Page 66
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 3, Issue 2
ISSN: 2470-9905
Crystallography 2017
October 16-17, 2017
2
nd
International Conference on
October 16-17, 2017 | Chicago, USA
Applied Crystallography
Serife Yalcin, Struct Chem Crystallogr Commun, 3:2
DOI: 10.21767/2470-9905-C1-002
How does crystallography affect material properties?
Serife Yalcin
Harran University, Turkey
Statement of the Problem: Developments in science and technology have required the production of new materials and design.
Knowing the properties of the materials used to obtain them are helpful to design and manufacture of materials that we need.
Crystallography studies have been very important for developing of materials because this studies deal with internal structure, in
particular the symmetry of crystal. The majority of the solid materials are composed of crystals. This explains how much important
crystallography is in material. The purpose of this study is to determine suitable materials for material science need.
Methodology & Results: Crystallography is the science of structure used for characterization of materials and to determine some
physical properties with microstructure and texture analyses. It includes the general features of structure and deals with the mapping
of all kinds of systems as geometrical representations. The same material with different crystallographic parameter has different
properties. It is hardly possible to develop materials science without crystallographic techniques. As a sample, we will focus on
structure of calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate is one of the most abundant and cheap material found in nature. It can be found in
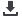
three forms: Calcite, aragonite and vaterite. XRD pattern of aragonite, calcite and vaterite shows difference as seen in Figure-1. These
patterns show difference depending on crystal structure. When Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) image investigate of different
forms of calcium carbonate, it has been observed difference among picture. Calcite structure shows square structure while aragonite
and vaterite structure show rod and flower type structure, respectively.
Conclusion & Significance: The results have showed difference depending on the form of calcium carbonate. Young modulus has been
obtained 76, 89-193 Pa for calcite and aragonite, respectively. Preparation of materials that is needs of human must be in coordination
with crystallography.
Figure-1: XRD pattern of aragonite, calcite and vaterite calcium carbonate.
Biography
Serife Yalcin has completed her PhD from Erciyes University and Postdoctoral studies from Caen University. She has published more than 40 papers in reputed journals
and has been serving as an Editorial Board Member of repute.
serifeyalcin@harran.edu.tr