ISSN : 2348-9502
American Journal of Ethnomedicine
Ethnomedicinal Plants and Associated Traditional Wisdom of Garo Community of Rongram, West Garo Hills District, Meghalaya, India
Worrel Kumar Bain1*, Shilpa Biswas2
1Department of History and Archaeology, North Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Meghalaya, India.
2Department of Geography,Kanchrapara College, West Bengal, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Worrel Kumar Bain
Department of History and Archaeology, North Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Tura Campus, Meghalaya, India
Tel: 8017571726
E-mail:worrel.bain@gmail.com
Received Date: July 19, 2021; Accepted Date: October 13, 2021; Published Date: October 23, 2021
Citation: Bain WK , Biswas S (2021) Ethnomedicinal Plants and Associated Traditional Wisdom of Garo Community of Rongram, West Garo Hills
District, Meghalaya, India. Am J Ethnomed. Vol:8 No:8.
Abstract
The study of ethno medicine concerning any community is a complex or convoluted method in and of itself. The present study recounts the Garo community's traditional knowledge of medicinal plants, which they employ in some secluded enclaves of northeast India. The current investigation, which was conducted using standardized anthropological methods and conversations with the local people and traditional healers, resulted in the documentation of sixty-one therapeutic plant species which are used to manage the primary health care practice of the Garo community at the Rongram Community and Rural Development Block (C & RD) of West Garo Hills District of Meghalaya, India. The Garo people used various underground plant forms as medicine, including roots, leaves, rhizomes, and barks. The study emphasizes the value of ethnobotanical research and the importance of documenting traditional wisdom related to therapeutic plant consumption for the more comprehensive welfare of humankind.
Keywords
Ethnomedicine; Garo community; Rongram; Ethnomedicinal plants; Traditional healer; Traditional wisdom; Diagnosis; and treatmen
Introduction
Tribal communities live in harmony with nature and have a deep interaction with the natural world. According to the World Health Organization, up to 80% of people in developing countries still rely on local medicinal plants for their primary health care (WHO, 2002).Up to 90% of the population in some African countries still uses plants as their sole source of medication (Hostettmann). Plants are the source of an estimated 25% of prescribed pharmaceuticals and 11% of WHO essential drugs. Many synthetic drugs are made from precursor molecules derived from plants (Rates). The Indian subcontinent is home to more than 53.8 million tribal people who live in 5,000 forest-dominated tribal communities that cover 15% of the total geographical area of Indian landmasses, making it one of the wealthiest emporia of ethnobotanical wealth (Chowdhury). Despite Meghalaya's growing recognition of traditional medicine, local knowledge of conventional medication is not well documented. Ethnobotanical knowledge must be preserved for biodiversity conservation as part of live cultural knowledge and practice between communities and the environment (Hostettmann).The Mongoloid racial stock is represented by Garos. They communicate in a Tibeto-Chinese language family. They have maintained the matriarchal family system since its inception, with no signs of deterioration. As a result of this practice, the mother is the family's head, and the father is relieved of the need to take a substantial role in society. They reside in the West Garo Hills in the eastern Himalayas, surrounded by nature. Garo religion is based on animalism. The idea of animism coexists with the concept of 'souls' as the 'elixir of life.' They are seen as indestructible, unsubstantial human pictures.They are nature worshippers and believe in spirits who live in nature and natural surroundings and maybe benevolent or malevolent for their life and livelihood. Nature is deeply rooted in the culture and tradition of Garos. The abundant availability of natural resources has made them heavily dependent on them for their survival. Natural resources abound in the West Garo Hills, including a diverse range of plant species. Their distribution and diversity vary by location and are influenced by environmental factors. The West Garo hills' remarkable variety of population and flora has provided an early benefit to its residents for monitoring and examining the plants and animals to create their conventional wisdom since time immemorial. The Garos are noted for their extensive knowledge of the intrinsic virtues of our mother nature, including the long-standing use of floras to treat a variety of ailments [1].
Ethno-medicine of the Garos is a more ancient, extensively practiced by the traditional healers (Ojha), and similarly an effective form of medicine, at least in the minds of its believers. Through trial and error, they have obtained a lot of experience using flora to treat numerous diseases as time has passed. They have a strong belief in ethnomedicine as a source of healing and rely only on their herbal remedy. The medicinal plants can be found at various altitudes and in many types of vegetation. The locals use these plants as herbal medicines, which are particularly helpful against multiple diseases and other health issues. TheOjhasare the traditional Garo priests and religious specialists who perform sacred rituals for the wellbeing of the Garo people on different occasions. TheOjhasare is believed to possess supernatural power and do well through chanting mantras and religious verses. Their healing system rests on traditional knowledge of identification of disease and the process of cure and indigenous medicine. The cause of the disease is assigned to natural and supernatural forces. The system includes the elements like magico- religious practices for appeasing supernatural power, maybe a spirit or ghost, eradication of evil spirits, magical verses, and the ethnomedicinal application[2]. Ojhaclaims that their herbal remedies had a strong potential for curing a wide range of illnesses through ethnomedicine. Only a few known local herbal practitioners/ traditional healers know about plant identification, collecting, and usage, governed by their traditional knowledge. The bulk of these plants are grown organically and picked by locals before being marketed to sellers, who subsequently sell to pharmaceutical and biomedical companies and export markets. Due to several reasons, these medicinal plants are endangered, and the knowledge system associated with them is on the verge of extinction. The present paper aims to gather detailed information on the Garo people's plant species and document their inherited culture and traditions, which may be threatened by modernization. This style of practice is dwindling day by day due to modernization and innovation in contemporary medicine. The deterioration of the resource base of these valuable medicinal plants, which could otherwise provide a perennial source of revenue for the poor, is caused by indiscriminate collecting and a lack of management plans. These plants are under threat from anthropogenic activity, resulting in a significant loss of national heritage. This necessitates rapid conservation measures for these species, both in-situ and ex-situ.
Material and method
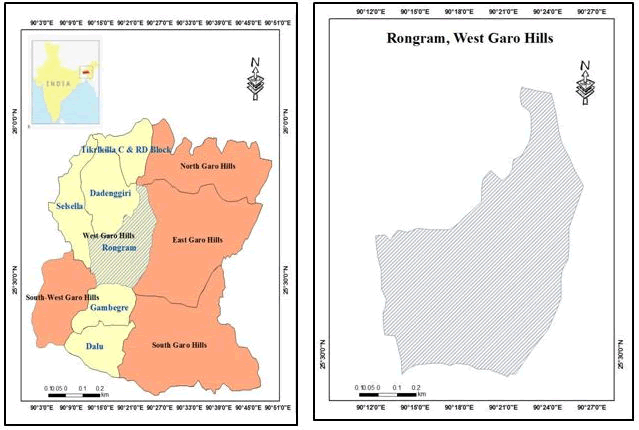
The survey was conducted in the Rongram Community and Rural Development Block (C & RD) of the West Garo Hills district of Meghalaya state of India. Six villages such as Bottregre, Chibokgre, Daldagre, Dipogre, Kalakgre, and Robagre have been selected for the study (see Image 1). According to the 2011 census, the total populations of Rongram are 58,745, and among them, 53,110 people come under Schedule Tribe community. The Garo community mainly inhabits the Rongram though few people of Khasi and Karbi communities are also live there. The researchers carried out intensive fieldwork in the villages to study and data collection. Standard anthropological methods have been used for data collection during the study, such as questionnaire method, interview method, case study method, observation method, informal conversations, and photographic documentation. Interviews were conducted at three levels: individual level, group discussion, and thorough discussion with the villagers. Information was collected from all aspects of medicinal plants, their habitat, identification, collection, preparation of medicines from the plant, and Diagnosis of diseases byOjha. Data was collected from the local people of all ages and theOjhas(see Table 1 & Table 2). Several informal meetings were conducted with the village heads (Nokma's), family heads (NokniSkotong) of the studied villages [3].
Taxonomists assisted in identifying the specimens obtained, and references to the 'Flora and Fauna of Meghalaya' were used. In this approach, a thorough list of plants used for therapeutic reasons by people in the investigated villages was compiled, including scientific and family names, local names, parts of the plant applied, usage, including illnesses healed. Key informants helped enormously to gain an insight into the Garo tradition and their belief system and understand the causes and implications of the changing social scenario. Visual and audio-visual documentation has been done to document the skills of ethnomedicine preparation by theOjhas. The information gathered throughout the investigation was described and explained before being interpreted. Few field data has been represented through the table as well as statistically.
|
Gender |
Age (years) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
20-40 |
40-60 |
Above 60 |
|
|
Male |
20.53 % |
26.84 % |
14.74 % |
|
Female |
13.68 % |
16.84 % |
37.89 % |
Table1: Age and Gender of local people Interviewed in study area.
| Gender | Age (years) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 20-40 | 40-60 | Above 60 | |
| Male | 6.67 % | 53.33 % | 20.00 % |
| Female | 13.33 % | 6.67 % | |
Table 2: Age and Gender of traditional healers (Ojhas) Interviewed in study area.
Results
The concept of health and illness among the Garos
The faith of the Garos shapes the view of health and illness. The Garos believe in good and evil spirits governing the world. Because all-natural calamities such as health, poor harvests, drought, and hailstorm are the result of evil spirits, while good health and vitality, good harvest, and prosperity are attributable to the intervention of good spirits, it is correct to say that the influence of evil spirits causes all-natural calamities. The traditional system of Garo propitiation of evil spirits and use of Ojhas' ethnic remedies is split into two sections: one that uses propitiation to get rid of sickness-causing demons, and the other that uses health derived from Ojhas. Their natural forest resources provide them a rich collection of medicinal plants that the community members successfully used to keep themselves fit and healthy (Image2). Due to contemporary medical services having not yet reached outlying rural hamlets, these residents are ecstatic about their health and keep themselves fit and healthy by using ancient methods. Traditionally, the collection of information about nature is derived from the amount of time and energy that has been invested in observing and understanding nature's activities. According to the local people, "the elder taught this knowledge to the young who again transmits it to the next generation. The younger generations are taught how to observe and read nature including the behavior of bird, insects, animals, plants, shrubs, weather, rain, etc. and earn knowledge of the environment we live in". This also manifests itself in their everyday activities and the way they conduct themselves. As a result of living in close contact with nature, the Garos have a complete grasp of their surroundings.
The traditional health care system of Rongram is focused on herbs and ritual therapy. In this regard, the locals rely more on Ojhas. During the fieldwork, it was discovered that the Ojhas possess have a broad understanding of the usage of plants or plant parts to treat common diseases and apply this knowledge to health care. It's worth noting that health care in Rongram, like in other rural sections of India, is characterized by medical plurality. Medical pluralism refers to the simultaneous existence of multiple medical systems in a community. Health care among the Garos comprises self-care using traditional ethnomedicine knowledge, a traditional healing system involving traditional healers, and a modern primary health care system. These medical systems are cutting-edge, unconventional, and alternative.
Figure 2: Collection of medicinal plants by the Ojhas at Rongram.
Diseases among the Garos
Ailments that have been treated according to the study, most plant species are applied to heal abdomen pain, followed by plant species applied to heal cut and wounds, such as blood clotting, skin problems, dysentery, kidney stone and diarrhea, fever and cough, boil/carbuncle, insect/snake bite, and eye treatment, as well as a fractured bone, jaundice, and throat problems. The 'other' category includes toothache, bleeding, diuretic and urine problems, headache, bodily soreness, paralysis, and liver disease. Helminthes diseases such as tapeworm and hookworm are also widespread because of the high consumption of carious of pork and beef [4].
Medicinal plants and its usableparts
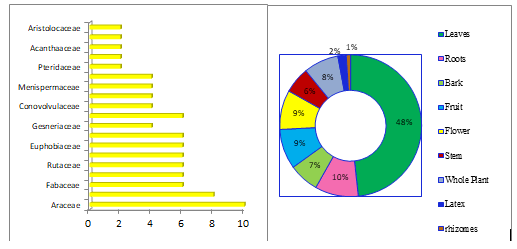
According to a study, traditional healers in and around the villages utilize 61 plant species referring to 79 genera and 50 families to treat various ailments (Table 3&Image 3). The Zingiberaceae family has the most medicinal plants (7 species), followed by Asteraceae (6 species), Piperaceae (5 species), Apocynaceae (4 species), and Aristolochia, Menispermaceae, Rutaceae, and Rubiaceae (3 species each) (seeFigure 1). Leaves are the most commonly utilised medicinal plant (48 %), followed by roots (8 %), bark (7 %), fruits (9 %), flowers (9 %), stem (6 %), whole plant (8 %), latex (2 %), and rhizomes (2 %) (1 %). (Figure 2).
