E u r o s c i c o n C o n f e r e n c e o n
3D Printing and Wireless
Technology
American Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology
ISSN: 2349-3917
S e p t e m b e r 1 7 - 1 8 , 2 0 1 8
L i s b o n , P o r t u g a l
Wireless and Printing Technology 2018
Page 20
I
ncol718 alloy specimens were fabricated by the selective laser melting (SLM)
method. The effect of parameters such as laser power and scanning speed on
the microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated. It is found the
energy density, a function of laser power, scanning speed and hatch distance is
greatly related to the mechanical properties. The specimen fabricated with laser
power 200 W, scanning speed 1000 mm/s, and hatch distance 0.1 mm and layer
height 0.02 mm achieved best mechanical properties. The as-fabricated tensile
strength reaches800MPa in the fabricationdirection, 15%higher than thestandard
property, while the elongation keeps 32%. Its microstructure in the vertical section
is regular columnar grains, 20 um wide. The stack of the melt pools are regular,
and the level of each layer is smooth. The soundness and columnar grains result
its high mechanical property.
Microstructure and mechanical property
characterization of Incol718 alloy specimen
printed by selective laser melting
Jinwu Kang
1
, JH Yi
1
, CY Deng
1
, YL Feng
2
,
PY Wu
2
and T Feng
2
1
Tsinghua University, China
2
Beijing e-Plus 3D Tech. Co. Ltd, China
Jinwu Kang et al., Am J Compt Sci Inform Technol 2018 Volume: 6
DOI: 10.21767/2349-3917-C2-004
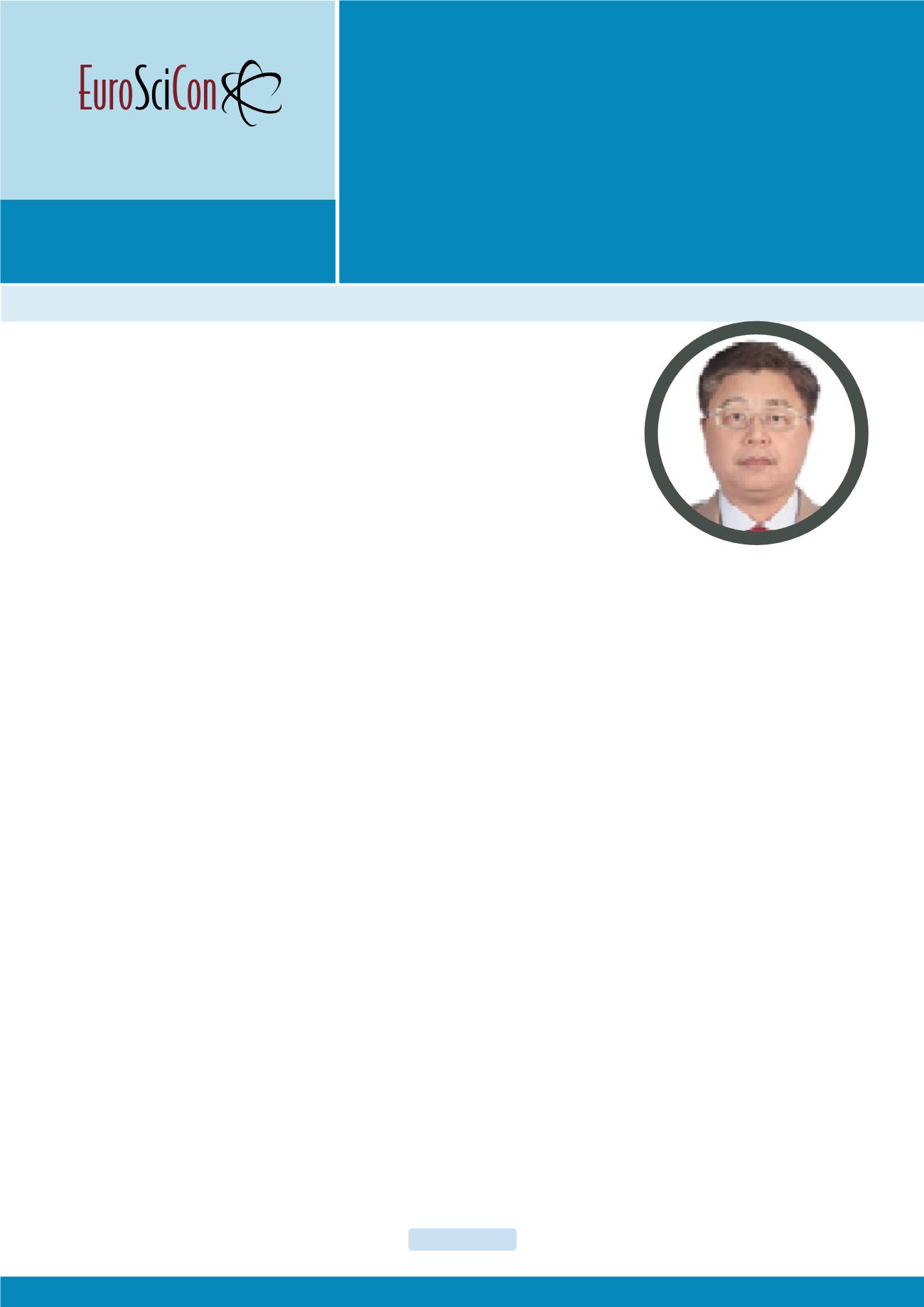
Biography
Jinwu Kang has received his PhD from Tsinghua University. He
is an Associate Professor of School of Materials Science and
Engineering, Tsinghua University. He performed his research
as Research Scientist at Worcester Polytechnic Institute, USA
fromMay’ 2001 to Jan’ 2003. He has been doing research about
the modelling and simulation of casting and heat treatment
processes of casting, 3D printing of sand moulds and metallic
parts in recent years. He proposed the description methods
for the deformation of castings, intensive riser cooling of
castings after their solidification and 3D printed hollow mould
for castings to realize controlled cooling at whole scale. He has
published 170 papers and received four academic awards from
the Ministry of Education, China for his distinguished research.
He is the Chief Editor of Materials Science and Engineering
International Journal.
kangjw@tsinghua.edu.cn