Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Plagued by Contamination Doubts: A Case Study
Anam Bibi*1, Dr. Kiran Ishfaq2, Dr. Faiza Ather2
1Department of Centre for Clinical Psychology, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
2Department of Psychiatry, Jinnah Hospital, Lahore,Pakistan
- *Corresponding Author:
- Anam Bibi
Department of Centre for Clinical Psychology, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
Tel no: 923475712438
E-mail: anamn590@gmail.com, anam.bibi@uow.edu.pk
Received Date: August 07, 2021; Accepted Date: November 12, 2021; Published Date: November 22, 2021
Citation: Bibi A, Ishfaq K, Ather F (2021) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Plagued by Contamination Doubts: A Case Study, Int J Case Rep, Vol:5 No:6.
Abstract
The intended document pertains to Cognitive Behavioral Management of Excessive Hand Washing, Checking Rituals and preoccupation with thoughts of contamination. Assessment was done through Obsessive Compulsive Inventory, Yale Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale and Subjective Ratings of Symptoms. Complete assessment lead to the diagnosis of 300.3 (F42) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Psychotherapy consisted of Cognitive and Behavioral Techniques which provided an estimate of 60 % improvement in the patient, and that improvement was also confirmed by the client’s Post Level Assessment at the end of therapeutic sessions.
Keywords
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder; Psychological Management; Contamination Doubts; Cognitive and Behavioral Techniques
Introduction
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is characterized by repetitive and uncontrollable thoughts that are recurrent and involuntary (obsessions) and repetition of some behaviors that the individual feels driven to act out them again and again (compulsions) Abramowitz, Taylor & McKay). Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is likely to cause clinically significant distress and restrain in several areas of functioning. In fact, according to WHO Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is characterized as one of the most debilitating condition in the industrialized world (Murray and Lopez).
CBT in combination with Drug Therapy is considered the first line treatment for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and 45 to 60 % mean improvement is reported in most of the cases (De Haan).
A number of Researches have emphasized the role of strict standards for oneself or perfectionism (Frost, Novara, & Rheaume), one’s belief to have more control over his thoughts and acts that is excessive sense of responsibility (Cougle, Lee, &Salkovskis), Belief that simply having a thought makes the likelihood of its occurrence definite (Rachman) and thoughts about thoughts (Clark, Wells & Matthews) in the development of OCD.
Large body of literature available about the treatment of OCD identifies remarkable role of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (Clark, Wells). Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) that consists of exposure both in reality and in vitro to the condition that causes recurrent thoughts while without performing the ritual or driven act is one of the successful treatment methods for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. From the last two decades ERP has markedly improved the prognosis of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (Abramowitz, Franklin, Schwartz & Furr).
Case Study
Participant
The client is a known case of psychiatric illness from 2015. In those days he was preparing for CSS exams but he had concerns about his failure to prepare as he considered that he had a poor educational background with lack of memorization skills. He had family pressure to get a job as his sister’s wedding was going to be fixed and he was the eldest son with a lot of burden of his family earning. In those days he had feelings of sadness with hopelessness about his future as he could not get a job however, he denied to have any other depressive symptoms in those days. His mother reported that soon after she noticed that he was irritable over the lack of cleanliness in home and he started taking more time for shower and whenever interrupted by his siblings during washing hands he got angry with verbal abuse and started washing again. He had repeated thoughts that he had not washed sufficiently. He used to think that drops coming out of wash basin and toilet will also contaminate him.
He remained with these symptoms for 3 years, later he also had anxiousness to pick things from the floor and from the side others were holding e.g. spoon and glass. Soon he started avoiding touching his feet with floor and sitting on ground. He used to end shower unless he had back pain and tiredness while using water for extensive hours as he could not satisfy himself. From last 3 months he has doubts that whether he has completed a task e.g. putting finger on the light for a long time and checking his bike to be properly parked again and again. He has feelings of anxiousness when someone is got touched with him while passing by him. He gets irritated when touches door knobs as he considers them contaminated. He has stopped his law practice in court because of his problem. He also has stopped using smart phone because of the fear that he would indulge in watching porn material again as he has guilt over watching it once. From last 3 months after completing a task the client feels driven to act it out again as he has doubts about its completion. Currently he is taking Paroxetine. Initially he was prescribed to take 20mg daily that was gradually increased to 40 mg.
Background Overview
The client came from a middle class locality whose father is a 60 years old land owner and reaps crops. He is reported to have dominance over home environment. His mother is a house wife of 56. He is a victim of domestic violence as his father, uncle and aunt used to beat his mother. He reported that his father frequently blamed him for his problem as he wanted him to get a job and the client’s problem is a hindrance to get a job. He reported that he blamed him to indulge in useless activities i.e. excessive hand washing and repetitive checking. The client reported to have congenial relationship with his mother.
The client is 2nd born among the 6 siblings. His elder sister is reported to have excessive use of water and hand washing but she has overcome it after her marriage as her paternal aunt did overcome. His schooling started at the age of 4 years. He reported that he used to get average grades. When he was in class 6 he was sent to his maternal uncle who motivated him for studies and later for CSS as he wanted to get a dominant job. Later he left preparing for CSS because of these problems and get enrolled in LLB. He is also facing difficulties in his occupational functioning.
The client’s mother reported that he always tried to put his best in doing tasks assigned by elders. He used to be alone struggling with his studies. He had few friends but none of them was very close to him. He had limited interest in sports and other games. She reported that he was very shy and reserved child during his childhood. However, she reported that he got frustrated over his father’s hostile behavior towards them and their mother but he used to remain silent despite having anger as he found himself helpless to change the circumstances.
Assessment
Assessment was carried out on both formal and informal level. Informal Assessment was done by Semi-Structured Clinical Interview (Zuckerman), Subjective Rating of Symptoms (Bourne) and Dysfunctional Thought Record (Wells) while formal assessment was done by administering The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (YBOCS) by Goodman and Colleagues and Obsessive Compulsive Inventory (OCI) by Foa and Collegues.
| Raw Score | Cut off range | Classification |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | 14 | Severe to Disabling OCD |
Table 1: Representing Client’s Pre-treatment Scores obtained on YBOCS: Yale Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale
| OCI sub scales | Pre-assessment |
|---|---|
| Checking | 20 |
| Hoarding | 0 |
| Neutralizing | 0 |
| Obsessions | 17 |
| Ordering | 08 |
| Washing | 32 |
| Total | 89 |
| Cut Off | 40 |
Table 2: Representing Scores on Obsessive Compulsive Inventory at Pre-treatment Phase
| Symptom | Rating (0-10) |
|---|---|
| Spending too much time in toilet and taking a bath | 10 |
| Cleaning after toilet for several minutes | 10 |
| Desire the toilet to be perfectly clean | 10 |
| Spending several minutes to wash hand after using toilet | 10 |
| Holding fallen things from the ground | 10 |
| Sitting on ground | 10 |
| Checking a task several times | 8 |
| Passing by a wall, still water, and passing by others | 8 |
| Touching the feet with floor | 9 |
Table3: Representing Pre-treatment Subjective Ratings of Symptoms
| List of Cognitive Distortions Identified |
|---|
| Overestimation of Danger |
| Inflation of Responsibility |
| Need for Certainty |
| Low Frustration Tolerance |
| Catastrophization |
| Personalization |
| Control Fallacies |
Table 4: Representing Cognitive Distortions Identified through Dysfunctional Thought Record
Proposed Diagnosis
(300.3 (F42) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder with fair insight)
Prognosis
• Acceptance of diagnosis and fair insight of his problem are positive prognostic factors.
• Long duration of symptoms might be a negative prognostic factor.
• Motivation to cope with his illness is a positive prognostic factor.
Case ConceptualizationManagement Plan
Management plan was comprised of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy.
• Patient’s family will be psycho-educated to ensure informed and compassionate family involvement in the recovery process and to make them understand their own role in perpetuating the problem. (Hyman, 1999).
• Deep breathing exercise and progressive muscle relaxation was used initially to reduce patient’s anxiety and restlessness. (Bourne, 2003).
• Imagery Modification was used to encourage him to image having successfully completing a task as a replacement for mental ‘’undoing’’ of the action. (Wells & Metthews, 1994, 1997).
• Thought Suppression Experiment was used to make the patient aware that thought increase by suppressing them (Clark, 2004).
• Detached mindfulness / letting go technique was used to help reduce his suppressing habit regarding obsessions. (Wells & Metthews, 1994, 1997).
• Verbal reattribution (evidence for and against and worst case scenario) was used to challenge the specific appraisal of intrusions. (Wells, 1994).
• Exposure and response prevention was done that helped break connection between intrusion and ritual and challenged beliefs in negative appraisals and the predictions arising from his beliefs i.e. challenged predicted catastrophe about results of not engaging in hand washing. (Wells, 1994).
• Doubt Reduction Procedures that made use of distinctive stimuli were used to reduce doubts about the completion of an action. (Tallis, 1993).
Summary of Therapeutic Sessions
In the first therapeutic session a comprehensive history of present illness was taken from the patient. Unconditional Positive Regard was given with Reflective Listening to build a warm therapeutic relationship and to make him understand that he is being listened. Subjective ratings were taken from the client.
In the second session Formal Assessment was done through Tests Administration. Predisposing, Precipitating and Perpetuating factors were identified through detailed interview in which the client was empathetically listened and given unconditional positive regard so that the client could comfortably discuss his problems in a warm and accepting environment.
During the 3rd therapeutic session normalization was done by providing prevalence rate of the problem to remove the quires and strange feelings associated with symptoms’ experience. Socialization was done by sharing the conceptualization with the client.
In the 4th session the client’s attendant was psycho-educated as how their reaction towards his illness may perpetuate his problem and that how their participation can help improve his condition. In order to deal with his frustration and irritation because of his problems, he was taught relaxation exercises such as deep breathing exercise and PMR training was also taught.
During the 5th session external cues such as using a public toilet, internal cues such as repeated thought that hands are dirty, rituals or compulsions such as checking and hand washing and situations or objects avoided i.e. not picking fallen objects were identified through clinical interview and the client was asked to give Subjective Unit of Distress from 0-10.
The 6th session comprised of giving Dysfunctional Thought Record to the client. The client was asked to note down the triggers that cause recurrent thoughts and impel him to act out compulsions, the intrusion and then the emotion and its intensity. He was asked note down the thoughts about these intrusive thoughts and then re-rate the intensity of his emotion and at last write down the compulsion or ritual that he performed.
Imagery Modification was practiced for checking rituals. The patient was asked whenever he has recurrent thought that he has not completed the task, imagine that he has completed it successfully by mentally altering the situation e.g. imagining the whole process of standing the bike successfully in case of the client.
During the 7th therapeutic session Thought Habituation Exercises (i.e. Imaginal Exposure & Written Exposure) was done so that the client may become habituated with the thought and they become neutral for him not causing any anxiety and distress.
During the 8th session the patient was asked to think of pink bear for 1—2 minutes then he was asked not think about it at all. Feedback was taken from him. He informed that when he tried to suppress the thought of thinking about the bear it came more and more into his mind. He was also told to practice by imagining the thoughts writing on a piece of paper and after making a paper boat from it letting that boat sail into the water, which is known as detached mindfulness exercise.
Sessions 9, 10 and 11 were carried out to examine the evidence for and against for intrusions to modify his thoughts. Similarly worst case scenario was also used to alter his thoughts about having obsessions. Islamic concept of washing and contamination was also given as evidence that proved effective. Other Cognitive Restructuring techniques were applied to modify his cognitive Distortions that were identified through Dysfunctional Thought Record.
A list of distressing events or triggers was made with the help of client. The client was asked to face the least fear or anxiety provoking item and stop engaging or reduce the amount of time engaging in the ritual. At first it was carried out in the therapy room i.e. asking the client to touch the door knob and then washing hands for half of the time that is usually taken and then 2nd time not washing the hands entirely after touching the door knob while facing the anxiety of being unclean. Similarly homework assignments were given to apply the technique in multiple situations i.e. putting feet on the floor and stop washing them and drop the keys and not washing hands after picking them. Subjective Ratings of symptoms was taken and OCI was administered.
In the 12th session with the help of client 5 different sized triangles of Yellow color were made and then given to client. Each of these triangles was numbered from 1 to 5. He was asked to place the biggest triangle whenever he completes a task from the list of tasks that cause him to engage in checking ritual i.e. standing his bike and putting register properly in bookshelf. He was instructed to imagine completing the task and then look at the missing shape as evidence whenever he has doubts about not completing the task. The different size of each image was used as a fading component. The procedure resulted in marked improvement for checking rituals after 2-3 weeks.
In the 13th session post-treatment assessment was done OCI was administered and Subjective Ratings of symptoms was taken. Follow-up sessions were planned in collaboration with the client to attain long term therapeutic goals.
Results and Discussion
At the end of therapy assessment was carried out again to get an estimate of the client’s level of improvement. It revealed significant improvement in the client as Cognitive and Behavioral Techniques proved effective to deal obsessive and compulsive symptoms.
Assessment results of Pre, Mid and Post level for OCI and Subjective Ratings are given below:
| Symptoms Rating (0—10) | Pre | Mid | post |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spending excessive time in toilet and taking a bath | 10 | 7 | 5 |
| Cleaning after toilet for several minutes | 10 | 7 | 4 |
| Desire the toilet to be perfectly clean | 10 | 10 | 8 |
| Spending several minutes to wash hand after using toilet | 10 | 8 | 4 |
| Holding fallen things from the ground | 10 | 5 | 1 |
| Sitting on ground | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| Checking a task several times | 8 | 3 | 0 |
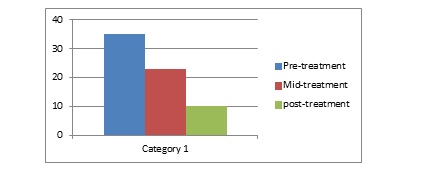
| Passing by a wall and passing by othersTouching the feet with floor | 89 | 75 | 52 |
Table 5: Representing Pre, Mid, and Post-treatment Subjective Ratings
| OCI sub scales | Pre-assessment | Mid-assessment | post assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Checking | 20 | 8 | 2 |
| Hoarding | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutralizing | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Obsessions | 17 | 15 | 9 |
| Ordering | 08 | 3 | 1 |
| Washing | 32 | 22 | 12 |
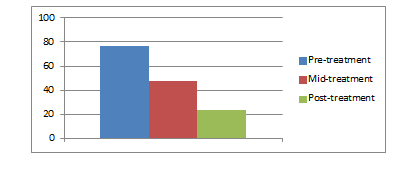
| Total Score | 77 | 48 | 24 |
Table 6: Representing Pre, Mid, and Post administration of Obsessive Compulsive Inventory
Discussion
Significant improvement in client’s compulsive behavior occurred as he significantly decreased the time to wash hands and taking shower that was several hours when he first came to therapy. Anxiousness over Obsessive thoughts was also significantly decreased in later sessions. The client started making eye-contact soon after the initial sessions that was poor on the day when he came to therapy. The client showed a marked improvement in checking rituals. Between sessions he started putting his hands on the arms of chair instead of his lap that was a significant response of Exposure and Response Prevention. At start he started sitting for a short time on a mat but as the therapy progressed he was able to sit for a longer period and then later he started sitting on the floor of home without mat. Later he started opening the door of therapy room while using his full hand from the place from where others open. He started using others pencil for a shorter time initially then he succeeded extending the time. The client’s reassurance seeking behavior also improved markedly during therapy. The Islamic concept of intentional and unintentional thoughts and washing proved helpful in cognitive restructuring. During Cognitive Restructuring Religious concept of intentional and unintentional thoughts proves effective for emotions attached with recurrent intrusive thoughts (Ishfaq).
As client reported that his paternal aunt and elder sister also had the same problem, research findings suggest the estimated odd ratio of OCD in first degree relationships as much significant (Chamberlain).
The client has conflictual relationship with his father and the client reported his father to be a dominant person at home since his childhood with lack of warmth and affection towards his children and wife. Research indicates a significant relationship between parenting style comprised of strict rules, rigidity, and lack of affection with recurrent intrusive thoughts and compulsions in OCD (Timpano, Keough, Mahaffey, Schmidt, & Abramowitz).
As the client reported significant stressors prior to the onset of his problem i.e. joblessness, failure to prepare for CSS exam and financial burden to support his family, many of the researches identify the role of stressful life events as triggers for OCD.
Through Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) the client was helped to experience anxiety provoking situations while preventing him to engage in compulsive behaviors i.e. asking the client to touch the door knob and then washing hands for half of the time that is usually taken and then 2nd time not washing the hands entirely, putting feet on the floor and stop washing them and drop the keys while not washing hands after picking them. Findings from Randomized Controlled Trials for the effectiveness of ERP for OCD compared with patients receiving ERP as an outpatient revealed marked reductions in their OCD symptoms following Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) (Franklin, Abramowitz, Kozak, Levitt & Foa).
References
- Abramowitz, JS, Franklin, M, Schwartz, S, Furr, J. Symptom presentation and outcome of cognitive-behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2003; 71:1049–1057.
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
- Andrews G, Crino R, Hunt C, Lampe L, Page A. The Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. New York: Cambridge University Press (1994).
- Bourne, J.E. The Anxiety and Phobia Workbook (3rd ed). New Harbinger Publications, INC.
- Clark, D. A. (2004). Cognitive-behavioral therapy for OCD. New York: Guilford Press.
- De Haan, E. (2006). Effective treatment of OCD. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 45(4), 383.
- Foa, E.B., Kozak, M.J., Salkovskis, P.M., Coles, M.E. & Amir, N. (1998). The validation of a new obsessive compulsive disorder scale: The obsessive compulsive inventory (OCI). Psychological Assessment, 10, 206-214.
- Franklin, M. E., Abramowitz, J. S., Kozak, M. J., Levitt, J. T., & Foa, E. B. (2000). Effectiveness of exposure and ritual prevention for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Randomized compared with nonrandomized samples. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68(4), 594-602.
- Goodman, W.K; Price, L.H; Rasmussen, S.A; et al. (1989). "The Yale–Brown Obsessive–Compulsive Scale. I. Development, use, and reliability". Arch Gen Psychiatry. 46 (11): 1006–1011.
- Salkovskis, P. M., Wroe, A. L., Gledhill, A., Morrison, N., Forrester, E., Richards, C., ...& Thorpe, S. (2000). Responsibility attitudes and interpretations are characteristic of obsessive compulsive disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38(4), 347-372.
- Timpano, K. R., Keough, M. E., Mahaffey, B., Schmidt, N. B., & Abramowitz, J. (2010). Parenting and obsessive compulsive symptoms: Implications of authoritarian parenting. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 24(3), 151-164.
- Wells, A. (1997). Cognitive Therapy of Anxiety Disorders : A Practice Manual and Conceptual Guide. UK: John Wiley & Sons.
- Zuckerman, E. L. (2010). Clinician’s Therasus: The Guide to Conducting Interviews and Writing Psychological Reports (7th ed.). New York: The Guilford Press.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences