Five Years Survival of Children with Leukemia in Basra Oncology Center
Ismael AI and Hassan JG*
Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, University of Basra, Iraq
- *Corresponding Author:
- Prof Janan G Hasan
Pediatrician Oncologist, Member of Royal College
Faculty Member of Washington University
Head Of Basra Pediatric Oncology Center
Basra Pediatric Specialty Teaching Hospital
Basra University, Medical College,Iraq
Tel: +964(0)7801000820
E-mail: jenan_ah03@yahoo.com
Received Date: January 26, 2017; Accepted Date: February 01, 2017; Published Date: February 15, 2017
Citation: Ismael AI, Hassan JG. Five Years Survival of Children with Leukemia in Basra Oncology Center. Cancer Biol Ther Oncol.2017, 1:1.
Abstract
Stem cell; Leukemia; Chemotherapy; Pediatric oncology; Bone marrow; Chromosome
Keywords
Stem cell; Leukemia; Chemotherapy; Pediatric oncology; Bone marrow; Chromosome
Introduction
Leukemia is the most common type of childhood cancer, accounting for more than 3000 new cases annually and 25% of all malignancies diagnosed in patients younger than 20 years in the United States. Subtypes and prevalence include acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) among 75% of cases; acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) in 20%, and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), less than 5%. Other types of chronic leukemia, including those of lymphocytic and myelomonocytic cell lineages, are extremely rare in childhood [1].
Statistics have shown that leukemia is one of the most common malignancies in Jordan, Lebanon, Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Libya, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, and the UAE. In most of these countries, leukemia is also the major form of pediatric cancer [2].
Leukemia is the most common childhood malignancy in Basra. Childhood leukemia rates in Basra were more than doubled over a 15-year period, Basra’s childhood leukemia survival rates compared unfavorably with Kuwait and Oman, as well as the United States, the European Union, and other countries [3].
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common pediatric malignancy, comprising 25% of cancers occurring before age 15 years and 19% among those younger than age 20 years. The 5-year survival rate increased from 83.7% in 1990-1994 to 90.4% in 2000-20005 [4]. Female to male ratio is 1:1.2, Peak incidence 2–5 years. Incidence in white children is twice as high as in nonwhite children [1].
Pediatric Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a heterogeneous class of leukemias that arise within the bone marrow precursors [5]. (AML) is relatively rare in children, accounting for 15-20% of pediatric leukemias, but causes a disproportionate number of childhood cancer deaths. For children less than 15 years of age overall survival rates are now approximately 60-70% [6].
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder of the primitive hematopoietic stem cell and is characterized by the presence of the Philadelphia chromosome.
This abnormal chromosome results from reciprocal translocation involving the long arms of chromosome 9 and 22 [7].
(CML) accounts for less than 5% of all childhood leukemias. It is slightly more common in males than in females. The incidence of (CML) is about 1–1.5 per 100,000 persons per year. There appears to be no association with social class or ethnicity, and its incidence appears to be remarkably constant worldwide [8].
Leukemia survival
Pediatric leukemia survival rates have improved dramatically over the past decades. However, current treatment protocols are still largely ineffective in cases of relapsed leukemia and are associated with a significant rate of chronic health conditions. There is a continued need for new therapeutic options [9,10].
Factors affect the survival
For All leukemia type in general a large population-based and long term study of pediatric leukemia survival, boys continued to show poorer survival. These disparities were not completely explained by treatment received, tumor prognostic or sociodemographic factors [10].
Some studies revealed a relation between residence of the patient with cancer in general and leukemia in particular and the survival rate [11,12], higher rate of 5-year survival was found among children with leukemia in major cities compared with children living in inner regional and outer regional localities was found in a study in Australia [13].
ALL survival
Survival prognostic factor is the choice of appropriate riskdirected therapy, with the type of treatment chosen according to the subtype of (ALL), the initial white blood count, the age of the patient, and the rate of response to initial therapy. One of the generally believed to adversely affect outcome include age <1 year or >10 years at diagnosis [14].
Survival is related to age, the choice of treatment of (ALL) is based on the estimated clinical risk of relapse in the patient, which varies widely among the subtypes of (ALL). One of the most important predictive factors is the age of the patient at the time of diagnosis the age at tumor diagnosis was a single most potent prognostic factor of childhood leukemia survival, with infants experiencing the poorest survival. This significant variability persisted after adjustment for the effect of other covariates. Therefore, there is a need to identify other prognostic factors that are associated with age in order to provide a meaningful explanation of the impact of age on pediatric leukemia survival [15].
Chromosomal abnormalities, including hypodiploidy, the Philadelphia chromosome, and gene rearrangements, and certain mutations, portend a poorer outcome in (ALL). More-favorable characteristics include a rapid response to therapy, hyperdiploidy, trisomy of specific chromosomes, and rearrangements of the TEL/AML1 genes [16].
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) SEER Program reported that 5-year survival for US patients younger than age 15 years with (ALL) increased from 80.2% to 87.5% between 1990-1994 and 2000- 2004. Five-year survival rates for adolescents age 15 to 19 years increased from 41.0% in 1980-1984 to 61.1% in 2000-2004 [17].
AML survival
The prognosis of children who have (AML) has improved greatly during the past 3 decades. Rates of complete remission (CR) in (AML) are as high as 80% to 90% and overall survival (OS) rates of 60% now are reported. This success reflects the use of increasingly intensive induction chemotherapy followed by post remission treatment with additional anthracyclines and highdose cytarabine or myeloablative regimens followed by stem cell transplantation (SCT) [18].
About 90% of children with (AML) achieve remission with one or two courses of intensive combination chemotherapy. Usually a total of four blocks of treatment are required. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is reserved for those children in whom response to chemotherapy is slow. The disease free survival is now in the region of 60% [19].
CML survival
In chronic phase (90%) patients sometimes enjoyed unimpaired lifestyles for periods of many months to years, with minimal therapy during the chronic phase of their disease. However, if untreated, most patients will experience progressive disease from 3 to 8 years after diagnosis. Overall, blast crisis will develop in 75% to 85% of all untreated patients with (CML). Blast crisis is a clinically high- risk form of (CML) that is difficult to control with chemotherapy and often leads to death within a short time, usually months [20].
Factors with prognostic significance in (CML) are age (less than 1 year old) have a higher chance of survival, low platelet count (less than 100×109/l or less), increased hemoglobin F (more than 10–15%) and more than 4% of blasts in peripheral blood as well as more than 5% in bone marrow appear to be associated with a poor prognosis [21,22].
Two-year survival rates improved from 53% in the first time period to 61% in the most recent because of reduced transplant related mortality. Relapse rates ranged from 14% to 22% [16].
The study aims to:
1. Analyze the outcome of the patient with leukemia in relation to factors like (sex, age, residence, risk group) and the effect of these factors on the patient survival rate.
2. Estimate the overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) rates to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
3. Study the five years survival rate in relation to the years of diagnosis.
Patients and Methods
A retrospective study was carried out on children less than or equal to 15 years of age who had suffered leukemia and have been admitted and diagnosed at Basra Maternity and Children hospital in pediatric oncology unit, the study inclusion criteria:
• Any patient registered at oncology unit less or equal to 15 years with leukemia (ALL, AML, CML).
• Time of admission from first of January of 2004 till end of December 2008.
• Received and completed the induction chemotherapy.
Leukemia cases were 258 patients their ages was less than 15 years, two hundred forty eight patients were included in the study male cases were 143 cases while 105 female. 205 with ALL, 32 with AML and 11 with CML. Ten patients were excluded, 6 because of lack of adequate information (because the family refused treatment or patient referred to other center or outside the country) and 4 died before starting therapy.
Study variables
Age at diagnosis: The age at diagnosis of patients was calculated from the date of birth till date of admission and extracted data from all patients 0 to 15 years of age at the time of diagnosis. Age groups was divided into 4 groups, namely: (a) <1 year, (b) 1–5, (c) >5–10, (d) >10 years. These age categories represent pediatric malignancies groupings used in most studies [10,15].
Year of diagnosis: This study takes data collected from the hospital registries for 5 years (2004-2008). Every year for which leukemia was diagnosed was accounted as well as mortality status of the patients. To provide some insight into the survival of these patients by group of years of diagnosis, a five-year interval categories was started from the year of diagnosis (2004– 2009, 2005–2010, 2006–2011, 2007–2012, 2008–2013). These categories simulate the five-year survival periods commonly used in assessing the clinical benefits of cancer therapeutics [10].
From 2004 to 2006 patients were treated according to UKALL 2003 protocol, but since 2007 the BFM (Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster) protocol was added to treatment with UKALL 2003 protocol.
Risk group: Patients with (ALL) were classified to standard risk group (those with age group more than 1 year and less than 10 years and an initial white blood cell counts less than 50000), while high risk group (those less than 1 year and more than 10 years and more than 50000 white cells.
The definition of central nervous leukemia (CNS) involvement was based on the presence of at least five white blood cells per micro liter of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with leukemia cells on cytocentrifuged smear, or the presence of cranial nerve palsies, or the detection of intracranial infiltrate in cranial tomography or magnetic resonance image [14].
Residence: The patients’ residence was assessed into four governorates Basra, Maysan, Thi-qar and Others, Basra was divided according to a design by Habib OS et al. [22] into 5 major areas: Basra center, northern area (Qurna, Medina, Hartha), western area (Al-Zubair district), eastern area (Shatt Alarab and Alshlamja), and southern area (Abu Alkhaseeb and Fao).
Five year outcome and survival: Relapse or death, were considered to be the end point of an event. Overall survival (OS) defined as the number of all patients included in the study from the date of diagnosis until the date of death. Event-free survival (EFS) was defined as time in first complete remission, until death or relapse [23].
Status of patients after 5 years from starting date of therapy was reviewed: if the patient is still alive this includes (ended treatment with complete remission or relapse), noncompliance or death.
Complete remission of leukemia patients is defined as the absence of leukemic blast cells in CSF or blood and 5% or fewer lymphoblast in marrow aspirate for at least 30 days; evidence of regeneration of normal marrow cells and absence of symptoms and signs of central nervous system, bone marrow and other sites (testes, ovaries, etc.) leukemia.
Relapse is defined as recurrence of more than 5% lymphoblast or localized leukemic infiltrate at any sites, central nervous system (CNS) leukemia relapse was diagnosed on the basis of cranial nerve palsies or the leukemic blast cells in Wright-stained centrifuged cerebrospinal fluid samples, (B.M) leukemia relapse diagnosed by bone marrow aspiration and (other sites) leukemia relapse was diagnosed by biopsy [10,18], time of relapse (within the 1st, 2nd till 5th year) also included.
Noncompliance defined as any patient with abandonment of treatment for more than 1 year. The time of death within the (1st, 2nd till 5th year) and causes of death were also included in this forma like infection (sepsis, pneumonia), bleeding (ICB or GIT bleeding) and other causes.
Methods
The 5-year survival rate (Overall survival and Event-free survival) was estimated in correlation with each variable alone to find the effect of each variable on the survival rate. Survival can be expressed in terms of the percentage of those cases alive at the starting date that were still alive after a specified interval. The choice of interval is arbitrary (in this study it was 5years interval.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was done using The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS), version 18.0, (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, U.S.A), data were expressed and comparisons of proportions was performed by crosstab using Chi-Square test to examine the association between the study variables and the outcome of the patients with leukemia [23]. Kaplan-Meier method was used to determine the overall and event free survival rate according to the year of diagnosis. For all tests p-value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
A five hundred seventy eight patients aged less than or equal to15 years were diagnosed with malignancy admitted to Basra pediatric oncology unite from first of January of 2004 till end of December 2008, leukemia cases were258 (44.6%) of all malignancy cases.
Distribution of patients with Leukemia according to their sex and age
A total of 248 patients with leukemia were included in the study, male cases of leukemia more than female, age groups (1-5) years shows the highest frequency of leukemia distributions among all age groups in this study followed by (>5-10) years age group. There is statistically significant differences (p<0.05) concerning the age and the female distribution while there is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) concerning the age and the male distribution in type of leukemia (Table 1).
Table 1 Distribution of patients with Leukemia according to their sex and age.
| Age in Years | Sex | p-value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | p-value | Female | ||||||||
| DX | DX | |||||||||
| ALL | AML | CML | Total | ALL | AML | CML | Total | |||
| No. % | No. % | No. % | No. % | No. % | No. % | No. % | No. % | |||
| <1 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0.426 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.009 |
| 100% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100% | 75% | 0.00% | 25% | 100% | |||
| 01-May | 52 | 5 | 5 | 62 | 44 | 4 | 0 | 48 | ||
| 83.80% | 8.10% | 8.10% | 100% | 91.70% | 8.30% | 0.00% | 100% | |||
| >5-10 | 45 | 4 | 0 | 49 | 27 | 12 | 2 | 41 | ||
| 91.80% | 8.20% | 0.00% | 100% | 65.90% | 29.20% | 4.90% | 100% | |||
| >10 | 20 | 3 | 2 | 25 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 12 | ||
| 80.00% | 12.00% | 8.00% | 100% | 58.30% | 33.40% | 8.30% | 100% | |||
| Total % | 124 | 12 | 7 | 143 | 81 | 20 | 4 | 105 | ||
| 50% | 4.90% | 2.80% | 57.70% | 32.70% | 8% | 1.60% | 42.30% | |||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to the type of leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) represent the highest percentage of leukemia types and had the highest percentage of patient who had 5-year overall survival (45.4%) and event-free survival (39.5%), lowest percentage of death (30.2%) followed by (AML), the relapse percentage was also lowest in (ALL) followed by (CML) while the noncompliance is highest in (AML) followed by (ALL). There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) (Table 2).
Table 2 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to the type of leukemia.
| Diagnosis | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Non- compliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| ALL | No. | 81 | 12 | 93 | 62 | 50 | 205 | 0.118 |
| % of DX | 39.50% | 5.90% | 45.40% | 30.40% | 24.80% | 100.00% | ||
| % of Total | 32.70% | 4.80% | 37.50% | 25.00% | 20.20% | 82.70% | ||
| AML | No. | 7 | 3 | 10 | 14 | 8 | 32 | |
| % of DX | 21.90% | 9.40% | 31.2 | 43.80% | 25.70% | 100.00% | ||
| % of Total | 2.80% | 1.20% | 4.10% | 5.60% | 3.20% | 12.90% | ||
| CML | No. | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 11 | |
| % of DX | 9.10% | 9.10% | 18.20% | 63.60% | 18.20% | 100.00% | ||
| % of Total | 0.40% | 0.40% | 0.80% | 2.80% | 0.80% | 4.40% | ||
| Total | No. | 89 | 16 | 105 | 83 | 60 | 248 | |
| % Total | 35.90% | 6.50% | 42.40% | 33.40% | 24.80% | 100.00% | ||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their ages
The table shows that age group (1-5) years had the highest percentage event-free survival (38.2%) and lowest death percentage (28.2%) followed by age group (>5-10) years which had also lowest noncompliance and the age group (<1) year had the highest percentage of death but no relapse in this age group, the relapse percentage is highest in age group (>10) years among all other age groups. There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) concerning the age and the outcome of the patients in this study (Table 3).
Table 3 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their ages.
| Age in years | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Noncompliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| <1 | No. | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 11 | 0.803 |
| % | 27.30% | 0.00% | 27.30% | 45.40% | 27.30% | 100% | ||
| 01-May | No. | 42 | 7 | 49 | 31 | 30 | 110 | |
| % | 38.20% | 6.40% | 44.60% | 28.20% | 27.20% | 100% | ||
| >5-10 | No. | 34 | 6 | 40 | 32 | 18 | 90 | |
| % | 37.70% | 6.70% | 44.40% | 35.60% | 20.00% | 100% | ||
| >10 | No. | 10 | 3 | 13 | 15 | 9 | 37 | |
| % | 27.00% | 8.10% | 35.1% | 40.50% | 24.30% | 100% | ||
| Total | No. | 89 | 16 | 105 | 83 | 60 | 248 | |
| % | 35.90% | 6.50% | 42.40% | 33.50% | 24.10% | 100% | ||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their sex
Male gender had a higher percentage of patients who had 5-year overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) than female while females had higher noncompliance percentage. There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) (Table 4).
