Impact of Thyroid on Liver Metabolism
Sabina Khanam*
Department of Biological Sciences, Yobe State University, Nigeria
- *Corresponding Author:
- Sabina Khanam
Department of Biological Sciences
Yobe State University, Nigeria
Tel: +234 706 336 6173
E-mail: sabinakhanam@ymail.com
Received Date: November 28, 2017; Accepted Date: December 08, 2017; Published Date: December 15, 2017
Citation: Khanam S (2017) Impact of Thyroid on Liver Metabolism. Endocrinol Res Metab. Vol.1 No.2:6
Abstract
Thyroid gland is an endocrine gland which secretes thyroid hormones useful for various metabolic processes in the body. It releases triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Thyroid hormones regulates the basal metabolic rate (BMR) of almost all the cells such as hepatocyte cells of liver, cardiovascular function, energy balance and lipid metabolism. Disturbance in the level of thyroid hormones may alter the normal bilirubin metabolism and normal hepatic circulation.
Introduction
Thyroid gland is an endocrine gland which secretes thyroid hormones useful for various metabolic processes in the body. It releases triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Thyroid hormones regulates the basal metabolic rate (BMR) of almost all the cells such as hepatocyte cells of liver, cardiovascular function, energy balance and lipid metabolism. Disturbance in the level of thyroid hormones may alter the normal bilirubin metabolism and normal hepatic circulation.
Liver Metabolism
Thyroid hormones which are released by thyroid gland regulates different metabolic processes in the body. By increasing basal metabolic rate (BMR) thyroid hormones plays important role in regulating thermogenesis. By regulating BMR of cells in the body including hepatocytes cells which are present in liver, thyroid hormones are essential for development, growth and functions of all tissues. It also regulates lipid metabolism and cardiovascular functions [1]. Hypermetabolic condition is a state when level of thyroid hormone increases in the blood which leads to increased intake of food, weight loss and elevated level of energy expenditure [2]. Normal thyroid function depends on the presence of trace elements such as zinc, copper, iron, iodine, selenium for metabolism and synthesis of thyroid hormones [3].
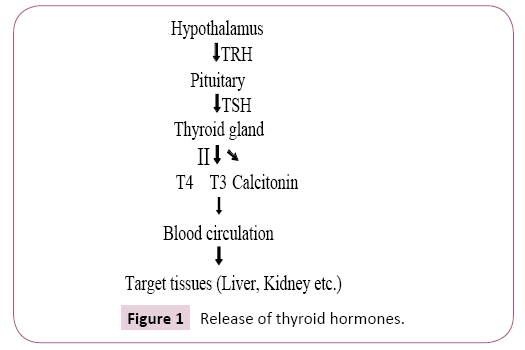
Such conditions are mostly due to thyroid hormones which work directly on the target tissues like liver, heart, adipose tissue and on skeletal muscles [4,5]. Liver metabolises thyroid hormones and regulate their endocrine effects. diseases liver alter metabolism of thyroid hormones and the functions of liver may disturb due to dysfunction of thyroid gland (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Table 1: Factors that affect thyroid function.
| Factors that inhibit proper function of thyroid | Factors that increase T4 to Reverse triiodothyronine (RT3) conversion | Factors that contribute proper production of thyroid hormone |
|---|---|---|
| Some autoimmune diseases | Low calorie diet | Nutrients: Vitamin B2, B3, B6, E, C and D |
| Stress | Kidney and Liver dysfunction | Iodine |
| Infection | Toxic substances | Zinc, Selenium |
| Radiation | Stress | Iodine |
| Toxic substances: Pesticides, Cadmium, Lead | Inflammation | Iron |
| Fluoride which is antagonists to iodine | Infections | |
| Age, Pregnancy | ||
| Drugs: dopamine, glucocorticoid |
Conclusion
Liver plays important role in thyroid hormone metabolism. For normal bilirubin metabolism and liver function serum level is very important in blood. Liver involved in thyroid hormone excretion, conjugation and the synthesis of thyroid hormone binding globulin. Disturbance in the level of thyroid hormones may alter the normal bilirubin metabolism and normal hepatic circulation. Dysfunction of thyroid gland may disturb liver function and viceversa [6-8].
References
- Brent GA (2012) Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J Clin Invest 122: 3035-3043.
- Kim B (2008) Thyroid hormone as a determinant of energy expenditure and the basal metabolic rate. Thyroid 18: 141-144.
- Betsy A, Binitha MP, Sarita S (2013) Zinc deficiency associated with hypothyroidism: An overlooked cause of severe Alopecia. Nt J Trichology 5: 40-42.
- Mullur R, Liu YY, Brent GA (2014). Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol Rev 94: 355-382.
- Silva JE (2006) Thermogenic mechanisms and their hormonal regulation. Physiol Rev 86: 435-464.
- Malik R, Hodgson H (2002) The relationship between the thyroid gland and the liver. QJM 95: 559-569.
- Kayacetin E, Kisakol G, Kaya A (2003) Low serum total thyroxine and free triiodothyronine in patients with hepatic encephalopathy due to non-alcoholic cirrhosis. Swiss Medical Weekly 133: 210-213.
- Sorvillo F, Mazziotti G, Carbone A, Morisco F, Cioffi M, et al.(2003) Increased serum reverse triiodothyronine levels at diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with compensated HCV-related liver cirrhosis. Clinical Endocrinology 58: 207-212.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences