NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 27
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
R
ecently an increasing interest is becoming evident for
incorporation of hybrid systems based on different fillers
in elastomeric matrices. This leads to already confirmed
benefits, regarding the properties of the nanocomposites, but
jet some new aspects and methods are needed to reveal and
understand the origin of the synergism between the nanofillers
and its influence on the macroscopic properties. In this study
electron spin resonance (ESR) investigations on hybrid natural
rubber based nanocomposites loaded with 2 phr of multi-
walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and various amounts of
expanded organically modified montmorillonite (EOMt) (0;
8 and 16 phr) were reported. The temperature dependence
of resonance line parameters in the range 160–353 K was
analyzed. From the obtained results it was evident that the
presence of the EOMt influenced the appearance of the ESR
spectra. The shape of the spectral lines was changed from
Lorentzian one for the sample that does not contain EOMt to a
Dysonian line for the sample that contains the highest amount
of EOMt. This was in good correlation with the argument that
the type of the ESR spectra line is closely connected to the
state of dispersion of the CNT in the matrix. Also the values
of the g-factor were shifted, from the values close to that of
the free electron for the sample that does not contain EOMt to
higher values with the increase of EOMt content. The observed
behavior of the double integral of the resonance spectra was
not temperature invariant, suggesting that it does not obey
a simple Pauli law behavior. Therefore, it was assumed that
the observed ESR signal originated not only from the metallic
but also from the intrinsic conduction electrons in MWCNT
and defects with an odd number of vacant carbon sites in the
honeycomb configuration that can also introduce spins.
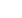
Figure 1:
The ESR spectra of 6 phr MWCNT in NR-based nanocomposites
containing different quantities of EOMt, at room temperature. Lorentzian
shapes of the resonance spectra prove the good dispersion of the nano-
tubes within the NR matrix, regardless of the presence of EOMt.
Recent Publications
1. Ivanoska-Dacikj A, Bogoeva-Gaceva G and Buzarovska
A(2015)Clay improveddispersionof carbonnanotubes
in different solvents. Contributions, Section of Natural,
Mathematical and Biotechnical Sciences 36(1):5-10.
2. Ivanoska-Dacikj A, Bogoeva-Gaceva G, Rooj S,
Heinrich G and Wießner S (2015) Fine tuning of the
dynamic mechanical properties of natural rubber/
carbon nanotube nanocomposites by organically
modified montmorillonite: A first step in obtaining
high-performance damping material suitable for
seismic application. Applied Clay Science 118:99-106.
3. Ivanoska-Dacikj A, Bogoeva-Gaceva G, Wießner S and
HeinrichG (2016) Rheometric anddynamicmechanical
analysis of complex natural rubber based composites.
Contributions, Section of Natural, Mathematical and
Biotechnical Sciences 37:5-14.
The use of electron spin resonance in studying the synergy
between organic and inorganic component in hybrid elastomer
based composites
Aleksandra Ivanoska Dacikj
1
, Gordana Bogoeva Gaceva
2
and
Srečko Valić
3
1
Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Macedonia
2
Ss. Cyril and Methodius University, Macedonia
3
University of Rijeka, Croatia
Aleksandra Ivanoska Dacikj et al., Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008