NanoMat 2018
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
Page 25
April 26-27, 2018
Rome, Italy
17
th
Edition of International Conference on
Emerging Trends in
Materials Science and
Nanotechnology
M
agnetite nanoparticles (MNPs) - based nanocomposites
are promising for drinking water and ballast water
treatments due to their easy synthesis and magnetic
recyclability. The bifunctional nanocomposite we recently
prepared by incorporating both MNPs and silver nanoparticles
into activated carbon matrix has demonstrated recoverability
and reusability with high antimicrobial efficiency for water
disinfection. However, prolonged exposure of MNPs to the
dissolved oxygen in water converts iron (II) ions to iron (III)
ions, weakening the magnetic responsiveness and reducing
the recovery rates for the nanocomposites. In this work, we
explore various strategies inhibiting the access of oxygen to
the MNPs and preventing them from being oxidized in water.
This includes capping the MNPs with inorganic, organic, and
surfactant agents. The effectiveness is evaluated based on
their oxidation resistance in water. The nanocomposites with
protected MNPs are evaluated for their recoverability and
ability to remove water pollutants and/or disinfect water.
Recent Publications
1. P Y Furlan, A J Fisher, A Y Furlan, M E Melcer, D W
Shinn and J B Warren (2017) Magnetically recoverable
and reusable antimicrobial nanocomposite based on
activated carbon, magnetite nanoparticles, and silver
nanoparticles for water disinfection. Inventions doi:
10.3390/inventions2020010.
2. P Y Furlan, A J Fisher, M E Melcer, A Y Furlan and J
B Warren (2017) Preparing and testing a magnetic
antimicrobial silver nanocomposite for water
disinfection to gain experience at the nanochemistry-
microbiology interface. Journal of Chemical Education
94(4):488-493.
3. P Y Furlan, Brian Ackerman, Mike Melcer and Sergio
Perez (2016) Reusable magnetic nanocomposite
sponges for removing oil from water discharges.
Journal of Ship Production and Design DOI: https://
doi.org/10.5957/JSPD.32.4.160017.4. S Perez, P Furlan, S Ellenberger, P Banker (2016)
Estimating diluted bitumen entrained by suspended
sediments in river rapids using O
2
absorption rate. Int.
J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13(2):403-412.
5. P Y Furlan and M Melcer (2014) Removal of organic
water pollutant surrogate by recyclable magnetite-
activated carbon nanocomposite: an experiment for
general chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education
91(11):1966-1970.
Biography
Ping Furlan is a Professor in Chemistry with 21 years of academic experi-
ence at the U.S. Merchant Marine Academy since 2011 and in the Univer-
sity of Pittsburgh during 1997-2011. She is an Active member of American
Chemical Society (ACS) and leader of various ACS major science outreach
programs and 2016 Middle Atlantic Regional Meeting. She has done her
research with numerous publications, grants and invited presentations
in the areas of developing nanomaterials for marine pollution prevention;
nanoscience and technology curriculum materials; and chemistry in mar-
itime industry curriculum materials. Her recent ACS recognitions include
2017 Middle Atlantic Regional Partners for Progress and Prosperity Award,
2016 Outreach Volunteer of the Year Award, 2016 National ChemiLuminary
Award Finalist, 2015 E. Ann Nalley Middle Atlantic Regional Award, and 2014
New York Section Distinguished Service Award for Leading National Chem-
istry Week.
furlanp@usmma.eduFacile preparation of oxidation resistant magnetite-based
nanocomposites for water treatments
Ping Furlan, Adam Fisher, Alexander Furlan, Monica Keeley, Michael Melcer,
David Shinn
and
John Warren
United States Merchant Marine Academy, USA
Ping Furlan, Nano Res Appl, Volume:4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C1-008
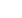
Figure 1:
Magnetically recyclable and reusable antimicro-
bial nanocomposite based on activated carbon, magnetite
nanoparticles, and silver nanoparticles for water disinfection