Table 4 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their sex.
| Sex | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Noncompliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| Male | No. | 54 | 9 | 63 | 48 | 32 | 143 | 0.848 |
| % | 37.80% | 6.30% | 44.10% | 33.60% | 22.30% | 100% | ||
| Female | No. | 35 | 7 | 42 | 35 | 28 | 105 | |
| % | 33.30% | 6.70% | 40% | 33.30% | 26.70% | 100% | ||
| Total | No. | 89 | 16 | 105 | 83 | 60 | 248 | |
| % | 35.90% | 6.50% | 42.40% | 33.50% | 24.10% | 100% | ||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients with Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) according to the risk group
The previous table shows that the patients with standard risk ALL is less than patients with high risk and have higher percentage of 5-year overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) and relapse patients but less percentage of death and noncompliance than high risk group. The difference was significant (p<0.05) (Table 5).
Table 5 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) according to the risk group.
| Risk Group | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Noncompliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| Standard risk | No. | 41 | 8 | 49 | 23 | 15 | 87 | 0.029 |
| % | 47.20% | 9.20% | 56.50% | 26.40% | 17.20% | 100% | ||
| High risk | No. | 40 | 4 | 44 | 39 | 35 | 118 | |
| % | 33.90% | 3.40% | 37.70% | 33% | 29.70% | 100% | ||
| Total | No. | 81 | 12 | 93 | 62 | 50 | 205 | |
| % | 39.50% | 5.90% | 45.40% | 30.20% | 24.40% | 100% | ||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their residence
The highest number of patient registered were from Basra followed by Maysan and Dhi Qar, the percentage of patients who had 5-year overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) were highest in other governorates followed by Basra the highest percentage of death in Dhi Qar and lowest in other governorates, relapse percentage is higher in Maysan with highest percentage of noncompliance followed by other governorates. There is statistically significant differences (p<0.05) concerning the residence and the outcome of the patients (Table 6).
Table 6 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their residence.
| Residence | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Noncompliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| Basra | No. | 63 | 10 | 73 | 52 | 29 | 154 | 0.045 |
| % | 40.90% | 6.50% | 47.40% | 33.80% | 18.80% | 100% | ||
| Maysan | No. | 8 | 3 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 38 | |
| % | 21.10% | 7.90% | 28% | 31.50% | 39.60% | 100% | ||
| Thi-qar | No. | 9 | 2 | 11 | 17 | 9 | 37 | |
| % | 24.30% | 5.40% | 29.70% | 45.90% | 24.40% | 100% | ||
| Others | No. | 9 | 1 | 10 | 2 | 7 | 19 | |
| % | 47.40% | 5.30% | 52.80% | 10.50% | 36.80% | 100% | ||
| Total | No. | 89 | 16 | 105 | 83 | 60 | 248 | |
| % | 35.90% | 6.50% | 42.40% | 33.50% | 24.10% | 100% | ||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their Residence in Basra
This table shows that largest number of patients residence in center then north and west areas, the south and east areas had the least patients number, higher percentage of relapse in south area but it had higher percentage of 5-year overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) cases then the western area of Basra, eastern area had no relapse cases but it had highest percentage of noncompliance. There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) concerning the residence in Basra and the outcome of the patients (Table 7).
Table 7 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to their residence in Basra.
| Basra | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Noncompliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| Center | No. | 22 | 4 | 26 | 20 | 8 | 54 | 0.879 |
| % | 40.70% | 7.40% | 47.10% | 37.10% | 14.80% | 100% | ||
| North | No. | 21 | 3 | 24 | 18 | 11 | 53 | |
| % | 39.60% | 5.70% | 45.30% | 34.00% | 20.70% | 100% | ||
| South | No. | 6 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 12 | |
| % | 50.00% | 16.50% | 66.50% | 25.00% | 16.50% | 100% | ||
| East | No. | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | |
| % | 28.50% | 0.00% | 28.50% | 43% | 28.50% | 100% | ||
| West | No. | 12 | 1 | 13 | 8 | 6 | 27 | |
| % | 44.40% | 3.70% | 48.10% | 29.60% | 22.30% | 100% | ||
| Total | No. | 63 | 10 | 73 | 52 | 29 | 154 | |
| % | 41.00% | 6.40% | 47.40% | 33.70% | 18.90% | 100% | ||
The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to the year of diagnosis
The table showed percentage of patients who had 5-year overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) had get increasing percentage and decreasing death percentage at 2007 and 2008, the relapse still approximately within its range slightly decrease in 2008 than in 2004. There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) concerning the yearof diagnosis and the outcome of the patients (Table 8).
