
E u r o S c i C o n C o n f e r e n c e o n
Nanotechnology &
Smart Materials
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN 2471-9838
O c t o b e r 0 4 - 0 6 , 2 0 1 8
Am s t e r d a m , N e t h e r l a n d s
Nanotechnology & Smart Materials 2018
Page 33
P
rogrammable introduction of heterogeneity at the nanoscale plays a key role
in the design of functional building blocks for catalysis, electronic devices,
and numerous other applications. Synthetic strategies for attaining well-defined
heterogeneity in structure, shape, composition and modulation of the electronic
structure at selected regions of the nano system is therefore highly desired. I will
present our research towards two methodologies for post-synthesis modification
and symmetry breaking of semiconducting nanostructures using nanowires as
the basic building blocks covering two aspects of post-synthesis modification
of nanowires: (I)
Ex-situ
doping of silicon nanowires.
Ex-situ
doping enables the
transformation of un-doped silicon nanowires into heterogeneously doped build-
ing blocks featuring sharp p-i-n junctions across the nanowire. Relying on surface
chemistry provides an accurate dose and initial positioning together with fine con-
trol over the diffusion processes. The monolayer doping methodologies are valu-
able for decoupling the doping step from the nanowire synthesis step, resulting in
ex-situ
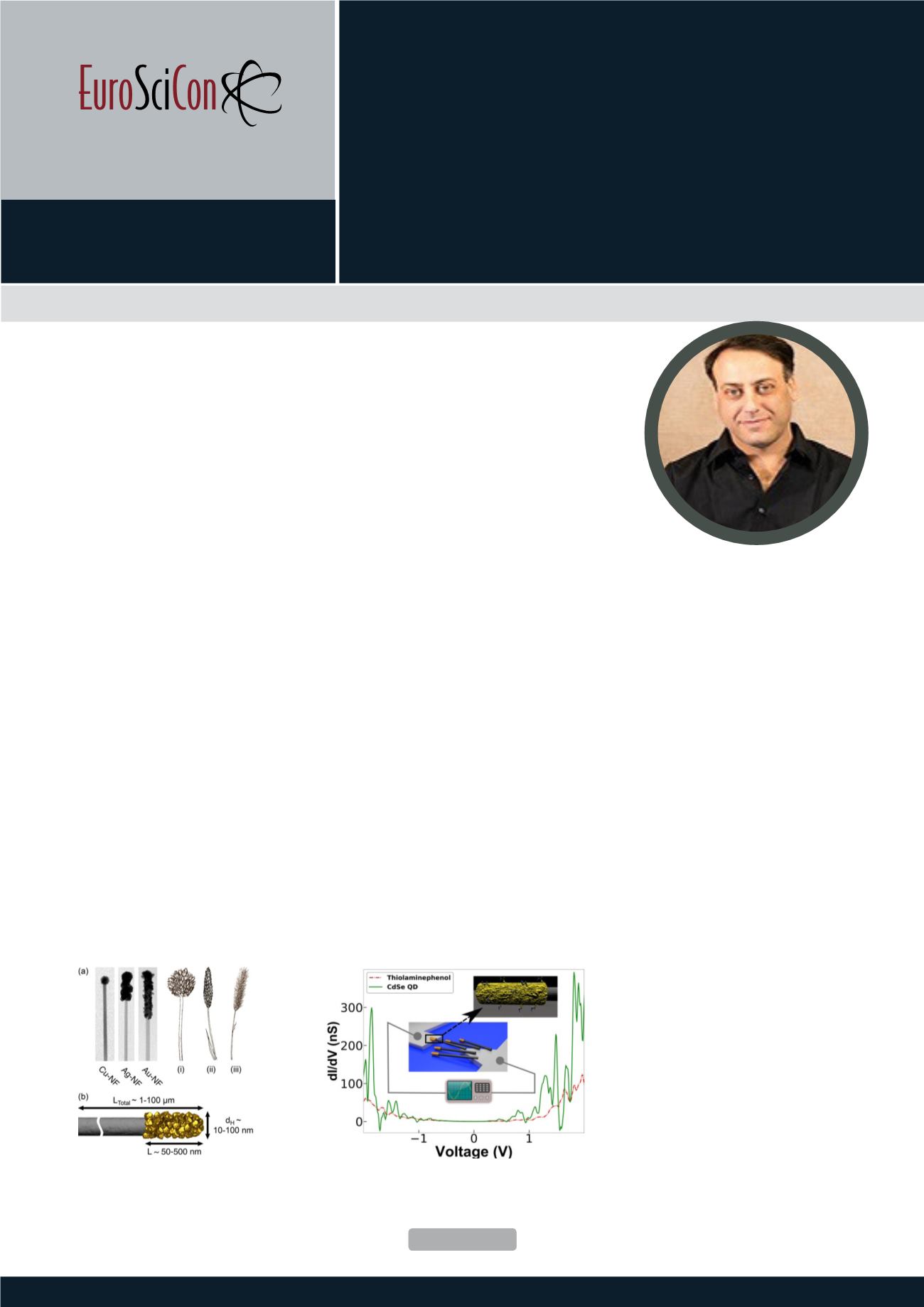
doping. (II) Self-processing synthesis of coinage metal-semiconductor hy-
brid structures. The hybrid nanostructures obtained for the coinage metals resem-
ble the morphology of grass flowers, termed Nano-floret hybrid nanostructures
consisting of a high aspect ratio SiGe nanowire (NW) with a metallic nanoshell
cap. The new class of structures is useful in a variety of applications owing to the
unique geometrical aspect ratio and electronic properties of the hybrid systems.
The synthesis involves a sequence of selective etch and deposition steps which
are self-initiated and self-terminated resulting in the hybrid nanostructures
Biography
Roie Yerushalmi has received his PhD in Chemistry from the
Weizmann institute of science, Israel, in 2005 (awarded the Ken-
nedy prize for outstanding PhD work). He pursued Postdoc in
the field of Nanoscience in the lab of Prof Ali Javey at UC Berke-
ley from2006-2008. In 2008, he joined the InstituteOf Chemistry
at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel. He is serving as
an Associate Professor at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
since 2015. His main research interests include development
of new surface chemistries, atomic and molecular layer deposi-
tion, nanowire synthesis methodologies, hybrid nanostructures,
ex-situ doping of nanostructures, nanostructure array assem-
bly, and comprehensive characterization of complex nanostruc-
tured systems by application of analytical methods. Design and
synthesis of hybrid nanostructures for photocatalysis, electrical
and optical applications, energy harvesting. He has received a
starting grant from the ERC (European Research Council), the
Krill Prize, Kennedy prize, and the career development award by
the Human Frontier Science Program.
roie.yerushalmi@mail.huji.ac.ilDiversification of nanowire building blocks
by post-synthesis modifications; monolayer
doping and self-processing synthesis
Roie Yerushalmi
Institute of Chemistry-The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel
Roie Yerushalmi, Nano Res Appl Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C6-024
Figure 1:
Nanoflora, hybrid nanostructures based on nanowire building
blocks used for sensing.
















