Notes:
Volume 2, Issue 2 (Suppl)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
ISSN: 2572-5548
Page 44
conferenceseries
.com
CO-ORGANIZED EVENT
August 31-September 01, 2017 Brussels, Belgium
&
International Conference on
Chronic Diseases
6
th
International Conference on
Microbial Physiology and Genomics
Remote monitoring to achieve self-management of type-2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective study
Hayat Mushcab
1
, George Kernohan
1
, Alan Nevill
2
and
Suzanne Martin
1
1
Ulster University, UK
2
Newman University, UK
Background:
The world’s population is aging, and more people are living with chronic conditions including diabetes mellitus.
Healthcare providers are moving towards the use of telemonitoring to identify patient self-management approaches and ensure
the delivery of health care at their home.
Aim:
To explore three telemonitoring technologies that intend to achieve self-management of type 2 diabetes mellitus thereby
improve HbA1c levels and quality of life.
Method:
Interrupted time series design to evaluate the impact of three different telemonitoring solutions provided by one large
combined health and social care trust with technology-naive people, aiming to manage their type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sample:
A total of 166 patients met the criteria at the diabetes clinic, with 29 patients consenting to take part in the study.
Results:
Participants’ baseline measurements were similar. The d-Nav solution exhibited significant improvement in HbA1c
over the other telemonitoring solutions. Participants showed acceptability and significant satisfaction of using all three solutions
and exhibited improved quality of life.
Conclusion:
This exploratory study demonstrates the feasibility of using telemonitoring to self-manage type 2 diabetes mellitus
offering a line of communication between the patient and their clinical care team at a distance.
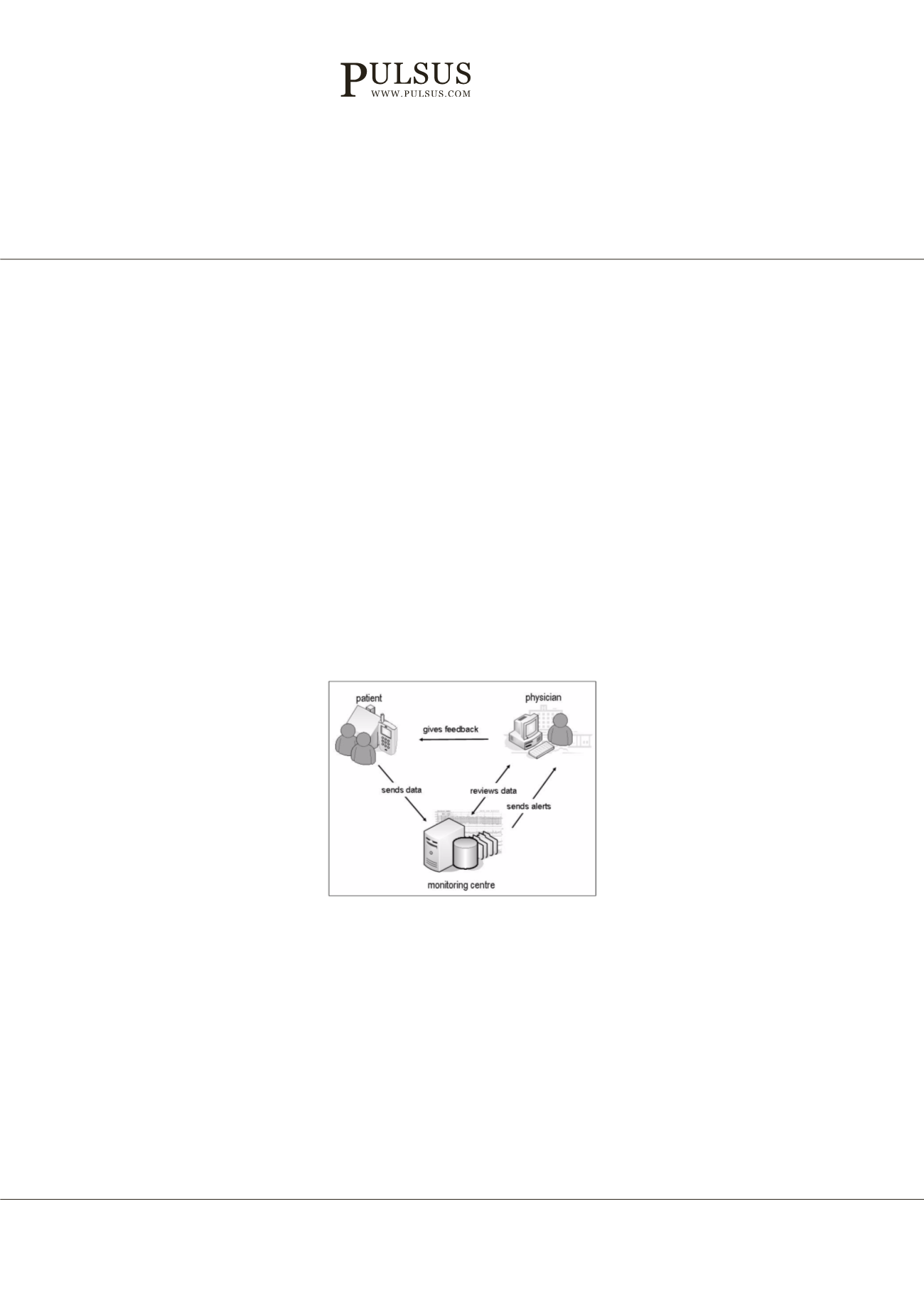
Figure1:
The architecture of telemonitoring system consists of three main entities: The patient, the server and the healthcare
provider.
Biography
Hayat Mushcab has completed her BSc in Health Information Management & Technology at King Faisal University. She completed her MSc in Computing and
Intelligent Systems at University of Ulster; PhD in the field of Telehealth/Telemonitoring and Connected Health at Ulster University in the Faculty of Life and Health
Sciences. She has five publications in international journals.
hayat.mushcab@gmail.comHayat Mushcab et al., Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2017, 2:2
DOI: 10.21767/2572-5548-C1-002