Table 8 The 5-year outcome and survival of patients according to the year of diagnosis.
| Year | 5-year outcome | Total | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | Died | Noncompliance | ||||||
| EFS | Relapse | Total | ||||||
| 2004 | No. | 7 | 3 | 10 | 12 | 9 | 31 | 0.782 |
| % | 22.60% | 9.70% | 32.30% | 38.70% | 29.00% | 100% | ||
| 2005 | No. | 16 | 2 | 18 | 19 | 8 | 45 | |
| % | 35.60% | 4.40% | 40% | 42.20% | 17.80% | 100% | ||
| 2006 | No. | 23 | 4 | 27 | 22 | 21 | 70 | |
| % | 32.90% | 5.70% | 37.60% | 31.40% | 30.00% | 100% | ||
| 2007 | No. | 22 | 4 | 26 | 16 | 11 | 53 | |
| % | 41.50% | 7.50% | 49% | 30.20% | 20.80% | 100% | ||
| 2008 | No. | 21 | 3 | 24 | 14 | 11 | 49 | |
| % | 42.90% | 6.10% | 49% | 28.60% | 22.40% | 100% | ||
| Total | No. | 89 | 16 | 105 | 83 | 60 | 248 | |
| % | 35.90% | 6.50% | 42.40% | 33.50% | 24.10% | 100% | ||
5-year overall survival and event free survival (EFS) analyses according to year of diagnosis
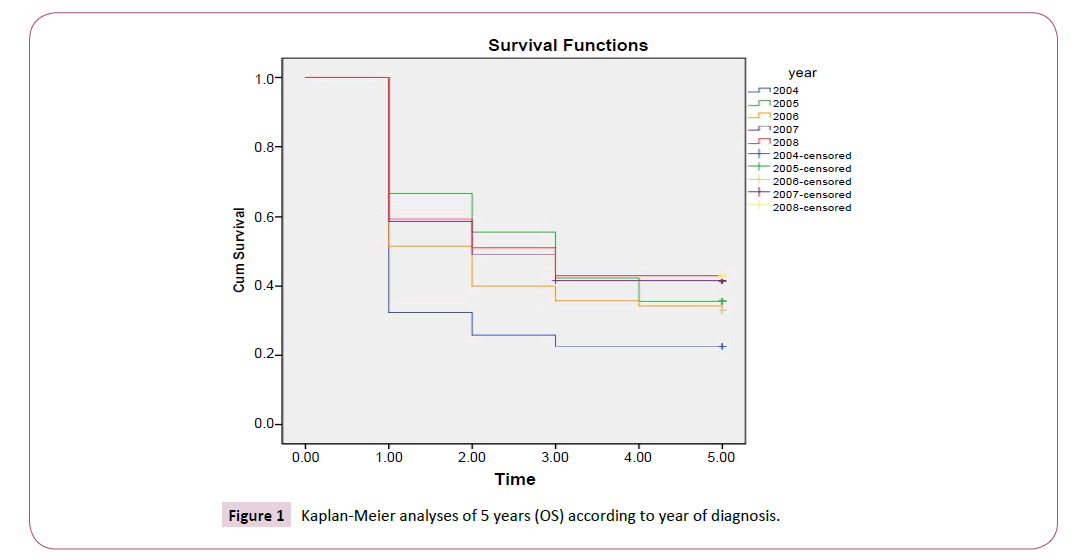
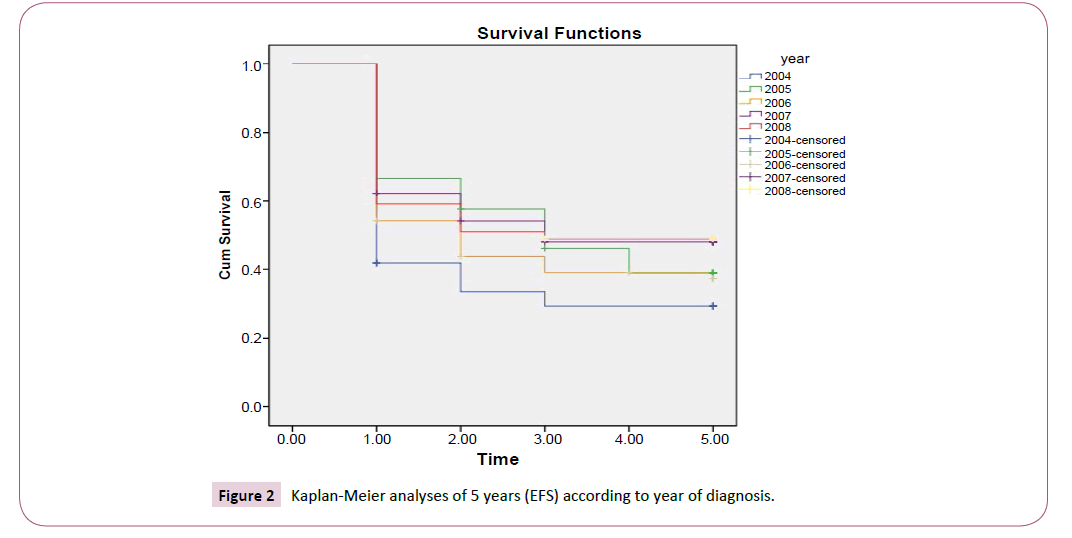
The overall survival and event-free survival were analyzed by Kaplan-Meier according to the year of diagnoses (Figure 1) and (Figure 2).
The previous figures showed that the results demonstrate steady improvement in clinical outcome over the last 2 years (2007, 2008) of the study, figures also demonstrated a sharp slope at the 1st year time period of treatment in (2004, 2005, 2006, 2007 and 2008) because of high number (death or noncompliance patients) The difference in event-free and overall survival rates has narrowed between (2005-2006) and (2007-2008) suggesting that relapses that occur after contemporary therapy are more refractory to treatment.
Time and site of relapse for patients with leukemia
Table show that the most common site of relapse is the BM (80%) of relapsed cases and the 1st year is the commonest period of relapse occurrence (50%), followed by the 3rd (22.5%) and the 2nd year (20%) of relapses. There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) concerning the Time and site of relapse for patients with leukemia (Table 9).
Table 9 Time and site of relapse for patients with leukemia.
| Site of Relapse | Time of Relapse | Total | p-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st year | 2nd year | 3rd year | 4th year | ||||
| B.M | No. | 16 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 32 | 0.616 |
| % | 50.00% | 18.80% | 25.00% | 6.20% | 80.00% | ||
| CNS | No. | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 | |
| % | 60.00% | 20.00% | 20.00% | 0.00% | 12.50% | ||
| Others | No. | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | |
| % | 33.30% | 33.30% | 0.00% | 33.30% | 7.50% | ||
| Total | No. | 20 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 40 | |
| % | 50.00% | 20.00% | 22.50% | 7.50% | 100% | ||
The cause and time of death in patients with leukemia
Causes of death in patients with leukemia (ALL, AML and CML) in the study and the time of their occurrence (within 1st, 2nd, till 5th year) are reported in Tables 3-10.
Table 10 The cause and time of death in patients with leukemia.
| Cause of death | Time | Total % |
p-value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st year | 2nd year | 3rd year | 4th year | 5th year | ||||||
| Bleeding | ICB | No. | 17 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 31 37.3% | 0.561 |
| % | 73.90% | 13.00% | 13.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 27.70% | ||||
| GIT | No. | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |||
| % | 50.00% | 50.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.40% | ||||
| DIC | No. | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | |||
| % | 50.00% | 33.30% | 16.70% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 7.20% | ||||
| Infection | Sepsis | No. | 6 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 19 | 30 36.2% | |
| % | 31.60% | 31.60% | 31.60% | 5.30% | 0.00% | 22.90% | ||||
| Pneumonia | No. | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 11 | |||
| % | 54.50% | 36.40% | 9.10% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 13.30% | ||||
| Relapse | No. | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | |||
| % | 62.50% | 25.00% | 12.50% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 9.60% | ||||
| Others | No. | 7 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 14 | |||
| % | 50.00% | 21.40% | 7.10% | 14.30% | 7.10% | 16.90% | ||||
| Total | No. | 45 | 21 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 83 | |||
| % | 54.20% | 25.30% | 15.70% | 3.60% | 1.20% | 100% | ||||
The highest death cases occurred during the 1st year of diagnosis followed by the 2nd and 3rd years. The most common cause of death is bleeding especially (ICB) 27.7%, followed by infection mostly (sepsis) 22.9% then other causes. There is no statistically significant differences (p>0.05) concerning the cause and time of death in the patients with leukemia (Table 10).
Discussion
In the Arabic Gulf region, leukemia is the second most common cancer. Between January 1998 and December 2004 there were 4,890 cases of leukemia accounted to 8.4% from all cancers. Leukemia incidence appeared to be slightly higher in males than females. Lymphoid leukemia was more common in males while myeloid leukemia was more common in females [24].
In Iraq leukemia and lymphoma are the most common pediatric tumor, the estimated EFS for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) was low compared with the international standard rate; however, abandonment of treatment was one of the important factors against improving the survival rate [25].
In this study the males with leukemia (57.6%) more than females (42.8%) and the male to female ratio was 1.36:1, the age group (1-5) years was the highest frequency of all other age a result which is comparable to that reported by Khoja T et al. (the male to female ratio was 1.3:1) [24], and study done by Holmes et al. [10] on groups of children diagnosed with leukemia (56.7%) were boys and (43.3%) were girls.
There was no difference in age distribution in male while there was difference in age distribution in female. In some studies there was no difference in age and sex distribution [10,15,26], while there was difference in age and sex distribution in other study [27].
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia comprised (82.7%) of all leukemia the survival rate was (39.5%) with high death and noncompliance percentage this agree with a study in Baghdad [25] found that the estimated event-free survival for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) was low compared with the international standard rate; however, abandonment of treatment was one of the important factors against improving the survival rate, while Mostert et al. [28] found that the survival rate of childhood (ALL) as high as 80% in developed countries but frequently is <35% in developing nations. This difference is believed to be attributable primarily to refusal or abandonment of treatment, both of which are almost unknown in developed countries.
Acute myeloid leukemia(AML) in this study comprised (12.9%) among other leukemias, survival is (21.9%). In Iraq still the overall survival for (AML) is below the standard owing to high percentage of relapses [25], during the subsequent therapies (AML) comprises only 15% to 20% of acute leukemia but accounts for a disproportionate 30% of deaths from these cases [29], Kaspres et al. [30] mention that AML survival currently achieved in more than 60% of children with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The most frequent type of treatment failure is relapse, occurring in 30% to 40% of patients. Chronic myeloid leukemia accounts for (4.4%) and this was approximately as the percentage in a study done by Millot et al. [31] who mention that chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a very rare disease in children, accounting for 2% to 3% of leukemias in children and adolescents , and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in other study it is less than 5% [1], Comparing the last years, the 5-year relative survival improved [32], there was no significant difference concerning the type of leukemia in this study, other studies showed that there is significant difference between type of leukemia with outcome [25,33,34], and this may be due to small sample size in this study with high percentage of noncompliance.
The study found that there was no statistically significant difference concerning the age and the outcome of the patients, a study Haiqing et al. [35] showed that age group (1-4) years had better outcome than other age groups and there was statistically significant difference concerning the age and the outcome of the patients this agree with other studies [33,34], and this may be due to high mortality rate in the current study in comparison to other studies.
Males had better outcome than female there was no significant difference concerning the sex and the outcome of the patients however the male had poor outcome in all age groups in other studies and there was statistically significant difference concerning the sex and the outcome of the patients [10,15], and this is may be due to high percentage of noncompliance in female patients
Number of patients with high risk group (ALL) is more than the standard risk group and there was statistically significant difference in the outcome, studies the high risk 24.4% less than the standard risk ALL 75.8% [36,37], and there was statistically significant difference in the risk group and outcome in patient in these studies and the standard risk had better outcome also.
The largest number of patient was from Basra (most of them at center and north area) more than other governorates and there was statistically significant difference between Basra and Maysan regarding the outcome of the patients this was similar to a study by Omran S Habib et al. [22], there was significant difference regarding the residence and the outcome of the patients, this is similar to a study in Iran [12] and Australia [13], and that may be due to the financial status of the patients family and distance between the hospital and their residence or exposure to carcinogenic agents in these areas.
Five years outcome of the patient became better for the last years and there was no statistically significant difference in year of diagnosis and the outcome of patients but there is statistically significant difference in these studies [27,34,35], and that may be due to short period of time in current study and long period of years covered by other studies.
The Kaplan-Meier analysis curves for (OS) and (EFS) demonstrate improvement in clinical outcome over the past years, the difference in event-free and overall survival rates has narrowed in the more recent periods and this results similar to a study which suggesting that relapses that occur after contemporary therapy are more refractory to treatment [38], but in this study there is sharp slop in the 1st year period due to shorter period of time and large number of death and noncompliance.
In this study the most common site of relapse is the B.M then the CNS and the 1st year is commonest period of relapse study by Arico et al. [27] who found: the bone marrow is the commonest site of relapse followed by CNS and other sites, a study by Dimov et al. [39] on APL patients found that of all patients with APL and the mean time of relapse within the 1st two years.
Most common death cases were due to (ICB) and sepsis and the majority occurred within the 1st year then the 2nd year after diagnosis and treatment starting, which agree with a study found that for most age groups of children, the risk of dying was greatest in the first year after diagnosis [40]. A study by Creutzig et al. [41] found that CNS bleeding then other causes (bleeding , organ failure) and infection common cause of early death.
Conclusion
In conclusions there was improvement in the 5 years overall (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) at last years of the study, but still there was high percentage of death and noncompliance so educational programs for families of patients with leukemia and psychosocial support by specialists to decrees the abandonment of the treatment and increasing survival rate.
References
- Green A, Rheingold SR(2011) Leukemia. In:Florin TA, Ludwig S, Netter FH (eds).Netter's Pediatrics (1st edn). pp: 338-344.
- TadmouriGO, Nair P (2012) Cancers in Arab populations: concise notes. Hamdan Medical J 5: 79-82.
- Hagopian A, Lafta R, Hassan J, Davis S, Mirick D, et al. (2010) Trends in childhood leukemia in Basrah, Iraq, 1993–2007. Am J Public Health 100:1081-6
- Hunger SP, Lu X, Devidas M, Camitta BM, Gaynon PS, et al. (2012) Improved survival for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia between 1990 and 2005. J ClinOncol 30:1663-1669
- Dores GM, Devesa SS, Curtis RE, Linet MS, Morton LM (2012) Acute leukemia incidence and patient survival among children and adults in the United States, 2001–2007. Blood119: 34–43.
- Creutzig U, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Gibson B, Dworzak MN, Adachi S, et al. (2012) Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in children and adolescents. Blood 120: 3187–3205.
- Bissett D, Cassidy J, Spence RAJ(2002) Etiology of cancer. Oxford handbook of oncology. Oxford University Press, Oxford. pp: 50-61.
- Tariq IM, John M,Sekeres MA, Kalaycio ME, Bolwell BJ (2007) Epidemiology, risk factors and classification of chronic myeloid leukemia.Clinical malignant hematology.McGraw-Hill, New York. pp:159-161.
- Brandao LN, Winges A, Christoph S, Sather S, Wilson JM, et al. (2013) Inhibition of MerTK increases chemosensitivity and decreases oncogenic potential in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer J 3:e101.
- Holmes L, Hossain J, Kendrick MD, Opara F (2012) Sex variability in pediatric leukemia survival: large cohort evidence. ISRN oncology439070:1-8.
- Jones KP, Kaatsch P, Foucher ES, Stiller CA, Coebergh JW(2006) Cancer in children and adolescents in Europe: Developments over 20 years and future challenges. Eur J Cancer 42:2183–90.
- Mousavi SM, Pourfeizi A, Dastgiri S(2010) Childhood cancer in Iran. J PediatrHematolOncol32:376-82.
- Youlden DR, Baade PD, Valery PC, Ward LJ, Green AC (2011) Differentials in survival for childhood cancer in Australia by remoteness of residence and area disadvantage.American Association for Cancer Research20:1649-56.
- David G, BleyerTA, Ritchey AK, Kliegman R, Nelson WE (2011) Theleukemias. Pediatrics (19thedn).Saunders, Philadelphia, USA. pp:1732-1736.
- Holmes L, Opara F, Des-Vignes-Kendrick M, Hossain J(2012) Age variance in the survival of United States pediatric leukemia patients (1973–2006). ISRN Public Health 2012:1-10.
- Arora M, Horowitz MM, CorteÃŒÂÂs FJ, Deininger M(2007) Chronic myeloid leukemia.Informa Healthcare, New York. pp:13-17.
- Pulte D, Gondos A, Brenner H (2009) Improvement in survival in younger patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from the 1980s to the early 21st century. Blood 113:1408-1411.
- Rubnitz JE, Gibson B, Smith FO (2010) Acute myeloid leukemia. HematolOncolClin North Am24:35-63.
- Halsey C, Chalmers EA (2012)Haematologicalinvestigations in children.In: Goel KM, Gupta DK (eds). Hutchison's Paediatrics (2nd edn). Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd, New Delhi. p.320.
- Clark JJ, Berman JN, Look AT (2009) Myeloidleukemia, myelodysplasia, and myeloproliferative disease in children. In:Orkin SH (ed). Oncology of infancy and childhood. Elsevier/Saunders, Philadelphia. pp:369-375.
- Kühne T(2011) Myeloproliferativesyndromes (chronic myeloproliferative disorders). In: Imbach P, Kühne T, Arceci RZ (eds). Pediatric oncology :A comprehensive guide (2nd edn). Springer, Heidelberg, New York. pp:51-53.
- Habib OS, Al-Ali JK, Hasan JG, AlrudainyLA ,Hasson HM, et al.(2007) Cancer registration in Basra 2005: Primarily result. Asian Pacific J Cancer prev8:189-190.
- Unal S, Cetin M,Tuncer AM, Gumruk F, Yetgin S (2008) The prognostic impact of myeloid antigen expression in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Turk JPediatr50: 533-536.
- Khoja T, Zahrani A (2010) Epidemiology of cancer in the Gulf region. Pan Arab Journal of Oncology 3:8-9.
- Al-Hadad SA, Al-Jadiry MF, Al-Darraji AF, Al-Saeed RM, Al-Badr SF, et al. (2011) Reality of pediatric cancer in Iraq. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 33: 154-6.
- Soheil Z, Amir AH, Mehran K, Esmaeil K (2012) Five-year survival rate of pediatric leukemia and its Determinants. Koomesh14: 13-19.
- Arico M, Schrappe M, Hunger SP, Carroll WL, Conter V, et al. (2010) Clinical outcome of children with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated between 1995 and 2005. J ClinOncol 28:4755-4761.
- Mostert S, Sitaresmi MN, Gundy CM, Sutaryo, Veerman AJ(2006) Influence of socioeconomic status on childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment in Indonesia. Pediatrics 118: 1600-6.
- Glavel J, Goubin A, Auclerc MF (2004) Incidence of childhood leukaemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in France: National Registry of Childhood Leukaemia and Lymphoma, 1990–1999. Eur J Cancer Prev13:97–103.
- Kaspers GJ, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, Gibson BE, Tamminga RY, et al. (2013) Improved outcome in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: results of a randomized trial on liposomal daunorubicin by the International BFM Study Group. J ClinOncol31:599-607.
- Millot F, Baruchel A, Guilhot J, Petit A, Leblanc T, et al. (2011)Imatinib is effective in children with previously untreated chronic myelogenous leukemia in early chronic phase: results of the French national phase IV trial. J ClinOncol29:2827-32.
- Corm S, Roche L, Micol JB, Coiteux V, Bossard N, et al. (2011) Changes in the dynamics of the excess mortality rate in chronic phase-chronic myeloid leukemia over 1990-2007: A population study. Blood 118:4331-4337.
- Sayed HA, El-Mahallawy HA, Kaddah AM, Ismael HT, Talaat SM(2009) Profile of infections in newly diagnosed patients with acute leukemia during the induction phase of treatment. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 21:315-22.
- Amir AH, Soheil Z, Mehran K, Esmaeil K, Abolfazl M(2013) Survival rate of childhood leukemia in shiraz, southern Iran. Iran JPediatr23:53-8.
- Ma H, Sun H, Sun X(2014) Survival improvement by decade of patients aged 0-14 years with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Rep4:4227.
- Laughton SJ, Ashton LJ, Kwan E, Norris MD, Haber M, et al. (2005) Early responses to chemotherapy of normal and malignant hematologic cells are prognostic in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J ClinOncol 23:2264-71.
- Abdallah Al-Nasser, Solh H, Vol ED, El-Hassan I, Al Sudairy R, et al. (2008) Improved outcome for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after risk-adjusted intensive therapy: a single-institution experience. Ann Saudi Med 28: 251-259.
- Pui CH, Evans WE(2006) Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 354:166–178.
- Dimov ND, Medeiros LJ, Ravandi F, Bueso-Ramos CE(2010) Acutepromyelocytic leukemia at time of relapse commonly demonstrates cytogenetic evidence of clonal evolution and variability in blast immunophenotypic features. Am J ClinPathol 133:484-90.
- Gatta G, Rossi S, Foschi R, Trama A, GrageraMR, et al. (2013) Survival and cure trends for European children, adolescents and young adults diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from 1982 to 2002. Haematologica98:744-52.
- Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, Dworzak M, Stary J (2004) Early deaths and treatment-related mortality in children undergoing therapy for acute myeloid leukemia: analysis of the multicenter clinical trials AML-BFM 93 and AML-BFM 98. J Clin Oncol 22: 384-93.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences