Some Pathophysiological Aspect of Urinary Markers of Yeast Overgrowth Enzymes in Untreated Seronegative Arthropathies Patients and Laboratory Evaluation for Integrative and Functional Medicine
Dejan Spasovski*
University Clinic of Rheumatology, “SS Cyril and Methodius” University, Skopje, Republic of Macedonia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Dejan Spasovski
University Clinic of Rheumatology,“SS Cyril and Methodius” University, Skopje, Republic of Macedonia.
Tel: +389 2 3147-668
E-mail: drspasovski@yahoo.co.uk
Received date: November 15, 2016; Accepted date: December 02, 2016; Published date: January 25, 2017
Citation: Spasovski D. Some Pathophysiological Aspect of Urinary Markers of Yeast Overgrowth Enzymes in Untreated Seronegative Arthropathies Patients and Laboratory Evaluation for Integrative and Functional Medicine. Jour Ren Med. 2017, 1:1.
Abstract
Aim: To compare diagnostic values and laboratory variables of alanine - aminopeptidase (microsomal AAP), γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), β2- microglobuline (β2-M), C Reactive Protein (CRP) and index for disease activity (PASI) in early diagnosis in previously untreated Psoriatic arthritis (Psa). To determine the effect of untreated Psoriatic arthritis on tubular function, sensitivity of the Brush Border region as well as the diagnostic value of the enzymes originating from proximal renal tubules.
Methods: From the standard methods of the International Federation for Clinical Chemistry (IFCC) we used the kinetic method for determination of alanine - aminopeptidase (microsomal AAP), γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT) and MEIA (Microparticles Enzyme Immunoassay (Abbot Axsym system) for determination of β2-microglobuline in urine. We examined samples (serum and urine) from 70 participants (35 Psa untreated, 35 healthy control group). RF and CRP are determined with Latex agglutination test in the same participants.
Results: From 35 examined patients with Psa, 12 pts showed presence of AAP enzymuria (test sensitivity was 34.28%), 8 pts showed presence of γ-GT (test sensitivity was 22.85%), while the presence of β2-microglobuline in urine was low (test sensitivity 0%).
Conclusion: AAP has better sensitivity than γ-GT and β2-microglobuline in the detection of asymptomatic renal endothelial changes in untreated Psa.
Keywords
Aminopeptidase (AAP); γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), β2- microglobuline (β2-M); Psoriatic arthritis (Psa)
Introduction
Brush border region (brush, layer, striated) is composed of microvilli covered with simple cubic and cylindrical epithelium, found in different location of the body. Diameter of the microvilli is 100 nm, while their length very from 100 nm to 200 nm. Because microvilli are small and dense in the brush border epithelium, they could be seen only with electronic microscope. With light microscope, they could be usually seen collectively as ‘fuzzy fringe’ (feathered, fibrillary, edgy, borderline), as part of the surface of the epithelium. The appearance of the ‘fuzzy fringe’ determines the name Brush border, because this structure resembles the painter brush.
Brush epithelial cells are found in two main locations in the human body.
1. In the intestinum: it is the place where absorption takes place. Brush epithelium in the intestinal cover layer is the place of terminal carbohydrate digestion. Microvilli that compose brush epithelium contain enzymes for this terminal part of digestion, located in the apical plasmatic membrane as an integral membrane proteins. These enzymes are located close to the transporters, which enables absorption of the digested food.
2. In the kidneys: where the brush epithelium is useful to make difference between proximal tubules (that possess brush epithelium) and distal tubules (that do not possess).
Brush border morphology with the brush epithelium, increases the cell surface, especially useful for absorption. The cells that absorb substances have great necessity of contact surface with substances in order to be efficaceous. The luminal surface of the epithelial cells from this segment of the nephron is covered with densely packed microvilli that form border, which can be seen under light microscope. The microvilli in great measure increase the luminal surface of the cells which in great measure facilitate their resorptive function. Membranes inverted inside that form microvilli are the places for numerous sodium pumps.
The cell cytoplasm is densely filled with mitochondria, found mostly in the basal region, inside the curves of the basal plasmatic membrane. The high quantity of the mitochondria gives the cells acidophilic appearance. The mitochondria are necessary for energy supply for the active transportation of the sodium ions outside the proximal tubules. The water passively follows sodium outside the cells according to the concentration gradient. The cubic epithelial cells that cover proximal tubules have extensive lateral interdigitations between adjacent cells, that seems as there are no cell borders seen under the light microscope. The end resorption of the content of the proximal tubules after drug intake or stop in circulation (in capillary) around tubules leads to disturbance of the cell morphology of the proximal tubule cells, including ejection of the nucleus in the tubular lumen, giving it dirty look in contrast to the clear appearance of the distal tubules, that have completely different characteristics.
Microvilli have the characteristics of PH parturition. It is the tendency of the acid matters to accumulate in the alkaline fluid compartments, while alkaline matters in acid compartments. So, acid drugs are secreted in great quantities when the urine is alkaline, and vice versa, alkaline drugs are secreted in great quantities when the urine is acid.
The aim of this study is to determine the effect of untreated Psoriatic arthritis on tubular function and sensitivity of the Brush Border of the proximal tubules. AAP, γ-GT, β2M are used as indicators for proximal tubular damage.
Renal markers for evaluation of the renal function
Several classes of measurable proteins in urine are used for evaluation of the renal disfunction.
1. Enzymes with high moleculare weihgt, that ussually are not filtered in the glomerulus, originating mainly from the proximal tubules (microsomal AAP, NAG).
2. Intermediare proteins that normaly are filtered in the glomerulus in small qantities and are reabsorbed in the tubules in great part (albumin, transferin).
3. Proteins with low moleculare weight that normaly are filtered in the glomerulus and are reapsorbed in the tubules (β2-microglobuline [1-6].
Alanine - aminopeptidase (AAP), (aryl amide amino acid, aminopeptidase, α-amino-acyl-peptide-hydrolase (microsomal) AAP, ES 3.4.11.2, previously 3.4.1.2) is a hydrolytic derivative of peptides, amides and p-nitroanilide.
AAP is found in numerous tissues, mostly in kidney, intestine, lungs and liver. AAP in different tissues has different electrophoretic conductivity. This enzyme has at least five different isoenzymes that could be separated from each other with electrophoresis, ion-changing chromatography or immunologically. In normal serum is found only one isoenzyme, while in hepatobilliar or pancreatic diseases are found additional fractions. The enzyme is also found in urine.
γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), (γ-glutamyl-peptide amino acid γ-glutamyl transferase, ES 2.3.2.2. γ-GT catalyzes the transfer of (γ-glutamyl groups with peptides (as glutathione) to other peptides or amino-acids.
γ-GT plays an important role in the glutathione metabolism. High enzyme concentrations are found in kidneys (proximal tubule), pancreas (acinarcells), prostate and liver. γ-GT is mostly located on the external part of the plasma membrane [7]. γ-GT isoenzymes in serum are result of the different posttranslational modifications as for example complex formations with lipoproteins or modifications of the carbohydrate part of the γ-GT molecule [8]. The possibility of the presence of isoenzymes in different tissues (liver, pancreas, kidney, duodenum) is due to the differences in carbohydrate part of the γ-GT molecule. Although the peptide part of the enzyme molecule is the same no matter the tissue of origin, these isoenzymes differ in kinetic, electrophoretic and immunological features.
The tubular function could be evaluated with mesurements of the excreted low molecular proteins in urine. β2-microglobuline β2-M is used as an indicator of the tubular disfunctions in glomerulonephritis [9] and is often used as sensitive marker for evaluation of the renal function [10-12]. β2-M is a small polypeptyde with low molecular weight (11.815 daltons). β2-M contains light chains of the main histocompatibility antigen (HLA). It influences production of the RF (IgM class). In normal individuals, β2-microglobuline is found both in serum and urine. 95% of the free β2-M is ultrafiltrated through renal glomerules and almost completely is reapsorbed in 99.9% with proximal tubular endocitosis and finally is catabolized in amino acids in healhty individuals. Due to this mechanism, normally in urine are detected in traces. Imparement in the glomerular filtration leads to increase in serum β2-M, while tubular damage leads to rise in urine β2-M.
Serum concentration of β2-M depends on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and shows significant negative correlation with inulin clearence. These findings show that with determination of the serum level of β2-M one could get an index for disfunction of the renal gromerulus.
In some pathological conditions, incresed quantities of β2-M are excreted in urine. It happens when β2-M serum concentration exceeds the renal threshold. The serum level of β2-M depends on the ratio of synthesis and release in serum pool and its relation with clearence. Such conditions are notified in patients with inflammatory diseases (Rheunatoid arthritis, SLE, Sy. Sjögren, Crohn disease, cancer, liver damage). β2-M concentration in urine could be increased also when reapsorption is decreased due to renal proximal tubular damage. Proximal tubular disfunction results with elevated concentrations of urine β2-M, alowing to make distinction between proximal tubular from glomerular renal impairment.
β2-M is used for evaluation of the GFR and renal tubular function, especially for tubulotoxic effect of different substances, such as heavy metals (cadmium and lead) and as a screening test for early detection of Balcan nephritis in regions where it is edemic. In urine β2-M is unstable if ph<6 and it is recommened to alcalize the urine with bicarbonates before it is tested. β2-M is considered the earliest protein of tubular proteinuria.
Material and Methods
Diagnosis of the patients included in the study is based upon revised diagnostic criteria for Classification of Psoriatic arthritis from 2005, proposed by the American Association for Rheumatic arthritis (ARA) [13]. Clinical evaluation for disease activity and disease diagnosis is based upon diagnostic criteria of Moll-Wright for Classification of Psoriatic arthritis [14]. Patients are dermatologically tested, including examination of the psoriatic changes of nails, psoriatic areas, and disease activity index (PASI) as well as evaluation of the peripheral and axial joints [15]. Oligoarthritis is taken in consideration when <5 joints are involved and polyarthritis when ≥ 5 joints are involved. Symmetric arthritis is considered when bilateral joints are involved >50%.
In the study are included 35 patients (8 women, 27 men) suffering from PsA and 35 patients (23 women, 13 men) as healthy control group. Median age was 50.18 years (SD ± 8.09) (35-65 years) in PsA group, while 48.2 years (SD ± 10.19) (29- 65 years) in healthy control group. Median disease duration was 30.17 (SD ± 40.13) in the interval of 1-60 months. None of the patients included in the study has previous or current history of renal disease. None of them previously used NSAIDs. The others negate use of other drugs before entering the study, especially drugs from the base line therapy such as methotrexate, antibiotics, or diuretics. Samples are collected in the period of two years [16].
Inclusion criteria
In the study are included patients suffering from Psoriatic arthritis, aged 18-65 years old, newly diagnosed and previously untreated.
Exclusion criteria
From the study are excluded all the patients with diseases or conditions that can directly or indirectly influence the results, such as:
1. Patients <18 and >65 years old.
2. Patients with previous history of diseases of the spleen, thyroid gland, liver damages, renal, hematological, cardiovascular, neurological, lung, auto-immune impairments.
3. Patients with diabetes mellitus, acute infections, AIDS, febrile conditions, malignant diseases.
4. Patients previously treated with antibiotics and salicylates <6 months before entering the study.
Patients with hypertension, uric arthritis, urinary infections, SLE, Sjogren disease, mixed connective tissue disease, vasculitis.
6. Patients treated with antihypertensive, antidiabetic and cardiological drugs.
7. Patients with previous history for blood transfusion and patients with increased body mass index.
8. Patients with hypersensitivity on drugs or some of their components.
9. Patients with history for drugs from the base line.
10. Patients with acute or chronic renal failure.
11. Patients who in 0-point had glycaemia, elevated serum urea and creatinine. Hypertension and impaired hematological and enzyme status.
All the patients took place in the study voluntarily, so the ethic criteria for inclusion in the study are fulfilled.
Laboratory evaluation
For clinical evaluation of the disease one have to examine the following parameters: complete blood count (CBC) and differential, reactants of the acute phase such as C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Rheumatoid factor (RF), Erythroid Sedimentation Rate (ESR), aspartate- aminotransferase (AST), alanine - aminotransferase (ALT), creatinine kinase (CK), lactate – dehydrogenase (LDH), serum urea and serum creatinine. The urine samples were taken not only for routine analyses, but also to determine the levels of AAP, γ-GT, β-2M. Due to the urine instability of β-2M<6pH it is recommended the urine to be alkalized before testing.
Serum creatinine is determined according to “Jaffe” method. Referent values are: serum creatinine 45-109 μmol/L, urine creatinine 7-17 μmol/L.
CRP is determined with the agglutination test (Latex CRP test) (BioSystems S.A. Reagents and Instruments Costa Brava 30, Barcelona, Spain). Referent values are: serum CRP<6 mg/L.
RF is determined with the agglutination test (Latex CRP test) (BioSystems S.A. Reagents and Instruments Costa Brava 30, Barcelona, Spain). Referent values are: serum RF <8 IU/ml.
ESR was determined with Westergren method. Normal values are: for men 7-8 mm, for women 11-16 mm.
GFR (Creatinine Clearance) was estimated by Cockcroft-Gault Equation.
Determination of the activity of alanine amino – peptidase (AAP): kinetic method
Alanine amino – peptidase (aryl amid amino acid, aminopeptidase, α-aminoacyl peptide hydrolase (microsomal), ANA, ES 3.4.11.2, former 3.4.1.2.) is hydrolized by peptides, amides and p-nitroanilide. During the process of hydrolization of peptides N–terminal amino acid is seceded (firstly anilide). The activity of AAP is determined by the methods similar to those for determination of leucine aminopeptidase. In this method is used L-alanine-4-nitroanilide as a substrate. The catalytic concentration of AAP is directly proportional to the absorption of p-nitroanilide is measured on 405 nm. Referent values: urine AAP 0.25-0.75 U/mmol cr eatinine.
Determination of the activity of γ-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT): IFCC method
γ-glutamyltransferase (γ-glutamyl) – peptide amino acid γ-glutamyltransferase ES 2.3.2.2. (γ-GT) catalyzes transfer of γ-glutamyl groups with peptides (such as glutathione) on other peptides or amino acids. γ-GT influences the release of glutamyl rest as glutamic acid. With transpeptidation glutamyl rest could be transferred again on a substrate (for example from γ-glutamyl-naphthylamide results γ-glutamyl- γ-glutamyl-α-naphthylamide) or other suitable acceptor (amino acid, di- or tri-peptide). The most suitable acceptor is glycylglycine.
Methods for measurements of the activity of this enzyme in serum use aromatic amides as substrates (γ-glutamyl-anilide and γ-glutamyl-naphthylamide). The superficial substrate peptide analogue γ-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide is most frequently used. It is suitable for determination of the enzyme activity kinetically and calorimetrically. γ-glutamyl--p-nitroanilide latter is substituted by L-γ-glytamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide (glucan) due to its high solubility. Glycylglycine was used as a substrate acceptor and buffer, due to its high catalytic activity. The International Federation of Clinical Chemistry standardize this method – (IFCC) and is considered as referent method.
Remarks
The IFCC method for measurement of concentration of the catalytic activity of serum and urine γ-GT is based on the principles developed by Orlowski, Meiser and Szasz, and their modification by Persijin and Van der Slik. As a substrate donor is used L-γ-glytamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide. In the IFCC method Tris (hydroxy methyl aminoethane is substituted with glycylglycine, which acts as buffer and substrate acceptor. Magnesium which earlier was used for maintenance of L-γ- glytamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide in the solution in IFCC method is omitted. This method is specific for determination of the activity of γ-GT [17-20].
Referent values: γ-GT (urine) 0.84-1.80 U/mmol cr eatinine.
Determination of the concentration β2- microglobuline (β2-M) in urine according to “MEIA” (Microparticles Enzyme Immunoassay) method (Abbot Axsym system)
Principles: Determination of Axsym β2-microglobuline is based on MEIA technology (Microparticles Enzyme Immunoassay) and enables quantitative determination of β2- microglobuline in serum, plasma, and urine in patients with Rheumatoid arthritis and renal impairment.
The reaction is based on the inter-reaction of β2-Mwith anti-β2-Mantibody, forming a mutual complex. This complex reacts with the Matrix cell and is bound to them. A conjugate of alkaline phosphatase is added, it bounds to the complex, forming sandwich complex. To this complex is added 4-Methylumbelliferyl Phosphate (4-MUP), reacting with alkaline phosphatase from the complex and a fluorescent product - Methylumbelliferon with light blue colour is made. From the degree of the optic fluorescence depends proportionally the concentration of β2-M. It is determined automatically (Abbot Axsym system).
Taking in consideration that β2-M is very sensitive to changes in urine pH i.e., very quickly is degraded in low pH levels. If pH <6.0 it is monitored, and if it is acid it should be alkalized.
Referent values: β2-microglobuline (urine) – 0.02-0.19 mg /L
Statistical analysis
For testing the significance of differences between two arithmetical means, i.e., proportions the Student-t-test is used to compare the mean parameters of certain numerical parameters between groups, as well as Wilcoxon-matched test for independent samples. Sensitivity and predictivity for positive and negative test of the examined markers is determined with the test for sensitivity and specificity. P-value between 0.05 and 0.1 is considered statistically significant. Analysis of the data is performed with the statistical package Statistical 7.0.
Results
From the 35 examined patients with PsA, 12 pts (34.28%) showed presence of APP enzymuria, 8 pts (22.85%) presence of γ-GT, while low percentage (0%) presence of β2- microglobuline in urine. RF was present in 0 pts. (0%).
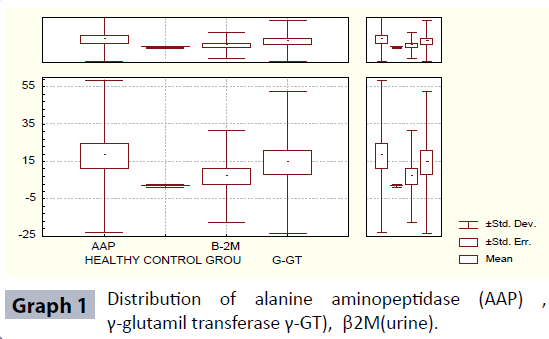
In the 35 pts with PsA, APP sensitivity was 34.28%, γ-GT sensitivity was 42.85%, β2-microglobuline was 0% and RF sensitivity was 0%. (Table 1 and Graph 1)
| Psa untreated group N° 35 value (M ± SD) |
Healthy control group N° 35 Value (M ± SD) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Positive/negative | Positive/negative | |
| AAP + >0,75 (U/mmol/creatinine) |
12/23 | 1/34 |
| γ-GT + >1,80 (U/mmol/creatinine) |
8/27 | 0/35 |
| β2 M +>0,19 (mg/L) |
0/35 | 0/35 |
| RF +30 > IU/ml | 0/35 | 0/35 |
| CRP +12 > mg/L | 13/22 | 1/34 |
Table 1 AAP, γ-GTβ2-microglobulinand other laboratory variables in Psa and healthy control group.
Diagnostic value of alanine aminopeptidase (microsomal AAP) γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), β2 microglobulin (β2M) in Psa
For AAP, γ-GT, β2 microglobulin as well as other laboratory variables in Psa, sensitivity, specificity, predictive values for positive and negative test, as well as accuracy is shown on Table 2.
| AAP Psa No 35 |
γ-GTPsa No 35 |
β2M Psa No 35 |
RFPsa No 35 |
CRPPsa No 35 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity % | 34.28 | 22.86 | 0 | 0 | 37.14 |
| Specificity % | 75.56 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 97.14 |
| Predictive value forpositive test% | 52.17 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 92.86 |
| Predictive value for negative test% | 59.65 | 56.45 | 50 | 50 | 60.71 |
| Accuracy % | 65.71 | 61.42 | 50 | 50 | 67.14 |
Table 2 Diagnostic performances of AAP, γ-GT, β2M and other laboratory variables in Psa.
AAP has better diagnostic performances than γ-GT and β2M taking in consideration sensitivity and specificity (sensitivity 34.28% vs 22.86% vs 0%) and almost equal specificity (specificity 75.6% vs 100 % vs 100%) in detection of renal impairment in untreated Psa.
1. There is statistical relation using Wilcoxon-matched test between AAP in PsA and healthy control group for p<0.05 (p=0.01). In the PsA group there is statistical relation between AAP and γ-GT for p< 0.05 (p=0.00); AAP and β2M (p=0.00);
2. There is statistical relation using Wilcoxon-matched test between γ-GTin PsA and healthy control group for p<0.05 (p=0.40); β2Min the PsA and healthy control group for p<0.05 (p=0.06).
3. There is statistical relation using Wilcoxon-matched test between AAP in Psa and age, disease duration (in months); PASI index, RF and CRP, serum creatinine, serum urea in the same group for p<0.05: AAP vs age p=0.00; AAP vs disease duration (in months) p=0.00; AAP vs PASI p=0.00; AAP vs RF p=0.02; AAP vs CRP p=0.041; AAP vs ESR p=0.00; AAP vs serum creatinine p=0.00; AAP vs serum urea p=0.00).
4. There is statistical relation using Wilcoxon-matched test between γ-GT in Psa and age, disease duration (in months), PASI index, RF, CRP, ESR, serum creatinine and serum urea in the same group for p<0.05: (γ-GT vs age p=0.00; γ-GT vs disease duration (in months) p=0.00; γ-GT vs PASI index p=0.00; γ-GT vs RF p=0.02; γ-GT vs CRP p=0.042; γ-GT vs ESR p=0.00; γ-GT vs serum creatinine p=0.00; γ-GT serum urea p=0.00.
5. There is statistical relation using Wilcoxon-matched test between β2M in PsA and age, disease duration (in months); PASI index, RF and CRP, ESR, serum creatinine and serum urea in the same group for p<0.05: β2M vs age p=0.00; β2M vs disease duration (in months) p=0.00; β2M vs PASI index p=0.00; β2M vs RF p=0.02; β2M vs CRP p=0.044; β2M vs ESR p=0.00; β2M vs serum creatinine p=0.00; β2M vs serum urea p=0.00.
Discussion
In the standard medical rheumatology, the biggest emphasize is put on Rheumatoid arthritis as the most exposed disease, neglecting somehow the other diseases especially seronegative Arthropathies, probably due to their lesser extent.
The explanation for the renal tubular enzymes is increased exfoliative turnover of the epithelial cells in Psa, which is adequately present also in proximal tubular epithelial cells.
Of all enzymes, greatest emphasize is put on NAG as dominant lysosomal tubular enzyme. Traditional treatment of Psa and RA, includes non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease modification drugs (DMARDs), steroids and immunosuppressive cytotoxic drugs. Methotrexate in low dose regime is the most frequently prescribed drug from DMARDs, while Ketoprofen (Niflamr, Ketonalr) and Paracetamol from NSAIDs.
Enzymes in urine could originate from plasma, glands from the urogenital tract, epithelial cells of the urinary tract, white blood cells, erythrocytes, and kidneys. There are 40 different enzymes in the urine belonging to different groups: oxydoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, while isomerases and ligases are not found in urine. Presence of so many enzymes in urine indicates the dominant role of the kidneys in their excretion.
The urine enzyme activity in urine normally is low and increases in renal tubular cell damage. Urinary enzymes especially NAG, AAP and AF are very sensitive indicators of renal parenchymal damage in comparison with functional measurements such as glomerular filtration rate and creatinine clearance. Relatively low sensitivity to GFR could be explained with great functional reserves of the kidneys and their great compensatory ability.
AAP sensitivity is greater in comparison with γ-GT and β2M (34.28% vs 22.85% vs 0%), with approximately equal specificity (75.6% vs 100 % vs 100%).
Statistical relation of disease duration (in months) and AAP and γ-GT and β2M enzymuria p=0.00 points out that untreated Psa damages the renal tissue as one of the visceral manifestations of the disease.
Untreated Psa primarily damages tubular Brush Border region and enzymes originating from it has greater sensitivity [21-29].
Conclusion
AAP has greater sensitivity than γ-GT and β2M in asymptomatic renal lesions in untreated Psa. AAP and γ-GT could be used in everyday clinical practice in diagnosis of early, asymptomatic renal lesions.
References
- Mueller PW (1993) Detecting the renal effects of cadmium toxicity. ClinChem. 39: 743–745.
- Maruhn D, Paar D, Bock KD (1979) Lysosomal and brush border membrane enzymes in urine of patients with renal artery stenosis and with essential hypertension. ClinBiochem. 12: 228–230.
- Vanderlinde RE (1981) Urinary enzyme measurements in the diagnosis of renal disorders. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 11: 189–201.
- Price RG (1982) Urinary enzymes, nephrotoxicity, and renal disease. Toxicology. 23: 99–134.
- Johnston IDA, Jones NF, Scoble JE, Yuen CT, Price RG (1983) The diagnostic value of urinary enzyme measurements in hypertension. Clin Chim Acta. 133: 317–325.
- Sanberg T, Bergmark J, Hultberg B, Jagenburg R, Trollfors B (1986) Diagnostic potential of urinary enzymes and beta-2-microglobulin in acute urinary tract infection. Acta Med Scand. 219: 489–495.
- Ormstad M, Tanaka S, Orrenius S (1982) Function of Glutamil-transferase in the Kidney. In: Siest G, Heusqheimm G (Eds) Gamma-Glutamyl transferase, Masson, Paris pp: 7-14.
- Goldberg MD (1982) Structural functional and clinical aspect of gama glutamyl transferase; In: Batsakis J, Savory J (Eds) CRC Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 12: 1-58.
- Portman RJ, Kissane JM, Robson AM (1986) The use of beta 2-microglobulin to diagnose tubular injury in pediatric renal disease. Kidney Int. 30: 91–98.
- BerggardI-Bearn AG (1968) Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight beta-2 mikroglobulin occurring in human biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 243: 4095-4103.
- Schardijn G, Van Eps L ( 1987) Beta-2-microglobulin: its signigicance in the evaluation of renal function. Kidney Internat. 32: 635-641.
- Suzuki S, Sato H, Inomata A, Maruyama H, Ueno M, Gejyo F, et al. ( 1992) Immuno-histological localization of beta-2-micro-globulin in renal tissue as an indicator of renal disfunction. Nephron. 60: 181-186.
- Helliwell PS, Taylor WJ (2005) Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 64 Suppl 2: ii3–ii8
- Moll JMH, Wright V (1973) Psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 3: 55–78.
- Schmitt J, Wozel G (2005) The psoriasis area and severity index is the adequate criteria to define severity in chronic plaque-type psoriasis. Dermatol. 210: 194–199.
- Szasz G (1969) A kinetic photometric method for serum gama-glutamyl-trans peptidase. Clin Chem. 15: 124-136.
- Orlowski M, Meister A (1963) Gamma-Glutamyl-P-Nitroanilide: A new convenient substrate for determination and study of L-and D-Gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase activities. Biochim Biophys Acta 73: 679-681.
- Persijn PJ, Van der Slik WJ (1976) A new method for the determination of gamma-glutamyltransferase in serum. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 14: 421-427.
- Shaw LM, Strømme JH, London JL, Theodorsen L (1983) International Federation of Clinical Chemistry. Scientific Committee, Analytical Section. Expert Panel on Enzymes. IFCC methods for measurement of enzymes. Part 4. IFCC methods for gamma-glutamyltransferase [(gamma-glutamyl)-peptide: amino acid gamma-glutamyltransferase, EC 2.3.2.2]. IFCC Document, Stage 2, Draft 2, 1983-01 with a view to an IFCC Recommendation. Clin Chim Acta 135: 315F-338F.
- Meister A, Tate SS, Ross LL (1976) Membrane-bound glutamyltranspeptidase. In: Martonosi AN (Ed), Enzyme in biological membranes. Plenum, New York 3: 315-347.
- Gladman DD, Shuckett R, Russell ML, Thorne JC, Schachter RK (1987) Psoriatic arthritis (PSA)-an analysis of 220 patients. Q J Med. 62: 127-141.
- Pipitone N, Kingsley GH, Manzo A, Scott DL, Pitzalis C (2003) Current concepts and new developments in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology. 42: 1138-1148.
- McHugh NJ, Balachrishnan C, Jones SM (2003) Progression of peripheral joint disease in psoriatic arthritis: a 5-yr prospective study. Rheumatology Oxford 42: 778-783.
- Palazzi C, Olivieri I, Petricca A, Salvarani C (2002) Rheumatoid arthritis, or psoriatic symmetric polyarthritis? A difficult differential diagnosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 20: 3-4.
- Helliwell PS (2004) Relationship of psoriatic arthritis with the other spondyloarthropathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 16: 344-349.
- Alenius GM, Berglin E, Dahlqvist SR (2006) Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) in psoriatic patients with or without joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 65: 398–400.
- Korendowych E, Owen P, Ravindran J, Carmichael C, McHugh N (2005) The clinical and genetic associations of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 44: 1056-1060.
- Inanc N, Dalkilic E, Kamali S, Kasapoglu-Gunal E, Elbir Y, et al. (2007) Anti-CCP antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 26: 17–23.
- Abdel Fattah NSA, Hassan HE, Galal ZA (2008) Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Egypt J DermatolVenereol. 28: 13–23.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences