Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
NanoMat 2018
Page 14
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
A
luminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) is a transparent conductor
that can be used in thin film form as transparent electrode
of electro-optical devices. For most of actual applications, a
large conductivity is required on large surface areas. The rapid
growth of transparent electronics and electro-optical devices
on flexible supports calls for the development of methods
that enable the synthesis of transparent conducting films
without thermal assistance while keeping high electrical and
optical performances. Magnetron sputtering has emerged as a
reference method for the synthesis of AZO films. It is particularly
due to, its scalability to industrial scale. Unfortunately, AZO films
usually produced without thermal assistance using magnetron
sputtering tend to a strong inhomogeneity of the electrical
properties with a large sensitivity to the process parameters
(composition of the gas phase, geometry of the experiment).
This presentation first highlights the interest of high power
impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) to synthesize AZO films
of high electronic conductivity on large surface areas andwithout
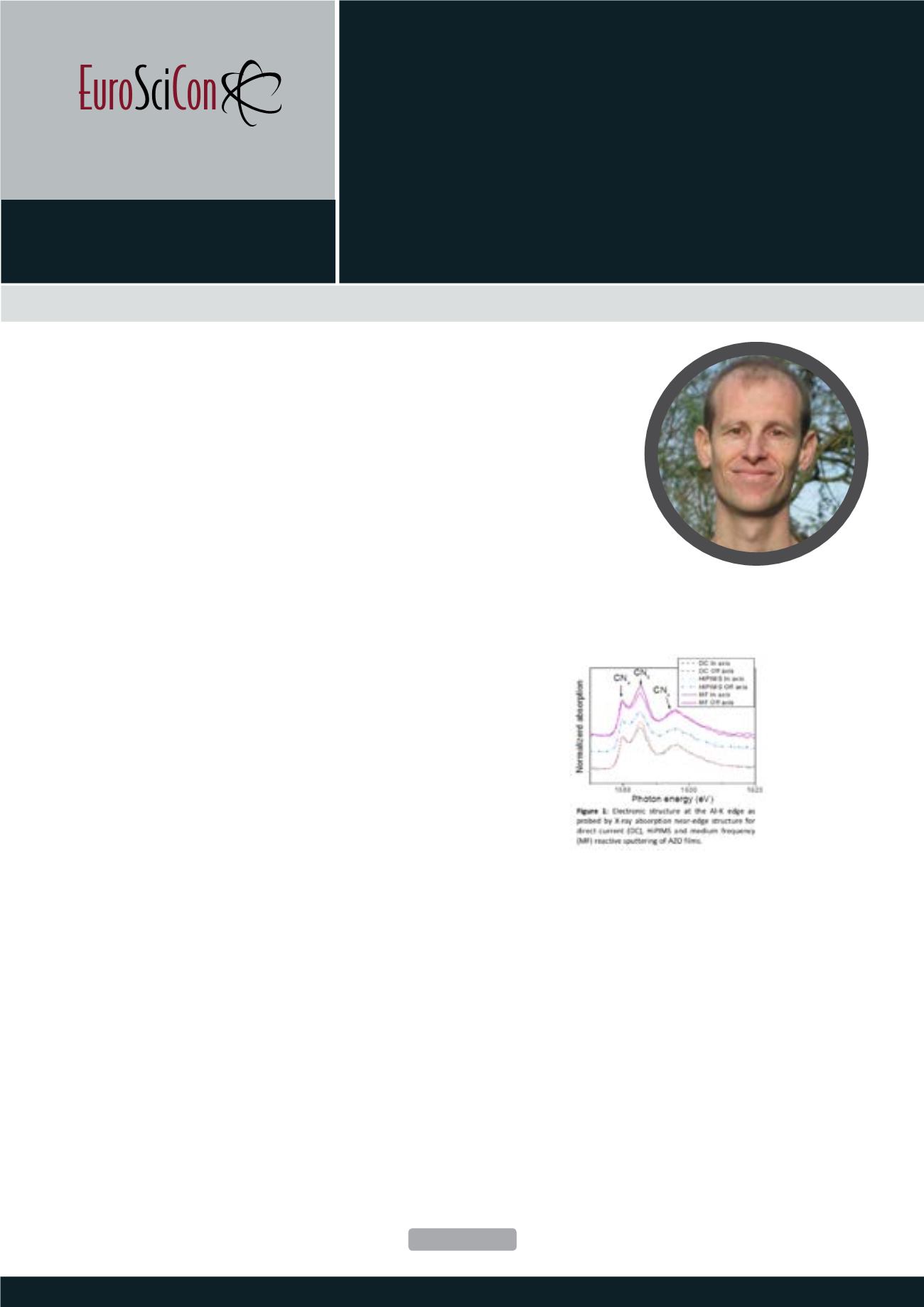
thermal assistance. Electronic structure measurements using
X-ray absorption spectroscopy evidence a correlation between
the distribution of the electrical behavior and dopant activation/
inactivation. A deactivation mechanism, complementary to the
well-known compensation of dopants, is proposed in the case
of conventional sputtering. A model explaining the minimization
of the deactivation amplitude is proposed in case of HiPIMS. In
a second part we will show how the electrical properties of AZO
films degraded after long term exposure to ambient moisture
can be restored by low temperature thermal annealing and how
thermal assistance during growth can prevent degradation upon
exposure to ambient moisture. Finally, self-nanostructured AZO
films could be obtained using HiPIMS under certain conditions
and their interest for flexible electronics is highlighted.
Recent Publications
1. D Horwat and A Billard (2007) Effects of substrate
position and oxygen gas flow rate on the properties of
ZnO: Al films prepared by reactive co-sputtering, Thin
Solid Films 515(13):5444-5448.
2. D Horwat, et al. (2010) On the deactivation of dopant
and electronic structure in reactively sputtered transpar
ent Al-doped ZnO thin films Journal of Physics D:
Applied Physics 43, 132003.
3. M Jullien, et al. (2011) Influence of the nanoscale
structural features on the properties and electronic
structureof Al-dopedZnO thinfilms: anX-ray absorption
study. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 95:2341-
2346.
4. M Mickan et al. (2016) Room temperature deposition
of homogeneous, highly transparent and conductive
Optimization of Al-doped Zno transparent
electrodes with and without thermal
assistance using HiPIMS
David Horwat
Institut Jean Lamour - University of Lorraine, France
David Horwat, Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-007