Volume 4
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
JOINT EVENT
October 04-05, 2018 Moscow, Russia
&
2
nd
Edition of International Conference on
26
th
International Conference on
Advanced Nanotechnology
Materials Technology and Manufacturing Innovations
Advanced Nanotechnology 2018
& Materials-Manufacturing 2018
October 04-05, 2018
Page 41
Status and future directions of adaptive, smart and sustainable machining systems for aerospace
applications
M
anufacturing remains the largest and most important wealth generating sector. Within this sector, material removal
is a key technology in the aerospace and automotive industries, contributing to more than $200 billion to the
economy in North America on annual basis. The demand for high productivity and high accuracy is steadily increasing,
along with the increasing attention to the impact on the environment. In this work, only conventional machining
processes are discussed, although a number of nonconventional processes are in demand in the aerospace industry. A
system approach to the machining system is presented in terms of its elements (machine, tool, work piece and fixture),
properties (materials, configuration, contact interfaces) and interactions (dynamic, tribological, thermal, thermo-elastic)
to set the framework for predicting the system response (quality attributes and machining-induced defects) to the
operational input (controlled cutting conditions and uncontrolled dynamic-tribo-thermo-elastic self-induced changes).
The paper provides a critical assessment of the current status of smart and sustainable material removal technologies,
and the research effort towards the development of new and hybrid machining strategies and processes for: (a) high
speed/high performance machining, sustainable manufacturing and tool life management, (b) machining of composites,
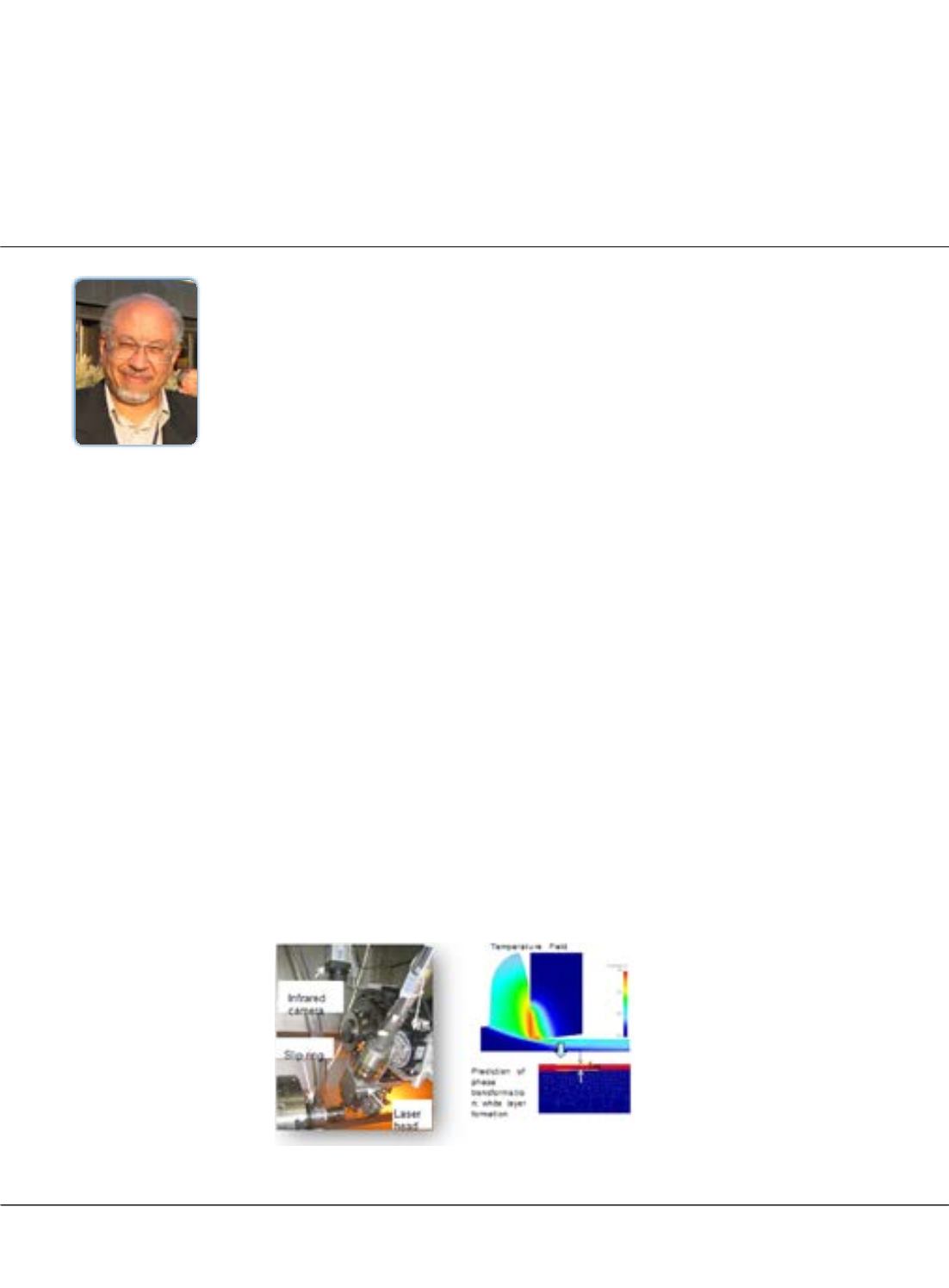
stacked materials, (c) high performance/ super abrasive advanced grinding and polishing, (d) physics-based modeling
and simulation of the machining system to achieve a virtual machining environment for the realization of the first part
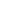
correct philosophy, and (e) adaptive machining, where model-based control systems of the part-machine tool interaction
and process monitoring allow the industry achieve unmanned closed machining key enabling technologies have been
identified to achieve these terminal objectives.This includes newprocesses for achievingmicro-nano-sizedmicrostructure
components, and to deal with new materials. Other new trends include the integration of non-conventional technologies
towards the development of new hybrid multifunctional machining processes.
Mahmoud Helmi Attia
1, 2
1
McGill University, Canada
2
National Research Council, Canada
Mahmoud Helmi Attia, Nano Res Appl 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C5-019