Occupational Health 2018
Journal of Nursing and Health Studies
ISSN: 2574-2825
Page 22
May 28-29, 2018
London, UK
4
th
Edition of International Conference on
Occupational Health and
Safety
T
he silica (mostly amorphous) containing submicron
spherical particles with a prevailing proportion of those
in the upper nanoscale range (mean diameter 90±30 nm)
induces, when instilled intratracheally into rat’s low airways,
a typical phagocytic cells’ response comparable with that to
very cytotoxic and fibrogenic standard quartz powder DQ12.
However, under a long-term (up to six months, five times a
weak, four h per day) inhalation nose-only exposure at realistic
concentrations (2.6±0.6 or 10.6±2.1 mg/m3 ) rats developed
but a quite negligible pulmonary silicosis along with very low
systemic toxicity. Such unusual discrepancy between acute
and chronic adverse effects of particulates could be explained
by the demonstrated low SiO2 retention in lungs and other
organs most probably due to a relatively high solubility of
these nanoparticles in relevant biological and model milieus.
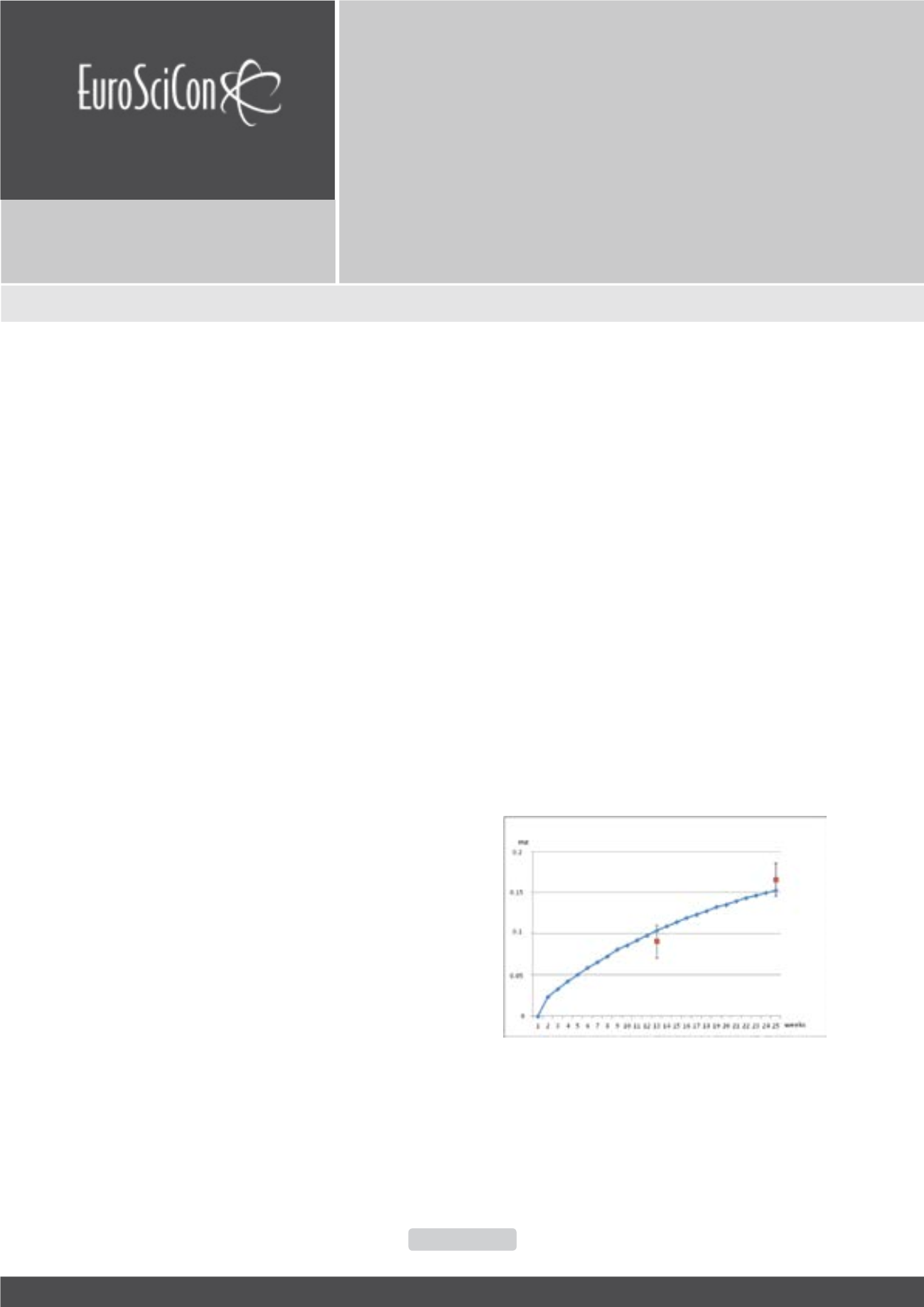
The multi-compartmental mechanistic model (figure 1) which
had been previously found adequate for imitating pulmonary
retention of different particles could be satisfactorily adjusted
to the present experimental results (figure 2) only when
operating with constants describing both the dissolution and
cell-mediated controlling mechanisms. The unexpectedly
mild adverse effects notwithstanding, the harmfulness of the
studied industrial aerosol deserves a cautious assessment as
a health risk factor because of its genotoxicity and trans-nasal
penetration of nanoparticles into the olfactory brain found by
us in the same inhalation experiment.
Figure 2. Silica content of rat lungs exposed
compartmental model for the kinetics of to 2.5 mgm3
aerosol concentratioin
Interplay of the pulmonary phagocytosis response to, and
the in vivo solubilization of amorphous silica nanoparticles
deposited in lungs of rats under long-term inhalation
exposures as determinants of their modest fibrogenicity and
low systemic toxicity
Svetlana N Solovyeva, Marina P Sutunkova, Boris A Katsnelson, Vladimir B
Gurvich, Larisa I Privalova, Ilzira A Minigalieva, Tatyana V Slyshkina, Irene E
Valamina, Oleg H Makeyev, Vladimir Ya Shur, Ilya V Zubarev, Dmitry K Kuznetsov
and
Ekaterina V Shishkina
Ekaterinburg Medical Research Center, Department of Toxicology and Biological Prophylaxis,
Russia
Svetlana N Solovyeva et al., J Nurs Health Stud 2018, Volume 3
DOI: 10.21767/2574-2825-C2-005