ISSN : 2249 - 7412
Asian Journal of Plant Science & Research
Floral Diversity and Community Structure in Fifa Nature Reserve
Abdullah Al-Oshoush*
Department of Ecology, Mutah University, Mutah, Jordan
- *Corresponding Author:
- Abdullah Al-Oshoush
Department of Ecology, Mutah University, Mutah,
Jordan,
E-mail: Abdullah.aloshoush@rscn.org.jo
Received date: June 01, 2022, Manuscript No. AJPSKY-22-13854; Editor Assigned date: June 03, 2022, PreQC No. AJPSKY-22-13854(PQ); Reviewed date: June 13, 2022, QC No. AJPSKY-22-13854; Revised date: June 23, 2022, Manuscript No. AJPSKY-22-13854(R); Published date: June 30, 2022, DOI: 10.36648/2249-7412.12.6.223
Citation: Al-Oshoush A (2022) Floral Diversity and Community Structure in Fifa Nature Reserve. Asian J Plant Sci Res Vol.12 No.6:223
Abstract
The vegetation cover at Fifa nature reserve was studied in the reserve during the period from January to April of 2019. It’s aimed to updating floral species checklist and establishment of plant herbarium. During this study, random route transect method was used and interviews with the local community to determine plants uses in the region. In addition, specimen for all recorded plants were collected to prepare herbarium of the reserve. The results documented existing of 123 species that belonging to 29 families and 96 genera in the reserve. According to their status at the national level, this survey recorded four critically endangered (RC) plants and four Vulnerable species (VU) and six Endangered plants (EN). Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Chenopodiaceae and Fabaceae families recording the highest number of individuals recorded. In addition, the vegetation components in the reserve is distributed on three strata, trees, shrubs and herbs. This variation of floral elements within such habitat of harsh environmental conditions, confirmed the healthy stand of vegetation cover at Fifa nature reserve and the priority to protect it.
Keywords
Flora; Fifa nature reserve; Ramsar site; Diversity; Ghor
Introduction
Jordan geology comprises three main features that are the Rift valley, the Mountain highlands and the eastern desert (locally known Badia) and considered as a milestone of the different ecosystems and environments [1]. In addition, the country has a wide variation of physical characteristics as altitude, with more that 1800m above sea level in the Southern Mountain, to 424 m below sea level at Dead sea, which is the lowest point on Earth. Likewise, the temperatures and annual rainfall are highly variated in the country from region to another, created a gorgeous wildlife status as a reflection of its varied physical characteristics, which have yielded an unusual case of richness in landforms and biodiversity in terms of ecosystems and species.
Geographically, the strategical location at the crossroads of Africa, Asia and Europe has made Jordan as a linkage for enrich of natural resources where the Rift valley provides a globally critical land bridge between the three continents that supports a large variety of ecologically diverse habitats of international importance and funnels millions of migrating birds each year [2,3]. Furthermore, Jordan located in the extreme southwestern part of the Fertile Crescent, which is the center of diversity and botanic regions due to the presence of various climatic conditions that create different ecosystems [4]. As a result, Jordan encapsulates four bio-geographical regions: Mediterranean, Irano- Turanian, Saharo-Arabian and Sudanian (sub-tropical). Because of climatic and geographic variations among the bio- geographical zones, the country comprises 13 vegetation types [1]. These distinguishing features of vegetation types and distribution among the country, contributes to record more than 2,500 plant species, which comprises 1% of flora of the world. Al-Eisawi records about 2,543 plant species that belongs to 142 families and 868 genera in Jordan [5].
As an effective tool of In-situ conservation, Jordan was a pioneer of establishing network of protected areas. The Royal Society for the Conservation of Nature (RSCN) had the governmental mandate to establish and manage the natural reserves to conserve the biodiversity components and insure sustainability of wildlife.
Fifa nature reserve was declared as a protected area in 2010 and was described as the lowest natural reserve on Earth.
The reserve established to protect both the sub-tropical and Saline vegetation basically, as well conserve all related species either flora or fauna. Since the reserve contains the best representation of Toothbrush tree (Salvadora persica), in addition to other indicator species as Acacia (Acacia tortilis and A. raddiana), Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera), and Syrian Christ-thorn (Ziziphus spina-christi).
