Volume 4
Nano Research & Applications
ISSN: 2471-9838
JOINT EVENT
October 04-05, 2018 Moscow, Russia
&
2
nd
Edition of International Conference on
26
th
International Conference on
Advanced Nanotechnology
Materials Technology and Manufacturing Innovations
Advanced Nanotechnology 2018
& Materials-Manufacturing 2018
October 04-05, 2018
Page 34
Arabadzhi Vladimir Vsevolodovich
Institute of Applied Physics (RAS), Russia
Arabadzhi Vladimir Vsevolodovich, Nano Res Appl 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.21767/2471-9838-C5-020
Radio-absorbing parametric material
F
or parameters that are constant in time, no structure of the absorbing coating (material) can simultaneously satisfy
the following four conditions: (a) effective absorption, (b) a spatial ultra-wide absorption band (i.e. the absorption
efficiency is independent of the spatial frequency or angle of arrival this wave), (c) a temporary ultra-wide absorption
band (i.e. the absorption efficiency does not depend on the time frequency of the incident wave), (d) the small thickness
of the absorbing coating compared to the length of the absorbed wave. The microstructure of the parametric coating
(material) considered in the presentation allows to simultaneously (jointly) satisfy the conditions (a)-(d) on the basis
of the use of elements (optoelectronic switches, optic fibers) of high resolution in space and time. The presentation is
considered with a structure (geometrically resembling a foam), consisting of a set of three-dimensional cells, separated
from each other by thin walls of controlled transparency. The wall of controlled transparency is a metal grid, where
linear elements are electrically connected with each other by optoelectronic switches. Each switch is controlled by pulses
of laser through optic fibers. The conducting state of the switches corresponds to opaque state of walls, and the non-
conducting state of switches corresponds to the transparent state of the walls. Control of walls transparency presents the
alternation in time (during the control period, which is much less than minimum period of the wave to be absorbed)
of relatively short time intervals of opacity and relatively long time intervals of transparency. The current distribution
of the incident wave field, instantly pierced by the emerging opaque walls, becomes the initial condition for oscillations
inside the cell (virtual resonator) and has time to become sufficiently small, since the minimum natural frequency is
very great and defined by very small geometric dimensions of each cell.
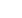
Figure:
One cell of parametric material: optic fibers supplies laser pulses of light to optoelectronic switches
Recent Publications
1. Vladimir V Arabadzhi (2017) Cyclical wave bolt for electromagnetic waves. IJEAS 4(11):137-143.
2. V V Arabadzhi (2005) Nonreflecting Switching Microstructure. Journal of Communications Technology and
Electronics 50(5):561-573.