Chemistry Education 2018
Journal of Organic & Inorganic Chemistry
ISSN: 2472-1123
Page 27
August 27-28, 2018
Zurich, Switzerland
8
th
Edition of International Conference on
Chemistry Education
and Research
Background:
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most common cause
of diabetic neuropathy (DN). In 2014 the WHO estimated an
overall prevalence of 422 million (8.5%). The incidence of diabetic
neuropathy approaches 50% in most diabetic populations; its
treatment still remains unresolved. The optimal therapy involves:
blood glucose level control, anticonvulsants, antidepressants and
opioid administration, though it does not change pathogenic pattern.
It has been identified that tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and
renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) play a significant role
in Type I and Type II diabetes development. The discovery of (pro)
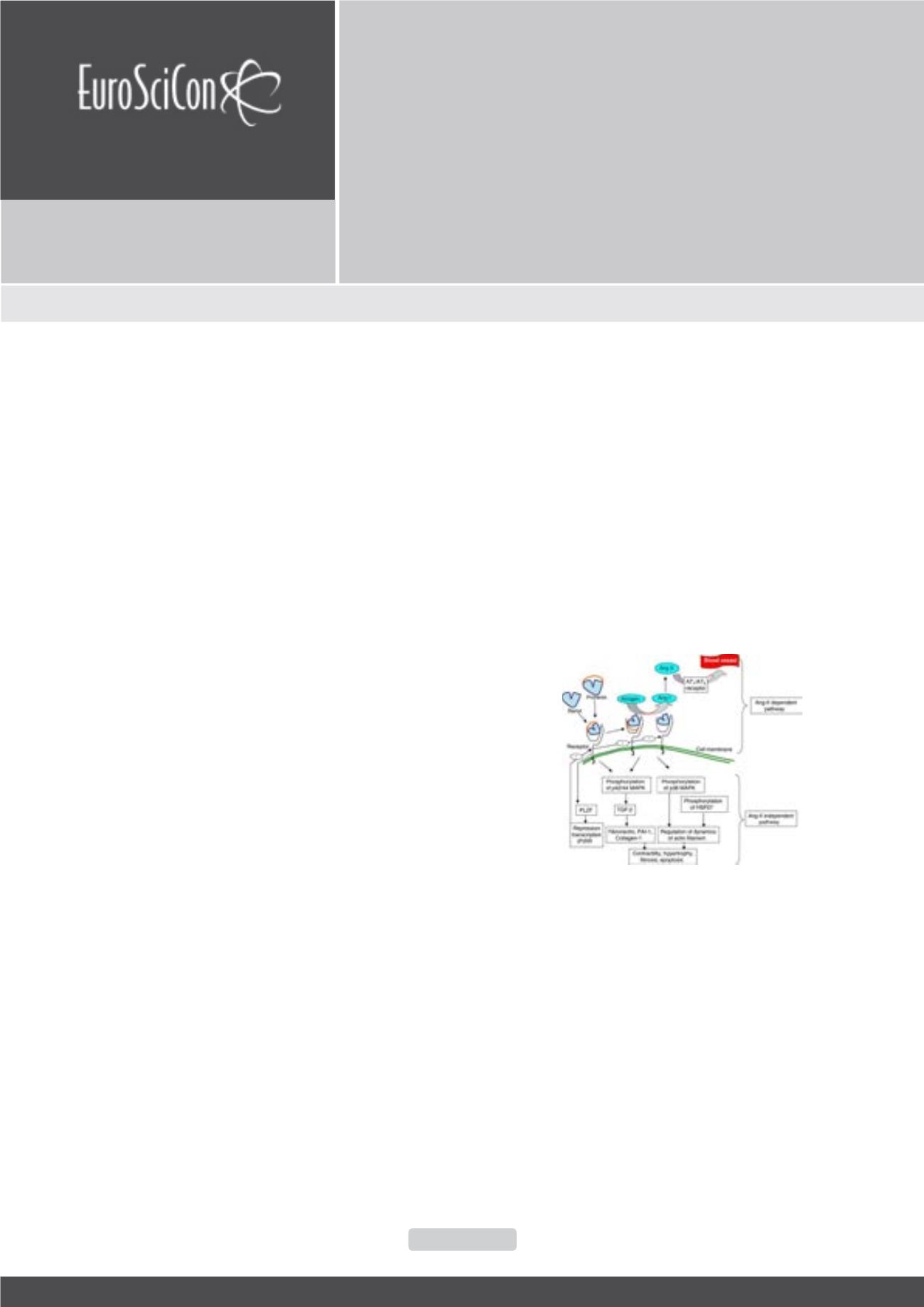
renin receptor, (P)RR, has made the renin–angiotensin system (RAS)
more multifaceted. After binding to the receptor, renin/prorenin carry
out their functions either in angiotensin-II-dependent or - independent
pathways that may facilitate the generation of angiotensin-I or
activation of second messenger, respectively. The data collected in
the present-day indicate the essential pathogenic role of TNFα and
RAAS in the development of T2DM and diabetic neuropathy (DNP)
through the activation of Ag II or/and transcription factor MAPK
and NFκB an important factors in the control of cell proliferation,
differentiation, and apoptosis. In our study we study aliskiren efficacy,
that indirectly inhibit the binding of renin to prorenin/renin receptor
(P)RR by changing the local conformation of renin. On the other hand,
this renin inhibitor significantly decreases the mRNA expression of
(P)RR in the kidney cortex of diabetic hypertensive Ren2 rats.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation:
The study population
consists of 30 individuals diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (DM)
complicated with DNP. The enrolled subjects are divided into two
main groups: group I to take aliskiren and group II with the same
pathology, proceeding with the treatment without aliskiren but given
telmisartan (ARB), for certainty of aliskiren efficacy. At the start of
the trial and on completion of the six weeks period TNFa level and
C-peptide (for T2DM) will be determined.
Findings:
Aliskiren improves conditions of T2DM patients with DNP.
Namely, the symptoms of neuropathy are reduced, the blood TNFa
level is reduced and C-peptide level is increased.
Conclusion & Significance:
Our results confirm hypothesis that
TNFα and RAAS may play a substantial role in the development and
progression of T2DM as well as in pathogenesis of DPN. Aliskiren
has modulatory impact on TNFα, as well as on renin/prorenin both
pathways. So, we have results for clinical and pharmacological
analysis of aliskiren application in diabetic neuropathy.
Recent Publications
1. Rabie E M, Heeba G H, Abouzied MM and Khalifa MM
(2015) Comparative effects of aliskiren and telmisartan
in high fructose diet-induced metabolic syndrome in
rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 760:145-53.
2. A H M Nurun Nabi and Fumiaki Auzuki (2010)
Biochemical properties of renin and prorenin binding to
the (pro)renin receptor. Hypertension Research 33:91-
97.
3. A Sadeghpour, M Rappolt, D Ntountaniotis, et al.
(2015) Comparative study of interactions of aliskiren
and AT1 receptor antagonists with lipid bilayers. BBA
1848(4):984-994.
Biochemical properties of ALS and TEL effects on (P) RR induced
processes in patients with diabetic neuropathies
Anna Sh Archvadze, A Kistauri, N Gongadze
and
K Chirakadze
Tbilisi State Medical University, Georgia
Anna Sh Archvadze et al., J Org Inorg Chem 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2472-1123-C5-014