ISSN : 2321-2748
American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics
Quantitative Estimation of Total Phenolics and Flavonoids in Soymida febrifuga leaves
Shubhangi K1, Kirti S2, Sofiya M3 and Suchita G1
1 Ideal College of Pharmacy and Research, Maharashtra, India
2 Government College of Pharmacy, Amravati, Maharashtra, India
3 DD Vispute College of Pharmacy, Panvel, Maharashtra, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Shubhangi K
Ideal College of Pharmacy and Research, Maharashtra, India.
Tel: 7303838048
E-mail: shubhi_bhide@rediffmail.com
Received Date: October 07, 2017; Accepted Date: October 25, 2017; Published Date: October 30, 2017
Citation: Shubhangi K, Kirti S, Sofiya M, Suchita G (2017) Quantitative Estimation of Total Phenolics and Flavonoids in Soymida febrifuga leaves. Am J Phytomed Clin Ther Vol. 5 No. 3:20. DOI: 10.21767/2321-2748.100333
Abstract
Soymida febrifuga is belonging to family meliaceae. The bark, fruit and leaves contains important constituents like Quercetin-3-O-L-rhamnoside, 3-O-rutinoside, lupeol, sitosterol, methyl angolensate, deoxyandirobin. The plant has found to be ethnobotanically important. The bark is acrid; refrigerant, anthelmintic, aphrodisiac, laxative; good for sore throat; removes “vata “ cures “tridosha” fevers, cough; removes blood impurities; good for ulcers, leprosy, dysentery (Ayurveda). The bark is the bowels and useful in fevers in fevers (Yunani). The bark is astringent, tonic and antiperiodic [1,2]. In intermittent fevers and general debility, in the advanced stages of dysentery, in diarrhea, and in other cases requiring the use of astringents, it has been used with success. The decoction forms a good substitute for oak-bark, and is well adapted for gargles, vaginal infections and enemas. Present study revealed the estimations of total phenolics and flavonoids were carried out according to standard procedure. Estimation of Total Phenolic Folin Ciocalteu Method and Aluminium chloride colorimetric method was used for flavonoids determination. Determination of total phenolics and flavonoids were carried out results methanol extract contains 21.7%, water 48.2% and total aqueous 32.23% w/w of and methanol contains 24.27%, water 42.86% and total aqueous 26.38% respectively.
Keywords
Soymida febrifuga; Phenolic; Flavonoids
Introduction
Soymida febrifuga A. Juss is a tall tree. Leaves 23-45 cm. long, crowded towards the ends of the branches; leaflets 3-6 pairs, opposite, 5-11.3 by 2.5-6.3 cm., elliptic or oblong, obtuse, glabrous penninerved, the nerves numerous and conspicuous beneath, base rounded, inequilateral, the lower side generally extending further down the petiolule than the upper; petiolules 3-6 mm long. Flowers in large terminal or axillary divaricately branched panicles often equaling the leaves, the branches of the panicle alternate ; pedicels very short; bracts minute, triangular, acute. Sepals 5, rotund, the margins membranous, slightly lacerate. Petals 5, obovate, 6 mm. long, clawed, often notched at the apex. Staminal tube about half as long as the petals, slightly urceolate; anthers attached by the middle of the back. Ovary glabrous; stigma, discoid, 1.5 mm. diam., 5-lobed, the lobes radiating to the centre. Capsules 2.5-6.3 cm. long, obovoid, 5-celled, 5-valved. Seeds winged. Distribution – Dry forests of the W. peninsula, extending northwards to merwara, the mirzapur hills and chota Nagpur, Ceylon [3-10].
Kingdom: Plantae; Subkingdom: Tracheobionta; Division: Magnolioplyto; Super division: Spermatophyta; Class: Mgnoliopsida; Subclass: Rosidae; Family: Meliaceae; Genus: Soymida; Species: febrifuga.
Chemical constituents
Bark contains bitter substances. Lupeol, sitosterol, methyl angolensate, deoxyandirobin from wood bark. Quercetin- 3-O-L-rhamnoside, 3-O-rutinoside from leaves [11]. Three tetratriterpenoids from fruits of Soymida febrifuga epoxyfebrinin B, 14, 15 – dihydroepoxyfebrinin B, febrinolide. The bark is acrid; refrigerant, anthelmintic, aphrodisiac, laxative; good for sore throat; removes “vata “ cures “tridosha” fevers, cough, asthma; removes blood impurities; good for ulcers, leprosy, dysentery (Ayurveda). The bark is the bowels and useful in fevers in fevers (Yunani). The bark is astringent, tonic and antiperiodic (Figures 1 and 2). In intermittent fevers and general debility, in the advanced stages of dysentery, in diarrhea, and in other cases requiring the use of astringents, it has been used with success. The decoction forms a good substitute for oak-bark, and is well adapted for gargles, vaginal infections and enemas. The bark of this tree is said to be a bitter tonic and a good antimalarial like cinchona. A decoction of the bark 1 in 20 was given in one ounce doses three times a day in cases of malarial fever and found to be beneficial. The action was not only very slow but very inferior to that of the alkaloids of cinchona (Koman) [12-15].
Plant material and extraction
Plant material: Fresh leaves of Soymida febrifuga collected in the month of August to September from Amravati District, Maharashtra. A voucher specimen was botanically authentified by Mrs. Bhogaonkar, Head Botany Department, Vidarbha Institute of Science and Humanities College, Amravati and deposited in the herbarium. The fresh leaves were dried in a hot air oven for 24 hr. at 55°C under shed and powder in a mixture grinder. The powder sieved (40 mesh) leaves packed in a paper bags and stored in air tight container until use [16,17]. Extraction was carried out by solvent extraction-50 gm of dry powder was extracted with 200 ml of solvent by Soxhletion for 20 cycles for Pet. ether, chloroform, methanol and water. And also the total aqueous extract was obtained.
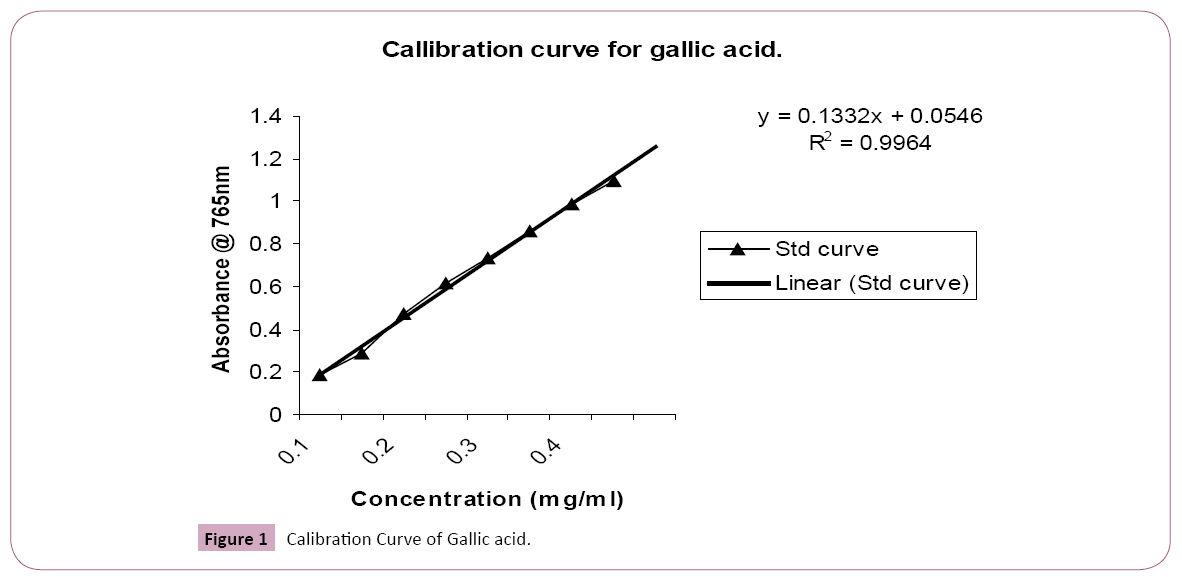
Method-estimation of phenolic constituent: Estimation of Total Phenolic (Folin – Ciocalteu Method) Preparation of Standard Calibration Curve: 1 ml aliquots of 50 – 500 μg / ml Ethanolic Gallic acid solution were mixed with 5 ml of Folin – Ciocalteu reagent (Ten fold diluted) and 4 ml of sodium carbonate (7.5%). The absorbance was read after 30 min. at 765 nm. Estimation of Total Phenolic in extracts.1 ml of each extract (50 mg/100 ml) was mixed with the same reagent as performed above. The absorbance was read after 30 min. at 765 nm for determination of phenolic. All determination was performed in triplicate [18]. Total content (%) of phenolic compound in plant different extracts was calculated as Gallic acid equivalent (GAE):
GAE=[(C × V)/M] × 100
where, C=the conc. of Gallic acid established from calibration curve mg/ml; V=Volume of extract (ml); M=the weight of dried plant extract (mg).
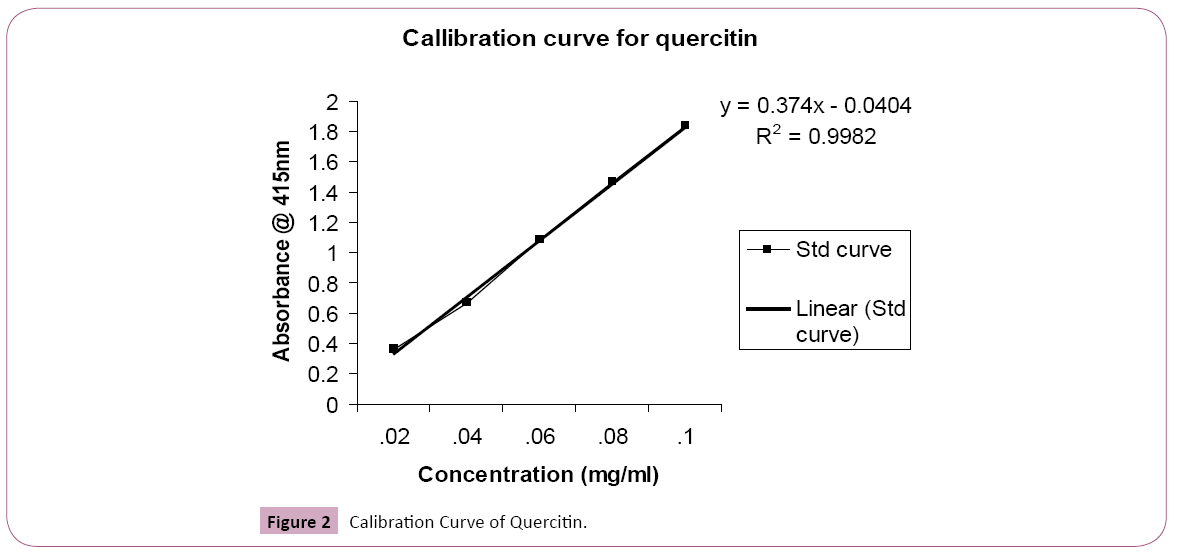
Estimation of total flavonoid content: Aluminium chloride colorimetric method was used for flavonoids determination. Each plant extracts (0.5 ml of 1:10 g/ml) in methanol were separately mixed with 1.5 ml of methanol, 0.1 ml of 10% aluminium chloride 0.1 ml of 1 m Potassium acetate and 2.8 ml of distilled water. It remained at room temperature for 30 min, the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 415 nm with a UV/ Visible spectrophotometer. The calibration curve was prepared by preparing quercetin solution at concentration 20 to 100 μg/ ml in methanol.
Results and Discussion
Estimations of various phytoconstituents were carried out according to standard procedure. Determination of total phenolics and flavonoids were carried out results are shown in Tables 1-4 respectively.
| S No. | Conc(mg/ml) | Conc(µg/ml) | Absorbance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.100 | 100 | 0.1821 |
| 2 | 0.150 | 150 | 0.2891 |
| 3 | 0.200 | 200 | 0.4689 |
| 4 | 0.250 | 250 | 0.6125 |
| 5 | 0.300 | 300 | 0.7325 |
| 6 | 0.350 | 350 | 0.8639 |
| 7 | 0.400 | 400 | 0.9856 |
| 8 | 0.450 | 450 | 1.0961 |
Table 1: Standard curve of Gallic acid at 765 nm.
| Extract | Abs. at 765 nm | % Content(GAE) | Mean (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| ME | 0.1077 | 21.54 | 21.7±0.16 |
| 0.1085 | 21.7 | ||
| 0.1093 | 21.86 | ||
| WR | 0.2414 | 48.28 | 48.2±0.44 |
| 0.2430 | 48.6 | ||
| 0.2386 | 47.72 | ||
| TA | 0.1644 | 32.88 | 32.23±0.58 |
| 0.1587 | 31.74 | ||
| 0.1604 | 32.08 | ||
Table 2: Results of Total Phenolics content (%) in each extract.
| SNo | Conc(mg/ml) | Conc (µg/ml) | Absorbance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.020 | 20 | 0.361 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 40 | 0.667 |
| 3 | 0.060 | 60 | 1.081 |
| 4 | 0.080 | 80 | 1.463 |
| 5 | 0.100 | 100 | 1.833 |
Table 3: Standard curve of Quercitin at 415 nm.
| SNo | Extract | Abs. at 765 nm | % Content(GAE) | Mean (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | Methanol | 0.527 | 23.72 | 24.27 ± 0.48 |
| 0.543 | 24.45 | |||
| 0.547 | 24.64 | |||
| (2) | Water | 0.959 | 43.62 | 42.86±1.31 |
| 0.910 | 41.34 | |||
| 0.959 | 43.62 | |||
| (3) | Total aqueous | 0.678 | 30.66 | 26.38 ± 1.13 |
| 0.654 | 29.56 | |||
| 0.691 | 31.26 | |||
Table 4: Results of Flavonoid content (%) in each extract.
Conclusion
Quantitative estimation for phenolics results that methanol extract contains 21.7%, water 48.2% and total aqueous 32.23% w/w of phenols by Folin- ciocalteu method. Foe steroids, pet. Ether extract contains 22.46 and chloroform 23.97% steroids results obtained by Liebermann-burchard color reaction. Aluminium chloride colorimetric method was used for estimation of flavonoids the results indicates that, methanol contains 24.27%, water 42.86% and total aqueous 26.38% flavonoids.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thanks Dr. Prabha Bhogaonkar, HOD Botany, VMV College, Amravati for her valuable guidance and authentication of plant.
References
- ChangCC,YangMH,WenHM(2002)Estimationoftotalflavonoidscontentinpropolisbytwocomplementarycolorimetricmethods.JournalofFoodandDrugAnalysis23:77-85.
- ChopraR,NayarS,ChopraL(1992)GlossaryofIndianmedicinalplants.CouncilofScientific andIndustrialResearch.3rdedn.
- ChopraR,NayarS,ChopraL(1980)GlossaryofIndianmedicinalplants. CouncilofScientific and Industrial Research.3rdedn.
- MabberleyDJ,WilliamR(1982)botanicaldescriptionofnewspeciesofSwietenia(mahogany)andotheroverlookedbinomialsin36vascularplantfamilies.Taxon31:65-70.
- DiwanPV,SinghAK(1993)Anti-inflammatoryactivityofsoymidafebrifuga(mansarohini)inratsandmice.PhytotherapyResearch7:255-256.
- PandeyG(2005)AnticancerherbaldrugsofIndia.CSIRPublication.
- GuptaAK(2003)QualitystandardsofIndianmedicinalplants.IndianCouncil of Medical Research.
- EdeogaH,OkwuD,MbaebieB(2005)PhytochemicalconstituentsofsomeNigerianmedicinalplants.AfricanJournalofBiotechnology4:685-688.
- HenrikTS,JesperBN,UllaWS(2001)InvitroscreeningofIndianmedicinalplantsforantiplasmodialactivity.JournalofEthanopharmacology74:195-204.
- PatelLM,ShauhanMB,DenassyTJ(1967)TanningofE.IkipsbyusingZinzyplusxylopyrus(ghat-borfruit)andSoymidafebrifuga(ron-bark)leather.Sci14:300.
- KirtikarK,BasuB(1975)Indianmedicinalplants.PeriodicalExperts.2ndedn.
- Kirtikar K,BasuB(1994)Indianmedicinalplants.PeriodicalBook.2nd edn.
- HoareauL,EdgarJ(1999)Medicinalplants:Are-emerginghealthaid.electronicJournalofBiotechnology2:1-15.
- SikarwarK,RawatM(2003)FolkuseofplantinveterinarymedicineincentralIndia.SecondworldcongressonBiotechnologicaldevelopmentofherbalmedicine.NBRI(Eng),p: 105.
- TylerV(1987)Thenewhonestherbal.ASensibleGuidetoHerbsandRelatedRemedies.
- VinodR(2003)PharmacognosyandPhytochemistry.Part 1.1stedn. p:103.
- WealthofIndiaRawMaterial.
- PurohitS(2001)Handbookofmedicinalplants-Acompletesourcebook.p:299.

Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences