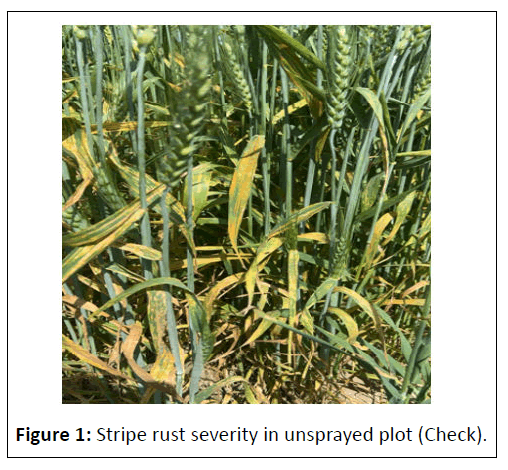
Field Evaluation of Systemic Fungicides against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici
Muskan Bhullar* and Seethiya Mahajan
Division of Plant Pathology, Guru Nanak Dev University, Punjab, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Muskan Bhullar
Division of Plant Pathology, Guru Nanak Dev University, Punjab,
India,
E-mail: Muskanbhullar18101010@khalsacollege.edu.in
Received date: April 24, 2024, Manuscript No. IPJPSAR-24-18972; Editor assigned date: April 27, 2024, PreQC No. IPJPSAR-24-18972 (PQ); Reviewed date: May 13, 2024, QC No. IPJPSAR-24-18972; Revised date: May 20, 2024, Manuscript No. IPJPSAR-24-18972 (R); Published date: May 27, 2024, DOI: 10.36648/ipjpsar.8.1.129
Citation: Bhullar M, Mahajan S (2024) Field Evaluation of Systemic Fungicides against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. J Plant Sci Agri Res Vol.8 No.1: 129.
Abstract
Wheat is a major staple food grown worldwide. India is the world's second-largest producer of wheat, after China. In terms of wheat output in India, Punjab is ranked second, after Uttar Pradesh. Many significant diseases limit wheat productivity, with stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) emerging as the most damaging and pervasive disease of wheat. It is referred to locally as "Peeli Kungi" (yellow) in Northern India. When host resistance is not available or has been overcome by the pathogen population, fungicide application is another option for stripe rust control. Until now, stripe rust on susceptible wheat cultivars is mainly controlled by fungicide applications. Thus, attempts have been made to screen various fungicides in field conditions for their relative efficacy against stripe rust. The experiment was laid out in a Randomized Block Design (RBD), with three replications and highly susceptible variety PBW 343 was tested. Five fungicides at dose rate 0.1% were evaluated during 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 cropping seasons, the least mean disease severity (0.17%) was recorded in two foliar sprays of Nativo 75 WG with mean disease control of 99.82% over the unsprayed check plot. It was followed by Custodia 320 SC, Fusion top, Tilt 25 EC and Opera 18.3 SE resulted in %MDS of 2.46, 3.85, 4.29 and 6.19 with 97.22, 95.64, 95.02 and 92.96 percent disease reduction over check.
Keywords
Wheat; Stripe rust; Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici; Fungicide; Mean disease severity; Management
Introduction
Bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is one of the most important cereal crops and consumed food crops in the world [1] and serving as a primary source of nutrition for millions of people, particularly in the northern and north-western parts of the country [2]. It offers a balanced diet, high in proteins, vitamins, and carbohydrates, and has chromosome number 2n=42 [3]. It is a domesticated and worldwide cultivated grass of Poaceae family, which is one of the most significant and diverse families of the kingdom plantae [4]. As the substantial increase in the population of the world demands a gradual increase in wheat production and covers one-sixth of the total arable land in the world is cultivated with wheat [5]. Rust pathogens are among the numerous biotic stresses that impair wheat production, and they are regarded as the most serious threats due to their significant global economic losses [6] and cause a significant reduction in yield and result in total production losses. The rust attacks all the above-ground parts of the wheat plant and is characterized by pustules (powdery masses) of the yellow spores that form stripes on the leaf surface. It is an excellent air traveller and can spread. Over long distances under favourable climatic conditions because of its proliferating attributes [7]. Among fungicides used to control stripe rust, researchers assayed different active ingredients at different concentrations rate such as epoxiconazole, pyraclostrobin and propiconazole and found their efficacies are highly correlated with their applied concentrations [8]. The class Strobilurin provide excellent control to stripe rust and are the most popular fungicides used in agriculture on a global scale [9].
Need of the Study
Stripe rust of wheat is a devastating disease of wheat that affects Punjab, Majha region North India and colder regions across the world. There is a large range of commercial formulations of fungicides for stripe rust management in all wheat-growing locations around the world, each having a single or several active ingredients in a mixture. Rust management using fungicides is routine practice worldwide and get first preference when susceptible varieties are grown, because of rapid disease outbreaks [10]. Despite of higher costs and environmental effects, fungicides are still efficient in avoiding a stripe rust epidemic and have contributed efficiently in preserving yield [11].
Research Methodology
The experiment was conducted India for two consecutive cropping season 2022-23 and 2023-2024 at the research field of P.G. Department of Agriculture, Khalsa College, Amritsar located in Majha, Punjab, India. The experimental locations are at 31.639°N latitude and 74.830°E longitude, with an elevation of 234 meters above sea level. The experiment was laid out in a Randomized Block Design (RBD), with three replications and highly susceptible variety PBW 343 was broadcasted in 18 plots (3 × 2 m2 each) uniformly. All cultural practices viz., field preparation, fertilizer dose, weedicide applications, irrigation practices were done according to package of practices of PAU, Ludhiana. The disease usually appeared as natural epiphytotic however, to avoid escape artificial epiphytotics were created by spraying the uredospore suspension of P. striiformis inoculums (1 × 106 uredospores/ml of water) yellow rust mixture of virulent pathotypes that were obtained from the Regional Station, Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research (IIWBR), Flowerdale, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh (HP) 45-55 days after sowing, using small hand sprayer evenly. Five fungicides namely azoxystrobin + tebuconazole (Custodia 320 SC), trifloxystrobin + tebuconazole (Nativo 75 WG), pyraclostrobin + epoxyconazole (Opera 18.3 SE), Propiconazole (Tilt 25 EC), and azoxystrobin (18.20%) + difenoconazole (11.40%) fusion top along with control (without any treatment) were used for field evaluation. Fungicides were applied twice on foliage at the specified dose rates. The first foliar spray of different fungicides was applied at 5 percent leaves showed initial signs of infection manually using hand sprayer delivering required amount of water and the second spray of same treatment was applied at 15 days’ interval. The data were recorded on disease severity using the modified Cobb’s scale as per Peterson et al. on 10 randomly selected plants and the mean disease severity was used to explain the results [12].
Disease severity
Disease severity in calculated on a percentage basis using disease severity’s estimated value on the interval scale [13].

Disease reduction
The percent disease reduction calculated using the formula given by Vincent [14].
• C=Disease reduction in control plots
• T=Disease reduction in fungicide treated plots
Statistical tools
After quantifying all parameters, data from field experiment (Randomized Block Design) were subjected to appropriate statistical analysis whenever necessary using standard procedures, described by Gomez et al. [15]. Critical Difference (CD) among the treatment in various experiment at 5 percent level were calculated.
Results and Discussion
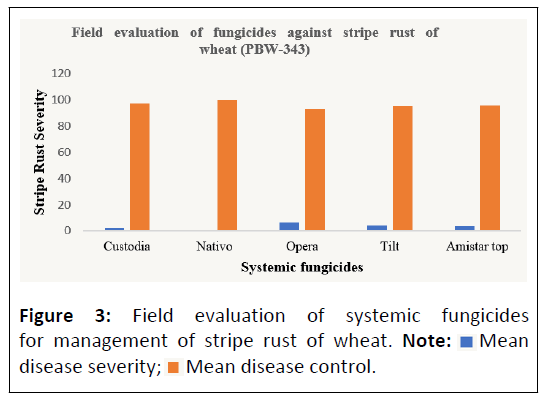
All the fungicides resulted in significant reduction in disease severity as compared with unsprayed check i.e., 79.8% and 94.6% in 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 respectively. Appearance of stripe rust was very severe due to favourable weather conditions during 2023-2024 as compared to previous year. Data presented in Table 1 shows that all the tested fungicides reduced disease severity significantly. The level of disease severity was far higher in the untreated control (79.8% and 94.6%) as compared to treated ones (Figure 1). Among the treatments presented in Table 1, tebuconazole (50%) + trifloxystrobin (25%), a Strobilurin fungicide, was shown to be substantially more effective than other treatments in decreasing stripe rust severity. Tebuconazole (50%) + Trifloxystrobin (25%) recorded the minimum mean disease severity of 0.17% and with a maximum disease reduction of 99.76% at 0.1% dose rate. Azoxystrobin + Tebuconazole and Azoxystrobin (18.20%) + Difenoconazole (11.40%) were closely followed by giving mean disease severity of 2.46 and 3.85 percent and mean stripe rust control of 97.22 and 95.64 percent, respectively. Propiconazole 25 EC also moderately reduced the yellow rust to mean severity 4.39% with disease reduction of 95.02% at 0.1 percent dose rate, whereas, Pyraclostrobin (13.5%) + Epoxiconazole (5%) showed the least effective result with maximum disease severity of 6.19% and minimum disease reduction of 92.96% at same dosage. The study showed that the combination fungicides Nativo 75 WG and Custodia 320 SC showed the best results followed by Fusion Top, Tilt 25 EC and Opera 18.3 SE.
| Sr. no | Treatments | Disease severity (%) | Mean disease severity | Disease control (%) | Mean disease control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-2023 | 2023-2024 | 2022-2023 | 2023-2024 | ||||
| 1 | Custodia 320 SC** (azoxystrobin + tebuconazole) |
1.73 (7.55) |
3.19 (10.2) |
2.46 (9.02) |
97.83 | 96.62 | 97.22 |
| 2 | Nativo 75 WG** (trifloxystrobin (50%) + tebuconazole (25%)) |
0.14 (2.14) |
0.21 (2.62) | 0.17 (2.36) |
99.82 | 99.71 | 99.76 |
| 3 | Opera 18.3 SE** (pyraclostrobin (13.5%) + epoxiconazole (5%)) (12.88) |
4.97 (12.88) |
7.41 (15.7) |
6.19 (14.40) |
93.77 | 92.16 | 92.96 |
| 4 | Tilt 25 EC (propiconazole 25 EC) |
3.34 (10.53) |
5.45 (13.5) |
4.39 (12.09) |
95.81 | 94.23 | 95.02 |
| 5 | Fusion top** (azoxystrobin (18.20%) + difenoconazole (11.40%)) |
2.87 (9.75) |
4.83 (12.6) |
3.85 (11.31) |
96.4 | 94.89 | 95.64 |
| 6 | Control | 79.8 (63.29) |
94.6 (76.5) |
||||
| CD0.05 SE (m) |
1.107 0.334 |
0.083 0.025 |
|||||
Note: *Average of three replications, figures in parenthesis is the arc sine transformed values, **Combination fungicides.
Table 1: Field evaluation of chemicals/fungicides against stripe rust of wheat (PBW-343).
The conducted experiment revealed that the minimum disease incidence of 0.17% was showed by Nativo. Application of fungicide Nativo (Figure 2) helped in rust reduction up 99.76% as compared to control treatment. Similar results were also observed by Wanyera et al., as they tested Nativo at different growth stages of wheat. Wanyera et al., concluded that the wheat rust can be managed effectively by the application of fungicide Nativo at tillering and flowering stages [16]. Second best management of rust disease was observed by fungicide Custodia 320 SC (2.46%) followed by Fusion top (3.85%), Tilt 25 EC (4.39%) and by Opera 18.3 SE (6.19%). Application of fungicides Custodia, Fusion top, Tilt and Opera showed reduction of 97.22%, 95.64%, 95.02% and 92.96% respectively in rust disease as compared to control treatment (Figure 3). Similarly, results coincide with Basandrai et al., showed Tebuconazole 25 EC @ 0.1% was the most effective with Mean Disease Severity (MDS) of 1.84% and Mean Disease Control (MDC) of 99.64% over the unsprayed check (48.39%) followed by Nativo 75 WG @0.05%, Amistar 250 SC, Propiconazole and Amistar Top 325 SC @0.1%, which were inconformity with our result [17]. These fungicides have different modes of action against the fungus, such as Demethylation Inhibitors (DMI) with triazole and imidazole chemical families, Succinate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors (SDHI) with oxanthiins and carboxamide families and Quinine Outside Inhibitors (QoI) with strobilurins family [18,19].
Figure 3: Field evaluation of systemic fungicides for management of stripe rust of wheat. Note: Mean disease severity;
Mean disease severity;  Mean disease control.
Mean disease control.
Conclusion
The experiment was laid out in a Randomized Block Design (RBD), with three replications and highly susceptible variety PBW 343 was tested. Five fungicides at dose rate 0.1% were evaluated during 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 cropping seasons, the least Mean Disease Severity (0.17%) was recorded in two foliar sprays of Nativo 75 WG with mean disease control of 99.82% over the unsprayed check plot. It was followed by Custodia 320 SC, Fusion top, Tilt 25 EC and Opera 18.3 SE resulted in %MDS of 2.46, 3.85, 4.29 and 6.19 with 97.22, 95.64, 95.02 and 92.96 percent disease reduction over check.
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful for the valuable guidance and support from the Principal and Head of Khalsa College Amritsar, Guru Nanak Dev University, ICAR-Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research, Regional Station, Flowerdale, Shimla for providing stripe rust inoculum, and the Division of Plant Breeding and Genetics, Punjab Agricultural University for providing wheat seed.
References
- Gad MA, Halim KYA, Seddik FA, Soliman H (2020) Comparative of fungicidal efficacy against yellow rust disease in wheat plants in compatibility with some biochemical alterations. Menoufia J Plant Prot 5: 29-38.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Sani Y, Scholz M (2022) Interplay of water-energy security and food consumption patterns towards achieving nutrition security in Katsina State, North-Western Nigeria. Sustainability 14: 4478.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari A, Singh V, Singh SP, Dubey S, Singh V (2021) Assessment of genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under sodic soil. The Pharma Innovation Journal 6: 12-17.
- Khalid A, Hameed A, Tahir F (2023) Wheat quality: A review on chemical composition, nutritional attributes, grain anatomy, types, classification and function of seed storage proteins in bread making quality. Front Nutr 10: 58-62.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Zhao J, Luo Q, Deng H, Yan Y (2008) Opportunities and challenges of sustainable agricultural development in China. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363: 893-904.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Afzal F, Chaudhari SK, Gul A, Farooq A, Ali H, et al. (2015) Bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under biotic and abiotic stresses: An overview. Crop production and global environmental issues, Springer international publishing, Switzerland: 293-317.
- Singh R, Mahmoudpour A, Rajkumar M, Narayana R (2017) A review on stripe rust of wheat, its spread, identification and management at field level. Research on Crops 18: 528-533.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Sharma RC, Nazari K, Amanov A, Ziyaev Z, Jalilov AU (2016) Reduction of winter wheat yield losses caused by stripe rust through fungicide management. Journal of Phytopathology 164: 671-677.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Li X, Wang Y, Qin Y, Yan B, et al. (2021) A comprehensive review of strobilurin fungicide toxicity in aquatic species: Emphasis on mode of action from the zebrafish model. Environmental Pollution 275: 116671.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Gomes C, Almeida AS, Coutinho J, Costa R, Pinheiro N, et al. (2018) Foliar fungicide application as management strategies to minimize the growing threat of yellow rust on wheat in Portugal. Emir J Food Agric 30: 715-724.
- Carmona M, Sautua F, Pérez-Hérnandez O (2020) Role of fungicide applications on the integrated management of wheat stripe rust. Front Plant Sci 11: 540218.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Peterson RF, Campbell AB, Hannah AE (1948) A diagrammatic scale for estimating rust intensity on leaves and stems of cereals. Can J Res 26: 496-500.
- Chiang KS, Bock CH, El Jarroudi M, Delfosse P, Lee IH, et al. (2016) Effects of rater bias and assessment method on disease severity estimation with regard to hypothesis testing. Plant Pathology 65: 523-53.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Vincent JM (1947) Distortion of fungal hyphae in presence of certain inhibitors. Nature 159: 239-241.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. 2nd edn, John Wiley and sons, New York, USA: 680 pages.
- Wanyera R, Wamalwa M, Odemba M, Wanga H, Kinyanjui P, et al. (2016) Management of wheat rusts at different growth stages using Nativo 300 SC (trifloxystrobin 100 g/L+ tebuconazole 200 g/L) fungicide. Aust J Crop Sci 10: 1273-1280.
[Crossref], [Google Scholar]
- Basandrai AK, Mehta A, Rathee VK, Basandrai D, Sharma BK (2020) Efficacy of fungicides in managing yellow rust of wheat. Journal of Cereal Research 12: 103-108.
- Mueller DS, Wise KS, Dufault NS, Bradley CA, Chilvers MI (2013) Fungicides for field crops. American Phytopathological Society, Minnesota, USA.
- Joshi KDG, Ullah AU, Rehman MM, Javaid J, Ahmad M, et al. (2017) Wheat yield response to foliar fungicide application against leaf rust caused by Puccinia triticina. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology 7: 160-168.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences