E u r o s c i c o n C o n f e r e n c e o n
3D Printing and Wireless
Technology
American Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology
ISSN: 2349-3917
S e p t e m b e r 1 7 - 1 8 , 2 0 1 8
L i s b o n , P o r t u g a l
Wireless and Printing Technology 2018
Page 17
T
he use of additive manufacturing in the medical field is expanding very fast
due to the ability to produce complex, low weight and personalized medical
devices in a wide range of biocompatible, degradable and non-degradable
materials such as polymers, metals, ceramics and composites. It also allows
printing biological materials such as cells. In this field, additive manufacturing is
being used to produce passive devices for repairing and restore applications and
active devices for repairing, restoring and regeneration. One of the key applications
of additive manufacturing in the medical field is the 3D bioprinting of tissue
engineering scaffolds. The design of optimized scaffolds for tissue engineering is
a key topic of research, as the complex macro- and micro-architectures required
for a scaffold depends not only on the mechanical properties, but also on the
physical and molecular queues of the surrounding tissue within the defect site.
Thus, the prediction of optimal features for tissue engineering scaffolds is very
important for its mechanical, vascular or topological properties. The relationship
between high scaffold porosity and high mechanical properties is contradictory,
as it becomes even more complex due to the scaffold degradation process. In this
researchwork, optimised design schemes based on 3Dmodelling (CAD (computer
aided design) modelling techniques and biomimetic modelling from micro-CT
(computed tomography) data) and numerical simulations (such as structural,
vascular and topology optimisation schemes) will be presented in order to aid the
design process of optimised scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.
Optimized modelling and design schemes for
tissue engineering scaffolds for 3D printing
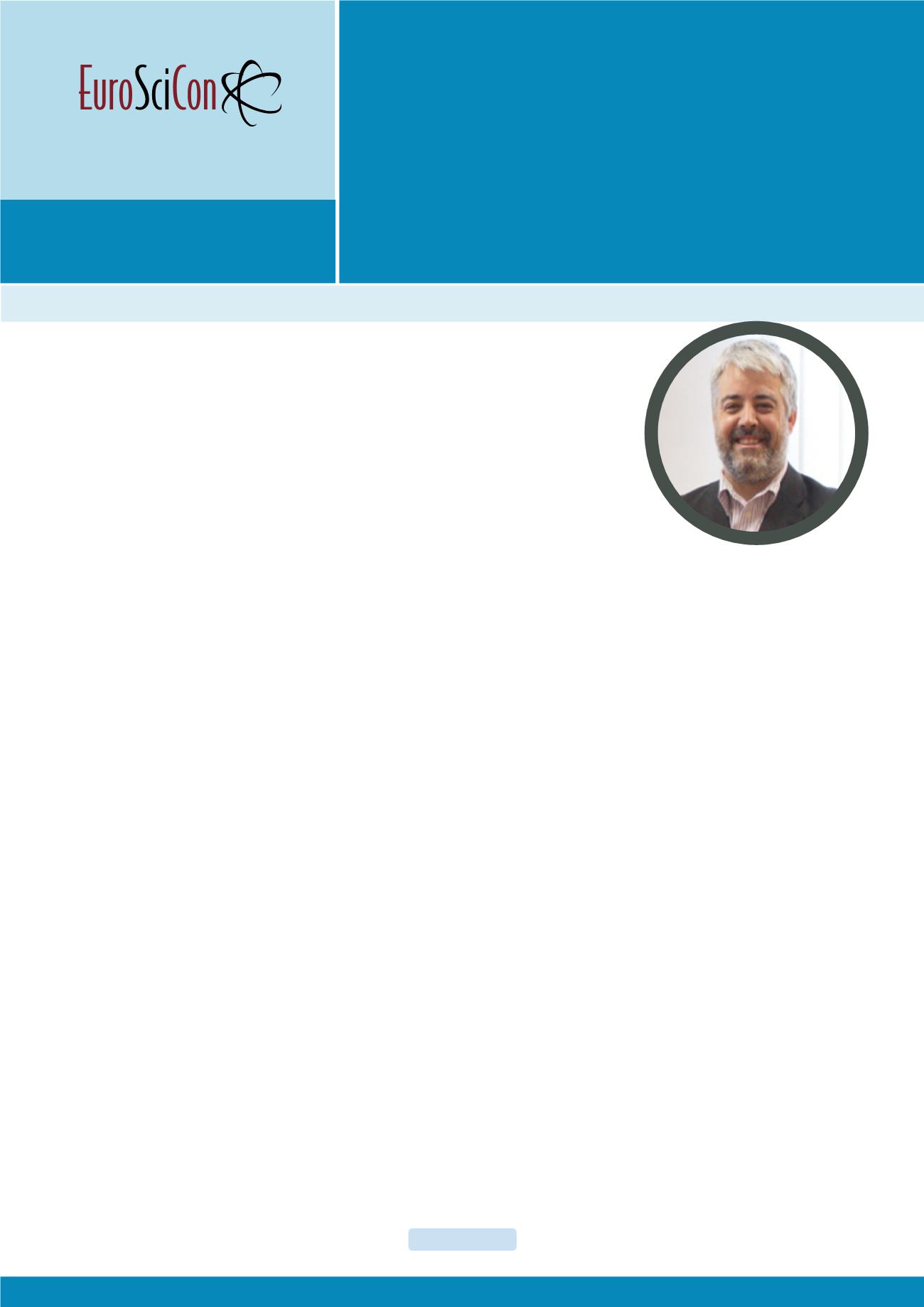
Henrique A Almeida
CIIC-ESTG, Instituto Politécnico de Leiria, Portugal
Henrique A Almeida, Am J Compt Sci Inform Technol 2018 Volume: 6
DOI: 10.21767/2349-3917-C2-004
Biography
Henrique Almeida is an Associate Professor at School for
Technology and Management (ESTG) (Mechanical Engineering
Department) and Research Member of Centro de Investigação
em Informática e Comunicações of Polytechnic Institute of
Leiria (IPL). He has received his PhD degree in Mechanical
Engineering from University of Aveiro. He is a Member of the
Editorial Board of journals from Springer
(Progress in Additive
Manufacturing
), Emerald (
Rapid Prototyping Journal
), Crimson
Publishers and Editorial Board Reviewer of several journals
from Frontiers (
Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering
). He has
more than 250 publications as journal papers, book chapters
and conference proceeding papers. He also has edited 10
books and 8 national Portuguese patents.
henrique.almeida@ipleiria.pt