusion:
This case highlights the significance of liver scintigraphy in a rare case of BCS. In cases like these, liver scintigraphy
is commonly overlooked due to other diagnostic imaging modalities.
naeemakarolia@gmail.comA rare case of Budd-Chiari syndrome on nuclear
medicine liver scintigraphy
Naeema Karolia
1, 2
1
Life The Glynnwood Hospital Nuclear Medicine
2
University of Johannesburg, South Africa
J. med phys & appl sci 2018, Volume: 3
DOI: 10.21767/2574-285X-C1-003
Figure 1
: Immediate images
Figure 2:
Immediate images