Nursing Diagnosis & Midwifery 2018
S e p t e m b e r 1 0 - 1 1 , 2 0 1 8
P r a g u e , C z e c h R e p u b l i c
Page 68
Journal of Nursing and Health Studies
ISSN: 2574-2825
E u r o S c i C o n E v e n t o n
Nursing Diagnosis &
Midwifery
T
he focus of the article is rather situated on current faults and recommendations for transfusion of red blood assessment, clinical
evaluation of changes in hematocrit. The main task of therapy for acute massive blood loss is not urgent thoughtless transfusion of
red blood cells for the fast recovery of the haemoglobin and haematocrit levels. The oxygen-carrying capacity of blood does not directly
reflect the delivery of oxygen to tissues. The severity of the patient's condition depends of individual ability of the organism to resist hypoxia,
mechanisms resulting in physiological compensation for the anemia caused by blood loss. The main tasks of therapy are timely maintaining
appropriate and effective compensatory adaptive reactions of an organism, providing of the sanogenetic processes. Quickly and comfortable
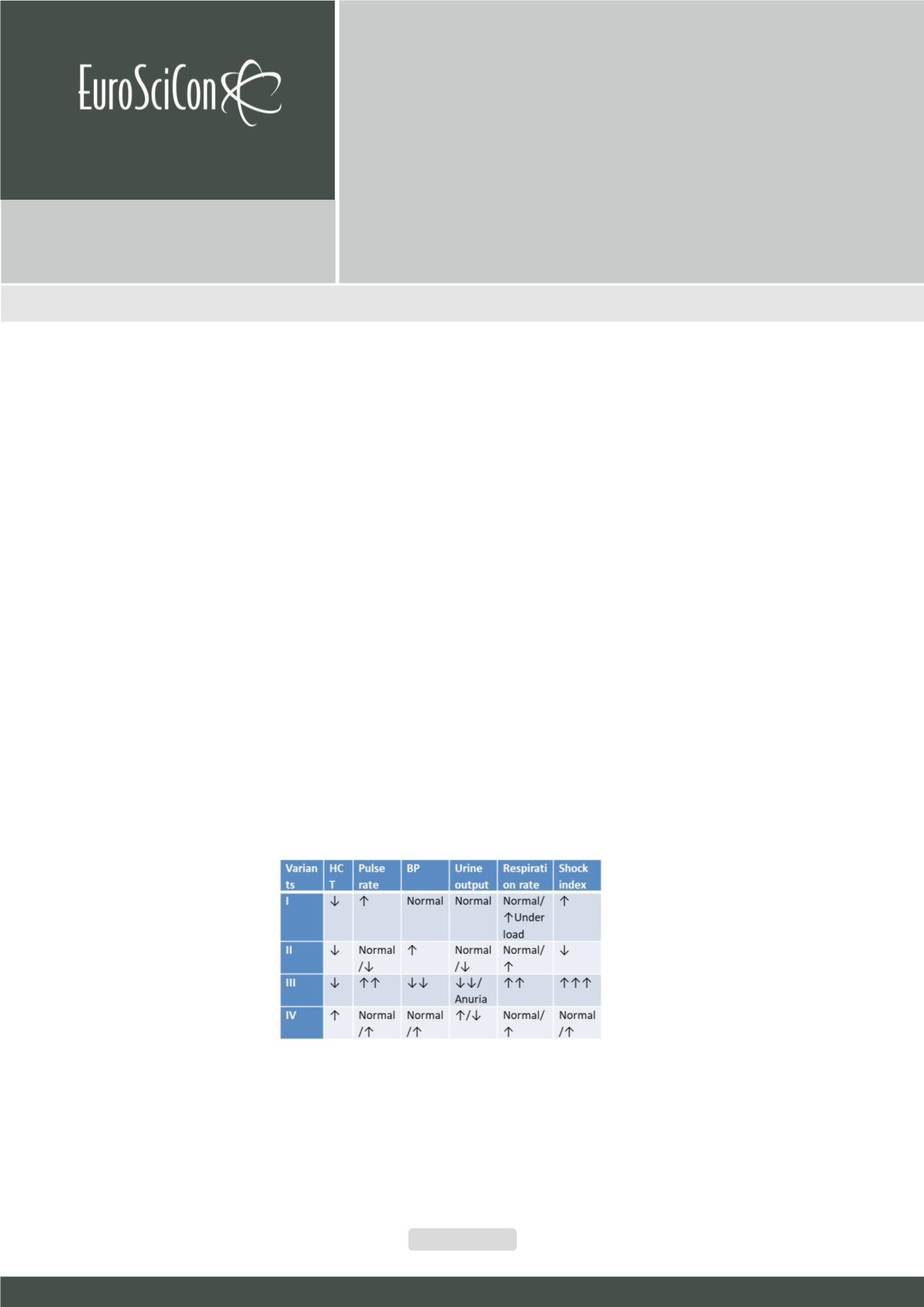
algorithm assessment changes in haematocrit was presented for used in practice. Objective analysis haematocrit and haemoglobin levels
should be carried out only in combination with data on blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, urine output and shock index. Examples
of clinical of the variants of changes in haematocrit on the background of the reaction of the basic organism physiological parameters were
presented in Table 1. This table is quick and comfortable algorithm assessment changes in hematocrit which need used in practice
www.nanolab.com.ua an.belousov2012@yandex.ua an.belousov2012@ukr.netCurrent faults and recommendations for
transfusion of red blood assessment and clinical
evaluation of changes in haematocrit
Andrey Belousov
Laboratory Applied Nanotechnology of Belousov, Kharkov Medical Academy of Postgraduate
Education, Ukraine
J Nurs Health Stud 2018 Volume: 3
DOI: 10.21767/2574-2825-C4-012
Table 1)
the variants of changes in hematocrit on the background
of the basic organism physiological parameters
Notes:
HCT–hematocrit; BP-blood pressure; Shock index=Pulse
rate/Systolic blood pressure (normal=0.54). Variant I is hemic
hypoxia. Variant II is hypovolemic state. Variant III is mixed
form of hypoxia (circulatory + hemic hypoxia) that is caused
by massive blood loss. Variant IV is hypovolemic polycythemia