Page 39
conferenceseries
.com
Polymer Sciences | ISSN: 2471-9935
October 02-03, 2017 Chicago, USA
3
rd
International Conference on
Polymer Science and Engineering
Polymeric nanoparticles for antifungal ocular theraphy
Ebru Basaran
Anadolu University, Turkey
Introduction and Objectives:
Voriconazole (VOR) is a triazole antifungal derived from fluconazole is very active against various
fungi including those resistant to fluconazole.1 Treatment of ocular fungal infections remains problematic because of the relatively
short list of available therapeutic agents.2 Limited ocular bioavailability of active agents due to the characteristic properties of the eye
also limits the efficacy of the treatment. Therefore main approaches for the enhancement of ocular bioavailability of the formulations
applied are enhancement of the residence time of the active material at the site of action or enhancement of the ocular penetration of
the primary penetration site.
Materials and Methods:
Voriconazole was kindly gifted by Deva Holding (Çerkezköy, Tekirdağ), Eudragit® RS 100 was purchased
from Röhm Pharma Polymers (Darmstadt, Germany) and methanol was from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). All other chemicals
used were analytical grade.
Formulation of Polymeric Nanoparticles :
Spray drying method (Büchi B-190, BÜCHI Labortechnik AG, Switzerland) was used for
the preparation of polymer based nanoparticles.4 Compositions of the selected formulations were given in Table 1.
Characterization Studies of Polymeric Nanoparticles:
SEM, particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential analyses were
performed. In order to evaluate changes of the polymeric structure DSC analyses were also performed. A validated HPLC method
was used for the determination of incorporated PTX.
Results and Discussion:
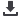
Morphological analyses showed that particles are round in shape. Particle size, polydispersity index, zeta
potential analyses with incorporated VOR amount of the formulations. Analyses results revealed that the particle sizes were in the
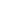
nanometer range with homogenous size distribution with no changes in the polymeric structure.
Conclusion:
As a conclusion VOR incorporated polymeric nanoparticles were successfully formulated by spray drying method
aiming efficient treatment of ocular fungal infections.
In vitro
and
in vivo
efficacy of the formulations will be studied as the second
part of the study.
Biography
Dr. Ebru Başaran has completed her PhD study with the thesis entitled “Formulation and
In Vitro
-
In Vivo
Evaluation of Cyclosporine A Incorporated Solid
Lipid Nanoparticles, Microemulsion and Polymeric Nanoparticles Aiming Ocular Application” at the Anadolu University Faculty of Pharmacy at Pharmaceutical
Technology Department in 2007. The doctorate study was awarded by NAGAI Foundation as the “Best Research Work” at FAPA meeting in 2008. She focused on
formulation and characterization of nano-microparticulate delivery systems for ocular application. Currently Dr. Başaran is working as an Assoc. Prof. at the Anadolu
University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Technology since 2017.
ebcengiz@anadolu.edu.trEbru Basaran, Polym Sci, 3:3
DOI: 10.4172/2471-9935-C1-002
Figure 1. SEM image of
polymeric spheres
Figure 2. DSC analyses of
the formulations prepared