NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 74
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
T
he surface condition of a component is usually the most
important engineering factor affecting its performance.
Almost inevitably the outer surface of a workpiece is subjected to
wear,fatigueandcorrosionwhileitisinservice.Averageroughness
(Ra) is important feature of the surface. It contributes slide wear,
friction, corrosion, oxidation, fatigue, physical properties (optical,
electrical, and thermal properties) and esthetic. Laser as a source
of high concentrated heating energy was used successfully in
surface treating of ferrous material products. Laser heating or
meltinginducesphasetransformationandstructuralchanges,also
low distortion with minimal disruption. These changes affect the
surface roughness either negatively or positively that is depending
on the processing set of parameters. Laser processing variables
comprise that related to laser source (power intensity, operation
mode and wavelength) and to the material (physical properties,
surface absorptivity and geometry) in addition to laser scanning
speed and shrouding gas flow rate. [8]. To avoid post processing
and get preferred surface roughness the relation between laser
parameters and surface roughness is to be investigated for a
given material. Many researchers study the effect of laser cutting
and heat treating parameters on surface roughness. In this work
investigation of the effect of processing variables on the average
surface roughness (Ra) of gray cast ironmelted by CWdiode-fiber
Yb:YAG laser. Power intensity (I), time of interaction (t), and gas
flow rate (g) were used as variables. It is found that for power
intensities that maintain melting, decreasing time of interaction,
increasing shrouding gas flow rate or increasing both of them led
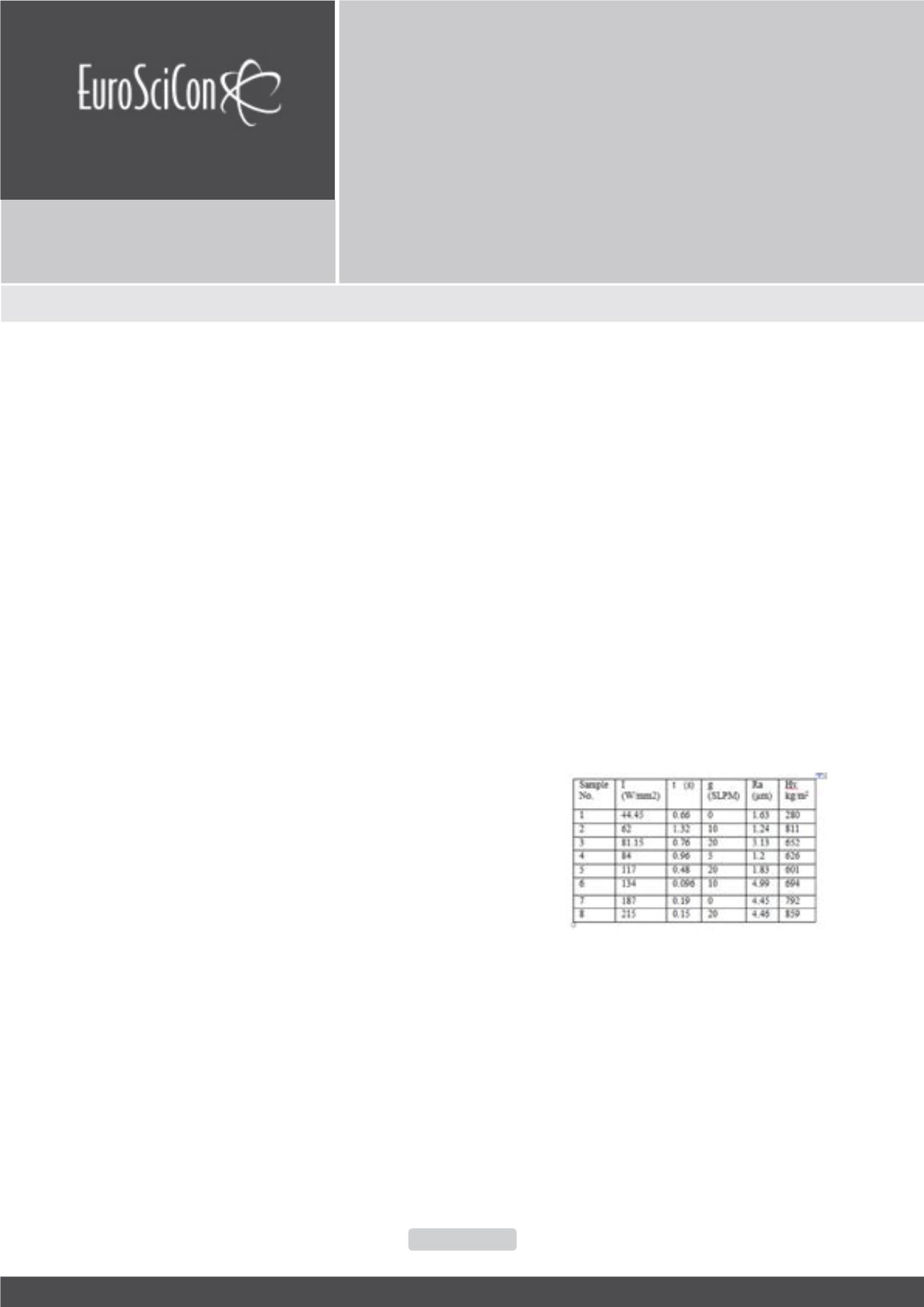
to increased average surface roughness. Table 1 represents the
processing parameters via the resulted microhardness and the
average surface roughness.
Recent Publications
1. Rehab H. Khanjar, Mohammed J. Khadhim and Adil
Abbas Alwan, 2017. Experimental investigation of
melting gray cast iron by laser. Journal of Material
Science Engineering Volume 6 Issue 5(Suppl) pp 77.
2. Rehab H. Khanjar, “ Analysis of gray cast iron
microstructure and hardening by using Yb:YAG Laser”,
PhD Thesis series, University of technology/Baghdad.
3. Mohammed J. Kadhim Rehab H. Khanjar and Adil Abass
Alwan. 2016. Performance evaluation of laser melting
gray cast iron. , The First International Conference for
Engineering Researches ICER(1-2/3/2017) Middle
Technical University, Baghdad, Iraq.
4. Khayria Salman, Rehab H. Khanjar and Shada M. Rajaa,
2011. The Effect of Liquid Nitriding and Carborizing
on Adhesive Wear resistance of carbon steel 1020.
Engineering & Technology Journal V 29, essue 5, pp
231-240.
Figure 1:
Nano particles and their effect on yield and economics of B.
juncea
Biography
Fifteen years of working research experience at National dairy Development
Board, CAR C-NEH Region, Directorate of Rapeseed-Mustard Research
and ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi. Specialized in
farming system research under hill and shifting cultivation for higher in-
come, micro-irrigation and resource conservation technologies in mustard
based cropping system. Handled externally funded and institute projects.
Published >65 international and national research papers, ten bulletin, four
extension folders, 15 book chapters and one book. Also handled 10 exter-
nally funded project including World Bank sponsored and 12 institutional
projects.
rehab@leetani.comThe Effect of laser melting on the gray cast iron surface
roughness
Rehab Hussein Khanjar
Dr., Middle Technical University, Institute of Technology/Baghdad, Iraq
Rehab Hussein Khanjar, Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-009