Moreover, Fifa nature reserve embedded within Fifa-Safi Important Bird Area (IBA) that identified by birdlife [6]. Also, different faunal species recorded in the reserve such as Spiny-tailed Lizards (Uromastyx aegyptia) which considered vulnerable species at the global level and mentioned as important indicator species in Fifa nature reserve [7,8]. In addition, Dead Sea Toothcarp fish (Aphanius richardsoni) described as globally endangered species that found in restricted springs as Fifa area [9]. Recently, Fifa nature reserve declared as “Ramsar site” in 2017, under Ramsar convention, which is a treaty of an intergovernmental importance that provides base of responsible use of wetlands resources, as well, support the conservation framework of such sites worldwide.
As other protected areas in Jordan, Fifa nature reserve is under different harmful threats that causing losses of wildlife components. These deteriorated factors are derived by either ecological- or human-induced factors. The ecological factor is represented by existing of invasive plants (Prosopis juliflora), whereas human-induced factors including expansion of agricultural land and using pesticide, chemical fertilizer as well ground water pumping. In addition, other human activities as illegal hunting, overgrazing, and Army activities which leading to habitat destruction and fragmentation as well, losses of wild species either flora or fauna.
Vegetation cover at Fifa nature reserve has been studies by RSCN flora team in different years, as a priority to prepare the management plan of the site. First survey was implemented in 2009 through an ecological rapid assessment, where the results recorded only 19 plant species belonging to 17 families, with five medicinal, one ornamental, six edible, five woody and five palatable plants.
The next survey has been implemented in 2011, total of 80 species were recorded during the survey that belonging to 60 genera and 30 families, with 46 palatable, 13 medicinal, six woody, five edible and three poisonous plants. In addition, the last updated of plant checklist was in 2014 with recording about 94 plant species within the reserve. All surveys that have been conducted in the reserve resulted with preparing a plant checklist, but not any distinctive survey was implemented to assess the actual status of flora in the reserve. Such information will be very valuable in term of its importance as a Ramsar site -as mentioned before-, as well as, preparing long term monitoring programs for ecologically indicator species that are of local and global importance for conservation purposes.
Materials and Methods
Physical description
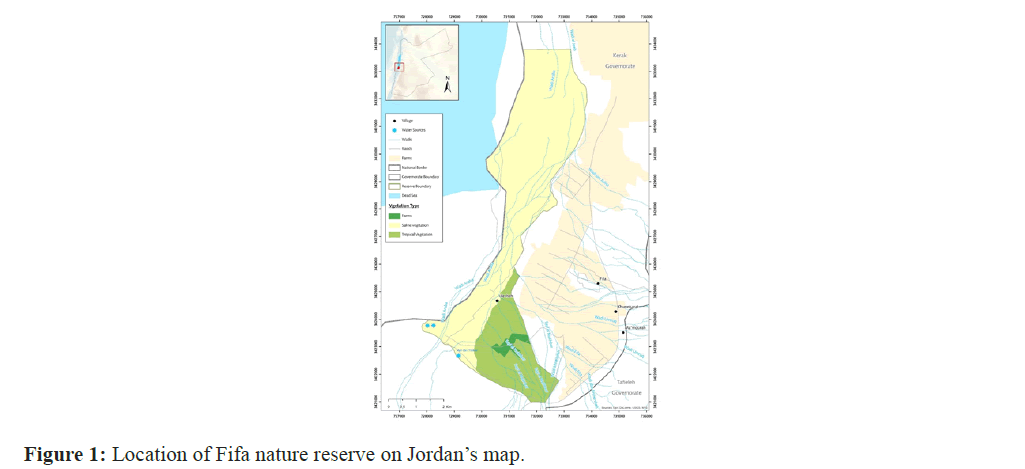
Fifa nature reserve is located at the southwestern part of Jordan within Karaka governate with smaller portion on the southeastern part within Tafilla governate. It is about 33.5 km South-Southeast of the Dead Sea and about 157 km North of Aqaba city, and form the international border of Jordan with occupied Palestine (Figure 1). The reserve characterized with being at the lowest elevation on Earth at 424 m below sea level. It is characterized by warm winter with a minimum average temperature of 10⁰C and hot summer with a maximum average temperature of 40⁰C, which is the hottest degree recorded in the country. The annual average precipitation is between 50 ml-100 ml, which is the lowest records in Jordan.
Vegetation cover description
Fifa nature reserve located within the Sudanian (sub-tropical) bio-geographical zone, which characterized with lowest annual rainfall recorded in Jordan and highest summer temperatures recorded also. Soils are mostly alluvial, saline, sandy and granitic types. The vegetation is with tropical element of small trees and shrubs as (Zizphus spinachristi) and annual herbs. There are two vegetation types dominating the reserve including:
Saline vegetation
It is in the north and southwestern part of the reserve with around 78% of the total area and characterized by high level of soil salinity that appears as distributed patches of light and dark color on soil surface. Dominant plants are Halophytes and succulent’s species as Tamarix tetragyna, T. aphylla, and Suaeda monica.
Tropical vegetation
It is restricted in the southeastern part with about 22% of the reserve total area. The soil present with this vegetation is alluvial with a light color and deficient of organic matter [1]. The leading plant species are Salvadora persica, Calotropis procera and Zizphus spina-christi, and Ochradenus baccatus (Figure 1).
Random route transect
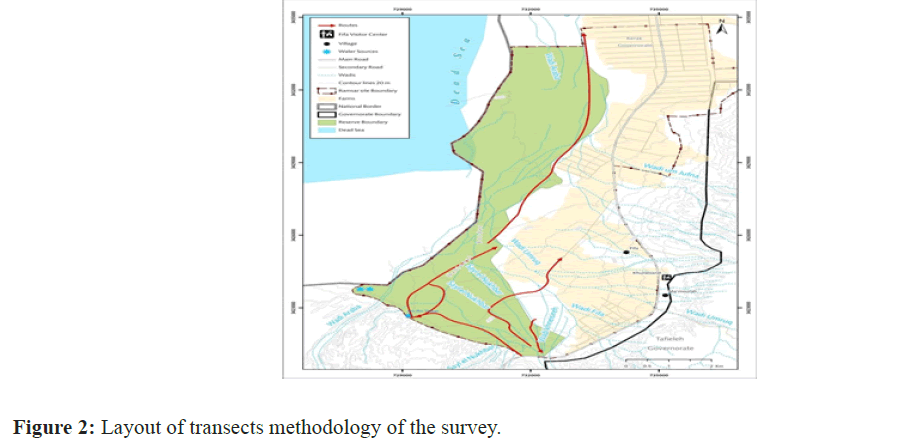
The random route transect method was chosen, to cover the total area of the reserve –as far as possible- since it is a suitable method of recording plants in this open habitat. To cover whole reserve area, five transects were chosen to cover tropical vegetation, and three route transects to cover saline vegetation. The transects were carried out during 22nd Feb to 15th March.
All plants that founded while walking randomly in the route transect were recorded on the Data sheet. A representative specimen was collected so it can be added later to the final checklist after been identified. Furthermore, any threats or human activities within the reserve were recorded. Because almost all the reserve is located in the buffer of international border, and thus the security issue is very strict (Figure 2).
Plant specimens collections
Representative specimens for all recorded plants in the checklist were taken at time of survey (vegetative, flowering, or fruiting). The team collaborates to collect, identify, and preserve each specimen. Each sample was pressed and dried to preparing reserve herbarium purposes.
During specimen’s collection, all information was documented greatly facilitated by the GPS unit, which uses satellite signals to calculate current geographical coordinates and altitude (Figure 3).
Interviews
Interviews with local communities adopted for documentation the botanical knowledge of Fifa village, since traditional farmers have ancient experience of species to be used for medicinal purposes. A total of 90 questionnaires have been used to collect data from local communities. Collected data was analyzed. Sample of used questionnaire is listed in Appendix 1.
Results
Species checklist
The following table is showing the total number of flora in Fifa nature reserve with total number of 123 species that belonging to 29 families and 96 genera (Table 1). According to Royal Botanical Garden (RBG) [10], the current list of Fifa nature in term of plant status at the national level includes four critically endangered plants that are Anthemis zoharyana, Launaea procumbens, Medicago ciliaris and Asphodelus refractus. In addition, four vulnerable species were recorded including Haloxylon persicum, Suaeda monoica, Acacia raddiana, and Acacia tortilis. In addition to six endangered plants Picris asplenioides, Atriplex holocarpa, Equisetum ramosissimum, Monsonia nivea, Calligonum comosum and Salvadora persica. Its worthy to mention that majority of listed plants are classified as Least Concerned (LC), whereas some species hadn’t enough information about their status and thus classified as Not Applicable (NA).
| Scientific name | Arabic Name | Synonum | Status* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aizoaceae | |||||
| 1 | Aizoon canariense L | حدق | LC | ||
| Amaranthaceae | |||||
| 2 | Aerva javanica (Burm.f.) Juss. ex Schult. | شجرة النعجة | Aerva persica | LC | |
| Asclepiadaceae | |||||
| 3 | Calotropis procera (Aiton) Aiton f. | العشير | LC | ||
| 4 | Leptadenia pyrotechnica (Forssk.) Decne. | سيسبان | Cynanchum pyrotechnicum | LC | |
| Asteraceae | |||||
| 5 | Aaronsohnia factorovsyi Warb et Eig | أقحوان أقرع | LC | ||
| 6 | Anthemis zoharyana Eig | اقحوان | CR | ||
| 7 | Centaurea sinaica DC. | مرار سينائي | LC | ||
| 8 | Ifloga spicata (Forssk.) Sch.Bip. | قرطف سنبلي | Chrysocoma spicata | LC | |
| 9 | Koelpinia linearis Pall. | كلابة | Koelpinia latifolia | LC | |
| 10 | Launaea angustifolia (Desf.) O. Kuntze | مرار | Launaea arabica | LC | |
| 11 | Launaea procumbens (Roxb.) Ramayya & Rajagopal | Ammoseris patens | CR | ||
| 12 | Launaea capitata (Spreng.) Dandy | مرار لبني | Sonchus capitatus | LC | |
| 13 | Launaea mucronata (Forssk.) Muschl. | مرار | Leontodon mucronatus | LC | |
| 14 | Launaea nudicaulis (L.) Hook.f | هندباء الحماد | Ammoseris nudicaulis | LC | |
| 15 | Leontodon laciniatus (Bertol.) Widder | ربيان صحراوي | Leontodon arabicum | LC | |
| 16 | Picris asplenioides L. | حوذان | Picris radicata | EN | |
| 17 | Senecio leucanthemifolius Poir | Senecio apulus | LC | ||
| 18 | Senecio vernalis Hoppe ex DC | صفيره | Senecio leucanthemifolius supsp. vernalis | LC | |
| Boraginaceae | |||||
| 19 | Arnebia decumbens (Vent.) Coss. & Kralik | كحل مضجع | LC | ||
| 20 | Arnebia linearifolia DC | كحل ضيق الأوراق | LC | ||
| 21 | Gastrocotyle hispida (Forssk.) Bunge | رمس | Anchusa deflexa | LC | |
| 22 | Heliotropium bacciferum Forssk. | لبيد | Heliotropium bacciferum var. erosum | LC | |
| 23 | Lappula spinocarpos (Forssk.) Asch. ex Kuntze | نفيلة شائكة الثمار | Anchusa spinocarpos | LC | |
| 24 | Trichodesma ehrenbergii Boiss. | ||||
| Brassicaceae | |||||
| 25 | Brassica nigra (L.) W.D.J.Koch | خردل أسود | LC | ||
| 26 | Diplotaxis acris (Forssk.) Boiss. | مقرة | LC | ||
| 27 | Diplotaxis harra (Forssk.) Boiss. | حراقة | Sinapis harra | LC | |
| 28 | Eremobium aegyptiacum (Spreng.) Asch. & Schweinf. ex Boiss. | غبيشة | LC | ||
| 29 | Eruca sativa Mill. | جرجير | LC | ||
| 30 | Erucaria rostrata (Boiss.) Greuter & Burdet | غراء | Erucaria boveana | LC | |
| 31 | Farsetia aegyptia Turra | الشجرة الغبراء | Farsetia aegyptia var. aegyptia | LC | |
| 32 | Lobularia libyca (Viv.) Webb & Berthel. | Alyssum canariense | LC | ||
| 33 | Matthiola parviflora (Schousb.) R.Br | منثور قشير البتلات | Matthiola parviflora | LC | |
| 34 | Morettia parviflora Boiss. | Morettia canescens var. parviflora | LC | ||
| 35 | Morettia philaeana DC. | Diceratella sahariana | LC | ||
| 36 | Plantago weldenii Rchb. | ||||
| 37 | Savignya parviflora (Delile) Webb | Savignya parviflora | NA | ||
| 38 | Schimpera arabica Hochst. & Steud. | صفاري | Schimpera arabica var. arabica | LC | |
| Capparaceae | |||||
| 39 | Cleome arabica L | شجرة الوحش | Cleome trinervia | LC | |
| Caryophyllaceae | |||||
| 40 | Gymnocarpos sclerocephalus (Decne.) Dahlgren & Thulin | Paronychia sclerocephala | LC | ||
| 41 | pergularia marina (L.) Besser | أم ثريب | Spergularia salin | ||
| 42 | Polycarpon succulentum (Delile) J.Gay | Alsine succulenta | |||
| 43 | Polycarpon tetraphyllum subsp. alsinifolium (Biv.) Arcang | Polycarpon alsinifolium | |||
| 44 | Polypogon adscendens Guss. | Polypogon adscensionis | |||
| 45 | Pulicaria crispa Sch.Bip. | جثجاث | Pulicaria undulata | LC | |
| 46 | Silene villosa Forssk. | كحلة | |||
| 47 | Telephium sphaerospermum Boiss. | ||||
| Chenopodiaceae | |||||
| 48 | Anabasis articulata (Forssk.) Moq | عجرم | LC | ||
| 49 | Anabasis syriaca Iljin | LC | |||
| 50 | Arthrocnemum macrostachyum (Moric.) K.Koch | العثنان | LC | ||
| 51 | Atriplex holocarpa F.Muell. | EN | |||
| 52 | Atriplex halimus L | قطف ملحي | LC | ||
| 53 | Atriplex leucoclada Boiss | رغل أبيض الفروع | LC | ||
| 54 | Bassia muricata (L.) Asch. | اللياء الابرية | LC | ||
| 55 | Chenopodium album L. | ذنب الكلب | LC | ||
| 56 | Chenopodium murale L. | رمرام | LC | ||
| 57 | Haloxylon persicum Bunge | الغضا | Anabasis saxaul | VU | |
| 58 | Suaeda aegyptiaca (Hasselq.) Zohary | Chenopodium aegyptiacum | LC | ||
| 59 | Suaeda monoica Forssk. ex J.F.Gmel. | السوادة | Lerchia monoica | VU | |
| 60 | Traganum nudatum Delile | ضمران | Traganum nudatum var. acuminatum | LC | |
| Cucurbitaceae | |||||
| 61 | Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad. | الحنظل | LC | ||
| Equisetaceae | |||||
| 62 | Equisetum ramosissimum Desf. | ذنب الفرس | Equisetum giganteum | EN | |
| Fabaceae | |||||
| 63 | Acacia raddiana Savi | طلح شعاعي | Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana | VU | |
| 64 | Acacia tortilis (Forssk.) Hayne | سمر | VU | ||
| 65 | Alhagi graecorum Boiss | عاقول | LC | ||
| 66 | Astragalus tribuloides Delile | LC | |||
| 67 | Hippocrepis areolata Desv. | Hippocrepis bicontorta | LC | ||
| 68 | Lotus halophilus Boiss. & Spruner | LC | |||
| 69 | Medicago ciliaris (L.) Krock. | Medicago intertexta subsp. Ciliaris | CR | ||
| 70 | Medicago laciniata (L.) Mill. | نفل | Medicago laciniata subsp. laciniata | LC | |
| 71 | Medicago littoralis Loisel. | Medicago littoralis subsp. cylindracea | LC | ||
| 72 | Polycarpaea robbairea (Kuntze) Greuter & Burdet | Robbairea delileana | |||
| 73 | Prosopis farcta (Banks & Sol.) J.F.Macbr | Lagonychium farctum | LC | ||
| 74 | Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC. | السلم | Mimosa farcta | INVASIVE | |
| 75 | Pteranthus dichotomus Forssk. | بسومة | Camphorosma pteranthus | LC | |
| 76 | Trigonella stellata Forssk. | حلبة مخملية | LC | ||
| Frankeniaceae | |||||
| 77 | Frankenia pulverulenta L. | الحمرة | Franca nodiflora | LC | |
| Geraniaceae | |||||
| 78 | Erodium laciniatum var. pulverulentum (Cav.) Boiss. | قرنوة مقسمة | Erodium bovei | ||
| 79 | Erodium touchyanum Delile | Erodium deserti | LC | ||
| 80 | Monsonia nivea (Decne.) Webb | Erodium niveum | EN | ||
| Juncaceae | |||||
| 81 | Juncus rigidus Desf. | Juncus arabicus | LC | ||
| Liliaceae | |||||
| 82 | Allium papillare Boiss | ||||
| 83 | Androcymbium palaestinum Baker | بصيلة | LC | ||
| 84 | Asphodelus refractus Boiss | CR | |||
| 85 | Dipcadi erythraeum Webb & Berth. | LC | |||
| Malvaceae | |||||
| 86 | Abutilon pannosum (Forst.f.) Schltdl | لواق | |||
| 87 | Malva nicaeensis All. | خبيزة | Althaea nicaeensis | LC | |
| 88 | Malva parviflora L. | خبيزة | Malva parviflora var. parviflora | LC | |
| Neuradaceae | |||||
| 89 | Neurada procumbens L. | Figaraea aegyptiaca | NA | ||
| Plantaginaceae | |||||
| 90 | Plantago cylindrica Forssk. | ربل أسطواني | NA | ||
| 91 | Plantago ovata Forssk. | ربل بيضوي | NA | ||
| Poaceae | |||||
| 92 | Aeluropus littoralis (Gouan) Parl | LC | |||
| 93 | Hemarthria altissima (Poir.) Stapf & C.E.Hubb. | Andropogon altissimus | |||
| 94 | Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. | قصيب | Phragmites australis var. altissimus | LC | |
| 95 | Schismus barbatus (L.) Thell. | نعيمة | Schismus barbatus subsp. arabicus | LC | |
| 96 | Stipagrostis plumosa Munro ex T.Anderson | Stipagrostis plumose var. aethiopica | LC | ||
| Polygonaceae | |||||
| 97 | Calligonum comosum L'Her. | عرطه | EN | ||
| 98 | Emex spinosa (L.) Campd. | الحبذان | Rumex spinosa | LC | |
| 99 | Rumex cyprius Murb. | حميض | Acetosa cypria | NA | |
| 100 | Salsola imbricata Forssk | Caroxylon geatulum | LC | ||
| 101 | Salsola vermiculata L. | روثا | Salsola vermiculata var. brevifolia | LC | |
| Resedaceae | |||||
| 102 | Ochradenus baccatus Delile | العلندر | LC | ||
| 103 | Oligomeris subulata "Webb," | Oligomeris subulata | |||
| 104 | Reseda arabica Boiss. | Reseda praetervisa | LC | ||
| 105 | Retama raetam (Forssk.) Webb | الرتم | Retama raetam | LC | |
| Rhamnaceae | |||||
| 106 | Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) Desf. | السدر | Rhamnus spina-christi | LC | |
| Salvadoraceae | |||||
| 107 | Salvadora persica L. | الأراك | Salvadora persica var. persica | EN | |
| Scrophulariaceae | |||||
| 108 | Linaria joppensis Bornm. | ||||
| 109 | Linaria haelava Delile | حلاوة | Antirrhinum haelava | NA | |
| 110 | Veronica anagallis-aquatica L. | Veronica anagallidiformis | LC | ||
| Solanaceae | |||||
| 111 | Hyoscyamus desertorum (Asch. & Boiss.) Täckh | سكران | Hyoscyamus albus var. desertorum | LC | |
| 112 | Lycium depressum Stocks | عوسج | Lycium turcomanicum | LC | |
| 113 | Lycium shawii Roem. & Schult. | عوسج | Lycium albiflorum | LC | |
| Tamaricaceae | |||||
| 114 | Tamarix aphylla (L.) H.Karst. | طرفاء مفصلية | Tamarix aphylla | LC | |
| 115 | Tamarix tetragyna Ehrenb. | اثل | Tamarix tetragyna var. deserti | LC | |
| Urticaceae | |||||
| 116 | Forsskaolea tenacissima L. | Caidbeja adhaerens | LC | ||
| Zygophyllaceae | |||||
| 117 | Fagonia bruguieri DC. | Fagonia bruguieri var. ehrenbergii | LC | ||
| 118 | Fagonia glutinosa Delile | Fagonia glutinosa var. chevalieri | LC | ||
| 119 | Fagonia scabra Forssk. | Fagonia sinaica | |||
| 120 | Nitraria retusa (Forssk.) Asch. | الغرقد | Berberis africana | LC | |
| 121 | Tetraena simplex (L.) Beier & Thulin | Zygophyllum simplex | |||
| 122 | Tribulus bimucronatus Viv. | NA | |||
| 123 | Tribulus pentandrus Forssk. | Tribulus longipetalus |
Table 1: List of recorded plant species in Fifa nature reserve
From other hand, the current results recorded plant species that have been thought to be lost from the area as Horse Tail (Equisetum ramosissimum).
Vegetation families
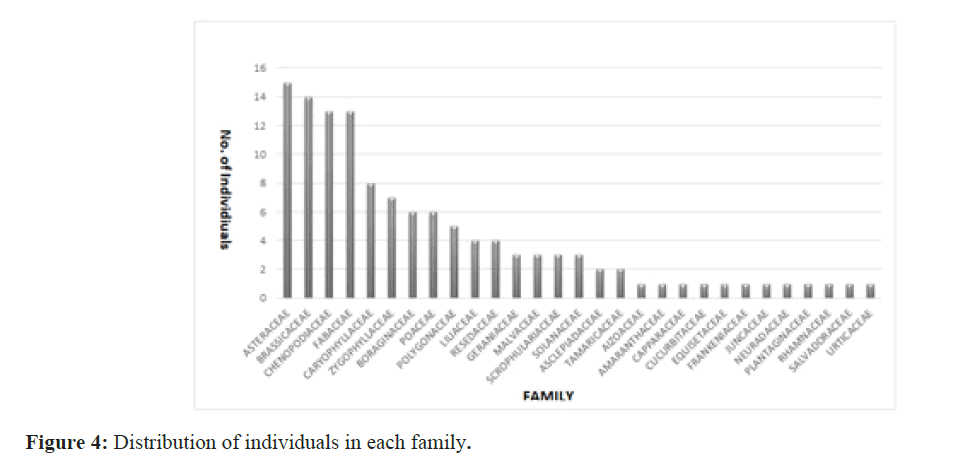
The results show that 29 plant families were recorded. As shown in Figure 4, there are three categories of families recorded in this survey. i) Category A: Three and less species with about 18 family, ii) Category B: Between four and eight families with seven records, and iii) Category C: More than nine species with four records that are Asteracaeae, Brassicaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Fabaceae descendingly (Figure 4).
Vegetation strata
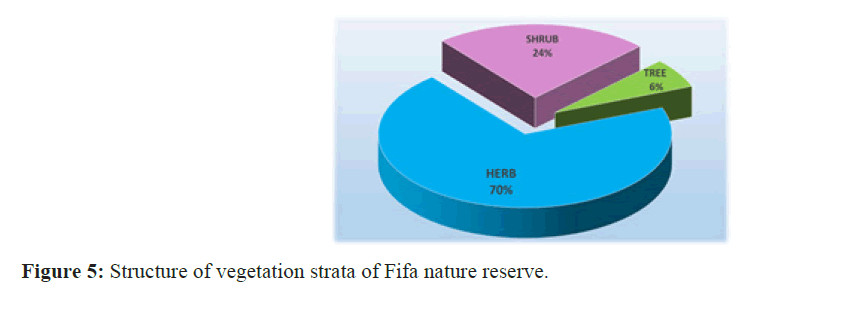
The current survey confirmed the diversity pattern of vegetation cover in Fifa nature reserve, including three strata that are trees, shrubs, and herbaceous of both annuals and perennials (Figure 5). Its worthy to mention that every stratum includes number of species of high conservation status as found in Table 1 above.
Medicinal uses of plants
In this survey, 17 plant species belonging to 14 families have been used to treat different diseases in the South Ghor area (including Safi and Fifa). It can be notice that just four species that used for medicinal uses by local communities are plants from sub-tropical region species and found in the nature, whereas the other 13 plants are introduced either from other parts of Jordan or outside the country and both of them are cultivated unfortunately.
The results of plant medicinal uses showed sharp decline in local knowledge and use of natural species in Traditional medicine. Nevertheless, this social heritage of plant uses still essential source of medicinal knowledge nowadays [11-14].
Description of vegetation cover
The number of recorded plants in the current survey is higher than all previous prepared lists that mentioned before. Recording distinctive number of plants in habitat of harsh environmental conditions mainly corroborates the importance of vegetation cover as essential pillar in ecological issue of the reserve. Furthermore, one of the most important outcomes of this survey that 13% of recorded plants are of important status at the regional level especially from woody species (This value comprises percentage of 14 out of 105 species that are evaluated). Such ecological features of Fifa nature reserve confirmed its value as shelter of different floral and faunal species of global and national importance, as well as, its unique importance as lowest reserve on Earth and lowest Ramsar site. RSCN (2014b) reported that Fifa Nature Reserve holds the largest population of Nubian Nightjar (Caprimulgus nubicus) in Jordan and in the region, as well Dead Sea Sparrow (Passer moabiticus) population has healthy representative in Fifa area, since appropriate habitats of Tamarisk (Tamarix spp.) are existed.
From other hand, obvious variation of vegetation layers at Fifa nature reserve is represented obviously. Figure 5 shows structure of vegetation strata, where herbaceous layer is dominating either with annuals or perennials species with 85 species, whereas shrubs were 29 plant and 8 trees. It is noticeable that major of shrub and tree strata are of halophytes such as Nitraria retusa, Juncus rigidus and Alhagi graecorum shrubs and Ziziphus spina-christi and Tamarix spp. trees. Also, number of these plants are of important conservation status as Salvadora persica as a tree, Calligonum comosum as a shrub, and Anthemis zoharyana as an herb. Meanwhile, Fifa nature Reserve encompasses 29 plant families that all recorded species belong to, or about 55% of these plants are belonging to 25 families otherwise. This distinctive structure of vegetation cover can provide wide variation of suitable habitats for different faunal species especially birds. Fifa-Safi Important Bird Area (IBA) is one of the 391 sites identified for their importance for birds in the Middle East, where it has been previously identified as Important Bird Area because it is an important stop over site for migratory birds.
Its worthy to mention that vegetation community map in Fifa nature reserve didn’t change mainly through last years, since last vegetation communities map of the reserve was prepared in late of 2014 as shown in Annex 3.
Plant uses
This survey must ring the alarm of loss Jordanian knowledge about uses of natural plants in medicine. Many plants are widely used by local communities, since many of which are a source of robust medicine against several chronic diseases. Many reports have mentioned the traditional use of medicinal plants as an effective therapy against many ailments worldwide [15].
Conclusion
The results concluded that the local knowledge about plant species used in folk medicine in the southern Jordan valley area is lost gradually. During the study, 17 plant species with medical use were registered through 90 questionnaires that were filled from the population in the region, which shows a sharp decline in the use of this type of medicine especially in young people. Nevertheless, it can be concluded that plants of Fifa nature reserve are held great promise to be a source of different medicines, where it is hoped that ethno-medicinal studies (ethnobotany) will be implemented on medicinal plants in the area through academia and specialized medical centers.
References
- Al-Eisawi D (1996) Vegetation of Jordan. UNESCO-Regional office for science and technology for the Arab States, Cairo, Egypt.
- MoE (Ministry of Environment) (2014) The fifth national report on the implementation of the convention on biological diversity. Amman-Jordan.
- MoE (Ministry of Environment) (2015) The National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP). Amman-Jordan.
- McArthur E, Fairbanks D, Daniel J (2013) Shrubland ecosystem genetics and biodiversity: Proceedings. Provo (13): 13-15.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Al-Eisawi D (2013) Flora of Jordan checklist-revised edition. The University of Jordan Press, Amman, Jordan.
- Evans MI (1994) Important bird areas in the Middle East. Birdlife conservation series No. 2. Birdlife International. Cambridge, UK.
- IUCN (International Union for the Conservation of Nature) (2012). IUCN red list of threatened species. http://www.iucnredlist.org
- RSCN (Royal Society for Conservation of Nature) (2014a) The spiny-tailed Lizard’s (Uromastyx aegiptia) Baseline Survey. Unpublished report.
- IUCN (International Union for the Conservation of Nature) (2014) IUCN red list of threatened species. http://www.iucnredlist.org
- RBG (Royal Botanical Garden) (2014 and 2017) Jordan plant red list. Vol. 1 and 2. Amman-Jordan.
- Ghazanfar SA, Altundag E, Yaprak AE, Osborne J, Tug GN, et al. (2014) Halophytes of Southwest Asia. Sabkha Ecosystems 5: 105-133.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Khan MA, Boer B, Ozturk M, Al Abdessalaam TZ, Clusener-Godt M, et al. (2014) Sabkha ecosystems: Volume IV: Cash crop halophyte and biodiversity conservation. Sabkha Ecosystems (14): E1.
- NCARTT (National Center for Agricultural Research and Technology Transfer) (2007) The second country report on the state of the plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. Amman- Jordan.
- Siddiqui S, Bhardwaj S, Khan SS, Meghvanshi MK (2009) Allelopathic effect of different concentration of water extract of (prosopsis juliflora) leaf on seed germination and radicle length of wheat (triticum aestivum var-lok-1). AEJSR 4: 81-84.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Hammiche V, Maiza K (2006) Traditional medicine in Central Sahara: Pharmacopoeia of Tassili N’ajjer. J Ethnopharmacol 105: 358–367.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]

Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences