Notes:
Volume 3, Issue 2 (Suppl)
Trends in Green chem
ISSN: 2471-9889
Environmental & Green Chemistry 2017
July 24-26, 2017
Page 55
5
th
International Conference on
6
th
International Conference on
July 24-26, 2017 Rome, Italy
Environmental Chemistry and Engineering
Green Chemistry and Technology
&
Clean and sustainable liquid hydrogen storage materials
Chang Won Yoon
1,2
1
Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea
2
Kyung Hee University, Republic of Korea
T
o address the increasing energy and environmental issues, efficient and sustainable energy carriers alternative to carbon based
fuels for the current power generation are being extensively investigated. One of the key issues for achieving the “hydrogen
economy” is to develop reliable hydrogen storage/release systems that store/release large quantities of hydrogen in a safe and
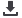
economically viable manner. In this context, liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) such as carbazole and methylcyclohexane
have attracted significant attention owing to their high reversibility as well as high volumetric hydrogen storage density. In addition
to this, carbon dioxide is a potential hydrogen storage medium that can store hydrogen as a form of liquid formic acid (HCO
2
H,
FA) with a significantly high volumetric H
2
storage capacity of 53 g.L
-1
, much higher than compressed hydrogen gas. Despite the
attractive hydrogen release properties of these materials, however, it is still needed to screen highly active and selective catalysts
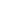
for the reversible hydrogen storage. In this contribution, Pd-based heterogeneous catalysts for FA dehydrogenation are introduced,
and relevant H
2
-release properties are discussed. Furthermore, liquid organic materials are also proposed as potentially reversible
hydrogen energy carriers, and their hydrogenation properties are discussed.
Figure: Catalytic Dehydrogenation Figure: A schematic image for FA dehydrogenation
over Pd/C
3
N
4
catalysts]
Biography
Chang Won Yoon is a Principal Research Scientist of the Fuel Cell Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST). He is also a Professor
of the KHU-KIST Department of Converging Science and Technology at Kyung Hee University as well as a Professor of the KIST School (E&ET). He received
his BS and MS in Chemistry at POSTECH in Korea and obtained the Doctoral degree (PhD, 2008) in Chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania (PENN) in
USA. He further conducted research associated with Clean Energy in Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley (2008-2010), and then joined the KIST in
2010. His research has been focusing on hydrogen production and storage particularly for fuel cell technologies as well as on catalysis for a number of chemical
transformations related to energy conversion.
cwyoon@kist.re.krChang Won Yoon, Trends in Green chem, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9889-C1-002