
Page 83
May 24-25, 2018
London, UK
Vascular Surgery 2018
3
rd
Edition of World Congress & Exhibition on
Vascular Surgery
Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Therapy
ISSN: 2573-4482
Objective:
This retrospective study determined the duplex
ultrasound scanning (DUS) criteria for detecting 50-69% and 70-
99% stenosis of the superficial femoral artery (SFA). Methods
Examinations of 278 limbs in 185 subjects with peripheral arterial
disease were performed. Duplex ultrasound scanning was used
to measure the residual diameter of the stenotic segment and the
diameter of the original lumen, the peak systolic velocity (PSV) at
the stenotic segment of the SFA (PSVst), the segment proximal to
the stenosis (PSVpro), and the popliteal artery (PSVpop; distal to
the stenosis). The ratios PSVst/PSVpro and PSVst/PSVpop were
calculated. Receiver operator characteristic curves were plotted,
with digital subtraction angiography as the reference.
Results:
The studied limbs included 205 limbs with stenotic SFAs:
43 (15.5%) with 50-69% stenosis, and 162 (58.3%) with 70-99%
stenosis. The control group consisted of 73 limbs: 44 (15.8%)
were normal and 29 (10.4%) had <50% stenotic SFAs. According
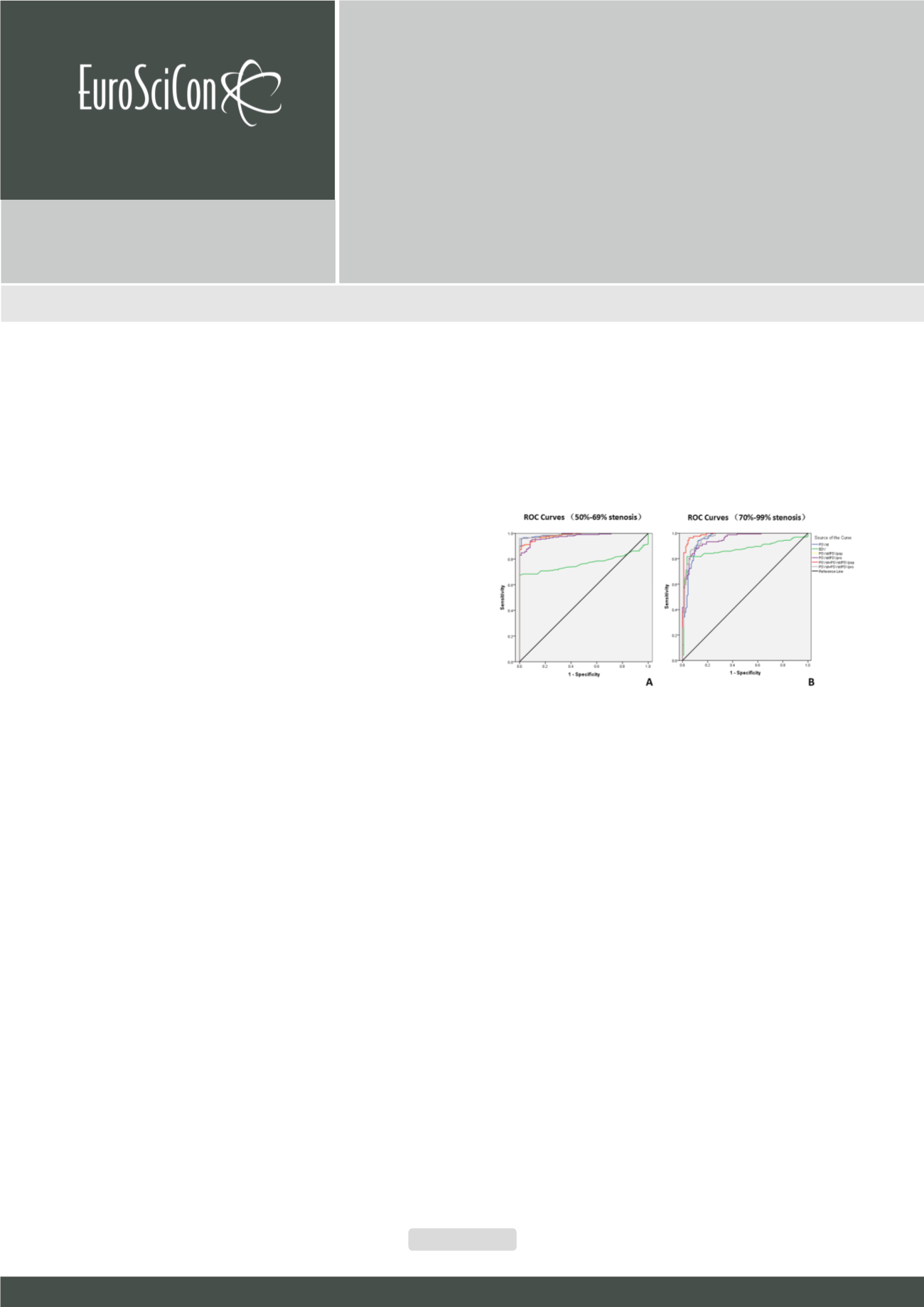
to the results of the ROC analysis, the optimal cut-off values for
detecting 50-69% stenosis of the SFA were PSVst ≥ 210 cm/s,
PSVst/PSVpop ≥ 2.5, or PSVst/PSVpro ≥ 1.7. PSVst was the most
useful hemodynamic parameter for predicting 50-69% stenosis,
with 95.6% sensitivity, 98.6% specificity, and 96.4% accuracy.
For predicting 70-99% stenosis of the SFA, the thresholds were
PSVst ≥ 275 cm/s, PSVst/PSVpop ≥ 4.0, or PSVst/PSVpro ≥ 2.5.
PSVst/PSVpop ≥ 4.0 was themost useful Doppler parameter, with
96.3% sensitivity, 93.9% specificity, and 95.3% accuracy. PSVst/
PSVpop+PSVst was the best combined parameter to detect SFA
70-99% stenosis with 96.3% sensitivity, 94.8% specificity, and
95.7% accuracy. Conclusions This study determined the cutoff
values of DUS hemodynamic parameters for diagnosing 50-69%
and 70-99% stenosis of the SFA. PSVst/PSVpop may be a better
ratio parameter than the traditional parameter of PSVst/PSVpro
for diagnosing SFA stenosis, especially for 70-99% stenosis
Recent Publications
1. Conte MS, Pomposelli FB, Clair DG, et al. Society for
Vascular Surgery practice guidelines for atherosclerotic
occlusive disease of the lower extremities: management
of asymptomatic disease and claudication. J Vasc Surg
2015; 61:2S-41S.
2. Cossman DV, Ellison JE, Wagner WH, et al. Comparison
of contrast arteriography to arterial mapping with color-
flow duplex imaging in the lower extremities. J Vasc
Surg 1989; 10:522-8; discussion 28-9.2.
3. Gao M, Hua Y, Zhao X, et al. Incidence and Predictors of
In-stent Re-Stenosis in the Superficial Femoral Artery:
Evaluation of Long-Term Outcomes by Color Duplex
Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 2016; 42:717-26.
4. Khan SZ, Khan MA, Bradley B, et al. Utility of duplex
ultrasound in detecting and grading de novo
femoropopliteal lesions. J Vasc Surg 2011; 54:1067-73.
5. Zwiebel WJ, Pellerito JS. Introduction to vascular
ultrasonography, 6th edition; Philadelphia,PA, Elsevier
Press, 2012;294-30.
Optimal Ultrasound Criteria for Grading Stenosis of
the Superficial Femoral Artery
Mingjie Gao, Yang Hua, Xinyu Zhao, Lingyun Jia, Jie Yang
and
Beibei Liu
Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, China
Mingjie Gao et al., J Vasc Endovasc Therapy 2018, Volume 3
DOI: 10.21767/2573-4482-C1-002
Figure 1:
ROC curves for 4 individual parameters and 2 combined parameters.
(A) 50-69% stenosis. (B) 70-99% stenosis. Blue, PSV at the stenotic segment;
green, EDV at the stenotic segment; yellow, PSVst/PSVpop; purple, PSVst/
PSVpro; red, PSVst+PSVst/PSVpop; grey, PSVst+PSVst/PSVpro. The black line
indicates the reference values. ROC= Receiver operator characteristic.
















