Journal of Clinical and Molecular Endocrinology
ISSN: 2572-5432
August 09-10, 2018
Madrid, Spain
Endocrinology 2018
Page 32
11
th
International Conference on
Endocrinology and
Diabetology
Statement of the Problem:
The formation of a systemic
disease such as diabetes, in which the vascular and nervous
system is involved in the pathological process, accompanied by
disturbances in the processes of vegetative regulation. At which
stages of carbohydrate metabolism disturbance (CMD) these
disorders begin is a matter requiring further study.
Purpose:
The purpose of this study is to state of mechanisms of
autonomic regulation at the stages of disorders of carbohydrate
metabolism (metabolic syndrome, carb tolerance, diabetes type
2- DT2).
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation:
112 patients were
examined. 1
st
group - patients with metabolic syndrome (MS)
without carb tolerance (CT) (28 people); 2
nd
group - MS with
CT (13 people) and 3
rd
group - patients with DT2 (71 people).
Autonomic regulation was studied by using spectral analysis
of daily variability of the heart rhythm (HR) power spectrum of
oscillation in three frequency bands: 0.004-0.08 Hz (very low
frequency – VLF), 0,09-0,16 Hz (low frequency – LF), 0,17-0,5 Hz
(high frequency – HF). In addition, Index of vegetative balanced
(IVB), IC (index of centralization) were analyzed.
Findings:
A decrease IVB (LF/HF) was observed in patients with
MS (0.6±0.1). At the same time, a significant difference in groups
2 and 3 (p<0.05) was found, which underlines the importance
of the stages of CMD. Evaluation of spectral analysis revealed
a significant increase of ULF% (Ultra low frequency) in the 3
rd
group which indicates disruption in adaptation and violation of
autonomic regulationofHR.The revealedsignificant difference in
the analysis of the IC in groups withMS and DT2 emphasizes the
importance of the stages of CMD. The increase in IC (4.1±0.9) in
the 3
rd
group confirmed the high activity of the central regulation
loop in relation to the autonomic. And this in the prognostic
attitude testified to depletion of regulatory mechanisms and
a high risk of development of “vascular accidents” (OR=2.7,
p=0.001).
Conclusion & Significance:
The revealed significant difference
of the CI in groups MS and DT2 emphasizes the importance of
the stages of CMD. Changing the IC towards the increase at the
stages of progression of CMD testifies to the activation of the
central contour of regulation and the gradual transition from the
control level to the administering level. The obtained data allow
considering this mechanism to be sufficient to increase the risk
of cardiovascular complications and defeat of target organs in
patients with MS and DT2.
Biography
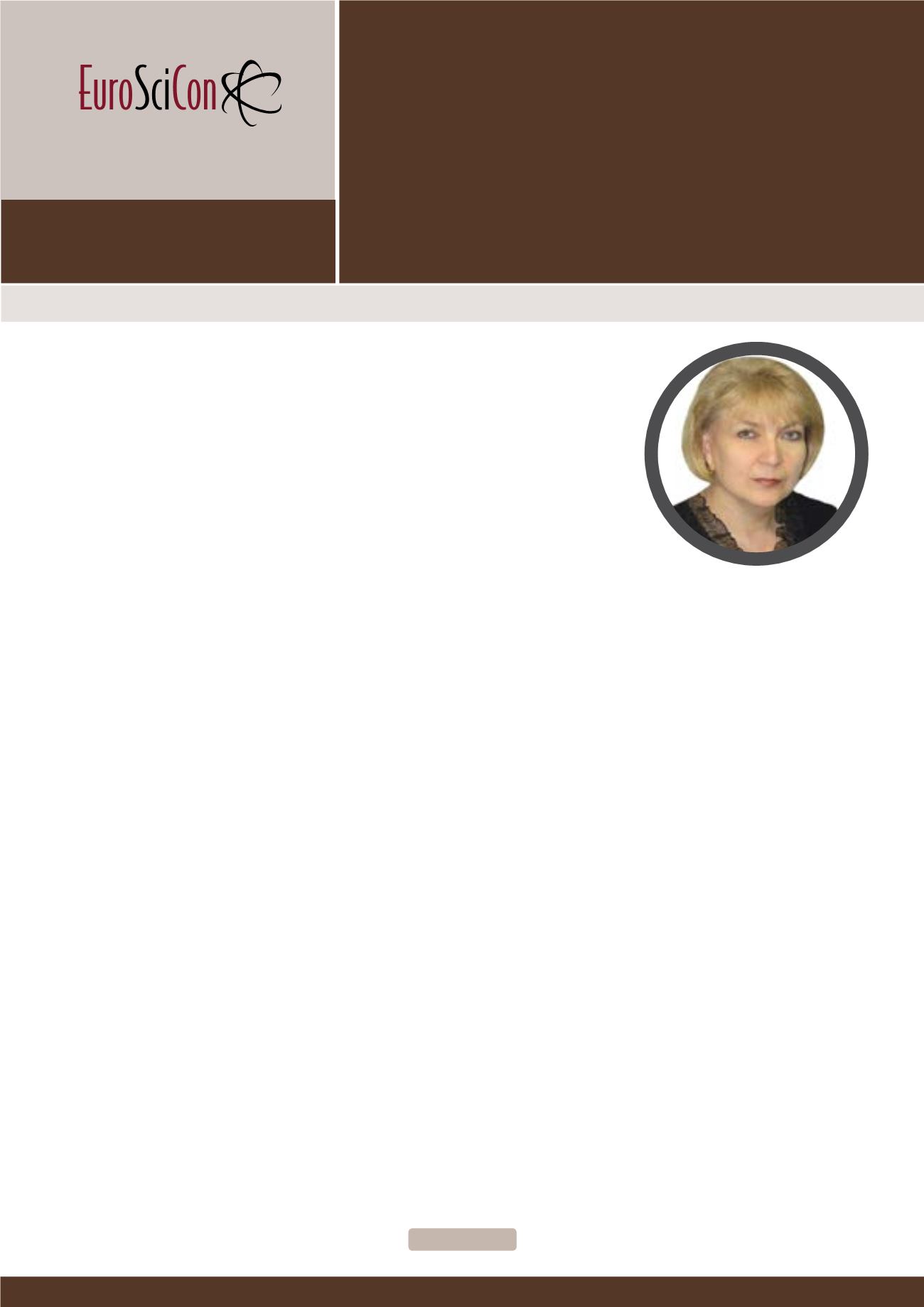
Irina Kurnikova is a Professor of Medicine, Curator of the Scientific Direction
of Endocrinology at RUDN University (Peoples’ Friendship University of Rus-
sia), Moscow, Russia. She has extensive experience in the field of scientific and
practical endocrinology. She has been dealing with problems of endocrinology
for more than 20 years. Her main areas of research include: the optimization
of the system approach to the treatment and rehabilitation of patients with di-
abetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid gland, disturbances in the system of
regulation of the organism and other endogenous factors (comorbidity, inter-
stitial humoral transport et al.). She has publishedmore than 20 articles in well-
known journals, the author of 25 books and manuals in Russian, 10 patents
for inventions.
curnikova@yandex.ruHeart rate variability at the stages of
carbohydrate metabolism disturbance
Irina Kurnikova
RUDN University, Russia
Irina Kurnikova, J Clin Mol Endocrinol 2018, Volume 3
DOI: 10.21767/2572-5432-C2-004