A p r i l 1 8 - 1 9 , 2 0 1 9
P a r i s , F r a n c e
Page 47
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Advanced Nanotechnology 2019
EuroSciCon Conference on
Advanced Nanotechnology
S
ubstituted pyrimidines are very important biologically and pharmaceutically active agents in the medicinal chemistry and drug
discovery processes. A multicomponent reaction (MCRs) is ideal synthetic strategy to construct diverse molecular scaffolds
of tetrazolopyrimidines starting from a few simple materials or intermediates. In connection with our continuous interest in
designing new efficient and green protocols for synthesis of new biologically active compounds, we developed sonochemical
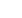
approach for the one-pot four-component synthesis of 5-methyl-7-aryl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylic esters,
obtained in the reaction of 2-cyano-guanidine, sodium azide, various aromatic aldehydes and methyl or ethyl acetoacetates in
the presence of a catalytic amount of new functionalized hybrid organic-inorganic nanoparticle magnetic metal oxide core–shell
based [1] catalyst Fe
2
O
3
@SiO
2
-(CH
2
)
3
NHC(O)(CH
2
)
2
PPh2.This is the first design, preparation, full characterization and application
of the present nanomaterial and also the first ultrasound irradiated synthesis of the biologically and pharmaceutically important
heterocyclic compounds in water used as a green solvent. The novel protocol offers several advantages such as high yields, short
reaction times, mild reaction conditions, environment-friendly reaction media, easy isolation of the products, simple preparation
and recoverability of the nanocatalyst by an external magnet and reusing several times without significant loss of activity. The
details of our studies, which describe a scope and generality of the one-pot, simple and high atom economy strategy of synthesis
of tetrazolopyrimidine derivatives with respect to various starting materials, will be presented.
O.Demchuk@IFarm.euNew magnetic nanoparticle catalyst for
the synthesis of pharmaceutically active
tetrazolopyrimidines
Oleg M Demchuk
1
, A Maleki
2
, J Rahimi
2
, A Z Wilczewska
3
and
R Jasinski
4
1
Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Poland
2
Iran University of Science and Technology, Iran
3
University of Białystok, Poland
4
Institute of Organic Chemistry-Cracow University of Technology, Poland
Nano Res Appl 2019, Volume:5
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C2-034
Cat
.
( 5 mol%)
,
H
2
O
Cat
. :
Ultrasonic
irradiation
15
-
20 min ,
80
-
90%
Fe
2
O
3
O
O
O
Si
HN P
SiO
2
O
+
H
O
3
4
+
O
O
O
R
2
R
1
N
H
N
N
N
N
OR
2
O
R
1
1
2
NH
2
NH
2
N
N
NaN
3
+
5
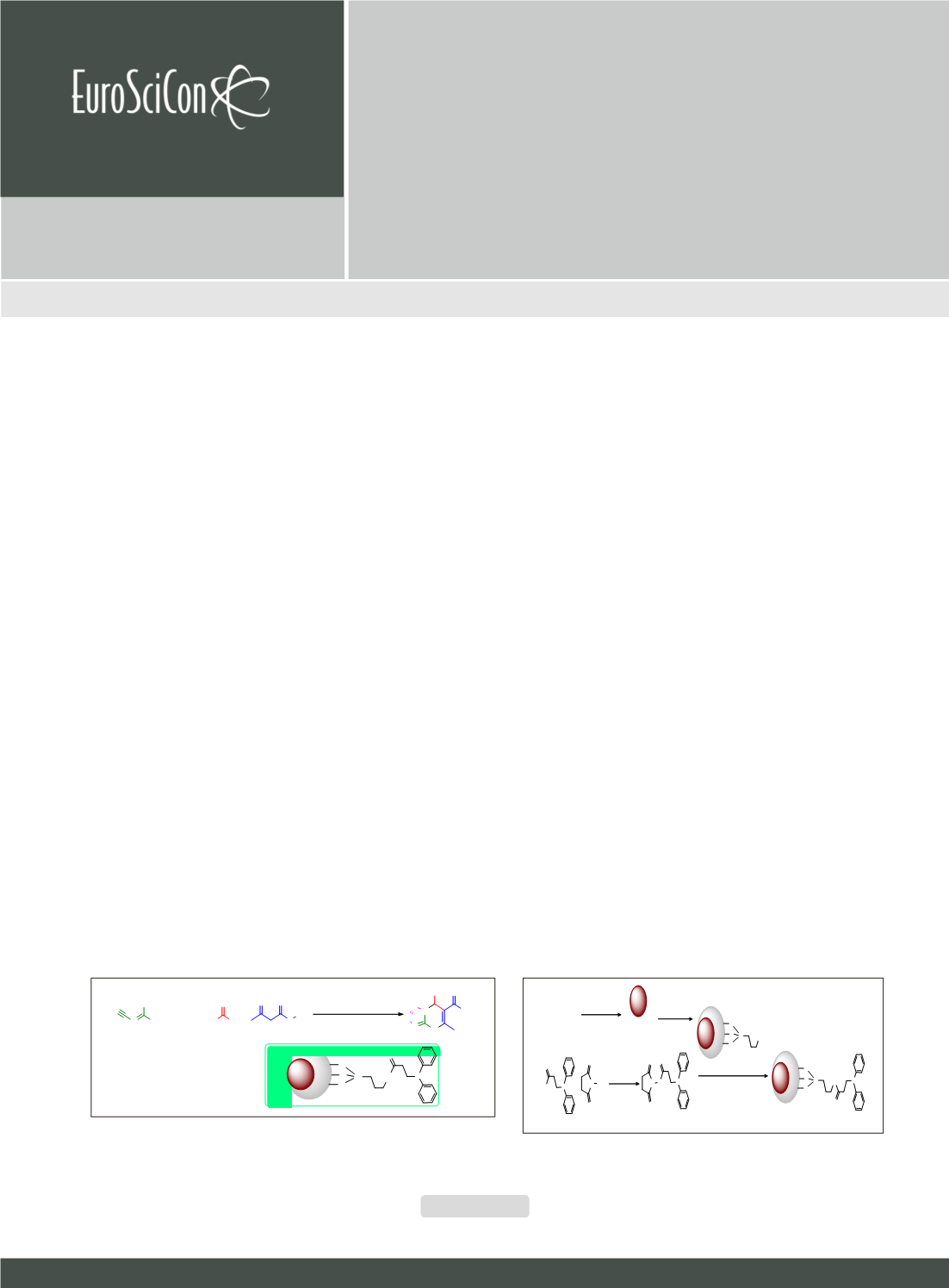
FeCl
2
+FeCl
3
NH
3
,
H
2
O
80
°
C , oleicacid
Fe
2
O
3
bare
NMP
APTMS ,
NH
3
H
2
O ,
EtOH , r .
t
.
Fe
2
O
3
O
O
O
Si
NH
2
P
SiO
2
O
MNPs @ NH
2
N
O
O
OH
HO
+
DCC ,
DCM
P
O
ON
O
O
P
O
Fe
2
O
3
O
O
O
Si
H
N
SiO
2
MNPs @ NHC(O)CH
2
CH
2
PPh
2
-
10
°
C
to r .
t
.
90%
DMF ,
DMAP ,
30
o
C ,
)))))))
77%
I
II
III