| Sl. No. | Scientific name | Local name | Part(s) used | Ethno medical preparation and usage | State of the plant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AchyranthesAsperaL. | Me’mangkatchi | Whole plant parts | Leaves are mashed appropriately with Curcuma longa Linn, Flacourtiajangomas (Lour) and consumed orally by adding water for uterine fibroid tumors. Infusions of whole plant parts can be administered orally at a dose of 1 cup daily after food for severe fever. | The IUCN Red List classifies this species as Least Concern since it is not cultivated and is familiar near the pond. |
| 2 | Aeglemarmelos (Linn.) Correa ex.Schultz | Bel | Leaves & Fruits | The leaves must be boiled with Asparagus OfficinalisWilld, CentellaAsiatica L, and Cajanuscajan Linn leaves and seeds. One cup of the combination can be administered once a day to treat a stomach ulcer. For smallpox, 1 cup of extracted juice from green or ripe fruits must be consumed every day before eating. | Cultivated in their gardens but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List |
| 3 | Aglaonemahookerianum Schott | Aglaonemahookerianum Schott | Leaves | On the broken area of the bones, leaf pastes are tied. | Although it is found in the wild, it has not yet been evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 4 | Albizzia chinensisRoxb. | Bolpu | Bark | For piles, a bark infusion can be given orally every day after food at a dose of 2-3 teaspoonfuls. | Although abundant in the wild, it has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 5 | Albizzia lebbeckBenth | Siris | Bark | Diarrhea can be cured by taking two teaspoonfuls of bark infusion twice daily after food. | Although abundant in the wild, it has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 6 | Aloe barbadensis Mill | Krito kumara/Aloe vera | Leaves | For burns and mouth ulcers, apply a paste produced from leaves to the affected areas of the body until the injury heals. Orally, crushed leaves can be used to treat urinary tract infections. | Cultivated but not yet evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 7 | Ananus cosmoses L | Anaros/Sakal | Leaves | For fever, malaria, tuberculosis, the decoction of whole plant parts can be drunk at the rate of 1-2 cups twice daily after food. | Cultivated but not yet evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 8 | Antidesmadiandrum Roth | Adurak/Arobak | Fruits | Fruits can be eaten raw for blood purification and constipation. | They have not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List because they are not grown but relatively conserved in their garden. |
| 9 | Aristolochiabracteata Lam | Soksobudu | Leaves | Leaves are pounded adequately for antiemetic, diarrhea, and dysentery and can be drunk by adding a small amount of hot water. | Domesticated species that have not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 10 | Artocarpus lakuchaRoxb | Arimu | Bark | A pinch of sugar can be added to the bark infusion to make it sweeter (extracted juice is bitter). | They have not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List because they are not grown but relatively conserved in their garden. |
| 11 | Arum dioscoridisSibth. & Sm. | Wang-Yong | Stem | Stems are smashed, and the extract is administered immediately to heal boils. | Cultivated, not yet assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 12 | Azadirachtaindica A. Juss | Neem | Leaves | To combat diabetes, fresh leaves are consumed raw. Bathing with a decoction of fresh leaves is indicated for skin ailments. An abscess can be treated with a leaf infusion. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 13 | Bombaxmalabaricum L | Bolchu | Bark | Barks of Cajanuscajan Linn, Zea mays Linn, Asparagus OfficinalisWilld., and roots of Lygodiumflexuosum Linn are all crushed nicely. To prevent UTI, drink 1 cup of the mixture infusion every day after eating. | They have not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List because they are not grown but relatively conserved in their garden. |
| 14 | Buteamonosperma (Lam.) Kuntze | Bolkui | Bark, Root, Flowers | Crushed barks, combined with leaves of CentellaAsiatica L, Asparagus OfficinalisWilld, and Cajanuscajan L, are cooked in 1 liter of water. For piles, 1 cup of the combination should be taken orally once a day after food. The paste roots can be used as an ointment for external treatment to treat goiter. The decoction of flowers can be administered orally for skin disorders. | They have not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List because they are not grown but relatively conserved in their garden. |
| 15 | Cajanuscajan Linn | Mendu | Stem bark, Bark, Seeds, Pods | Stem barks are utilized to bind upon the wrist and ankle for inhabited by evil spirits/possessed by deities. A decoction of bark given orally at a rate of 1-2 cups daily after food can help with piles. Decoction seeds and pods can be eaten orally to treat stomach ulcers. | Cultivated but not yet evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 16 | CaryaarboreaRoxb. | Gimbil | Bark & Flower | Two teaspoonfuls of bark decoction taken orally after food can help with internal bleeding, blood clots, and puerperal fever. The juice is regarded as a type of local syrup. Flowers and fresh bark juice mixed with pure honey are excellent for cough and cold. | Although abundant in the wild, it has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 17 | Carica papaya Linn. | Modipol | Roots | The forehead can be rubbed with root paste. Crushed roots are wrapped in clean and fine clothes and sniffed if the person has a high fever (While smelling, to prevent the direct reaching of odor to the head, some portions of the paste is tied with cladding on the forehead). | This must be cultivated; it has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 18 | CarumkhasianumC.B.Clarke | Ajowan/ Dania dakgipa | Seed | Seeds are soaked in water overnight and then consumed at a rate of one glass daily after meals to combat dysentery. | Cultivated has not yet been evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 19 | Cassia fistula L | Snaru | Leaves | Decoction of leaves, together with leaves of ErythrinastrictaRoxb, and roots of Moringaoleifera Lam, can be used orally for arthritis and paralysis till the patient recovers. | They have not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List because they are wild but preserved in their garden. |
| 20 | Cassia tora Linn | Dadaret | Whole plant | 1-2 teaspoonfuls of complete plant infusion can be given orally until the patient recovers. | Although it is found in the wild, it has not yet been evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 21 | Coriandumsativum L. (173, Umbelliferae) | Loruphi | Fruits | To treat stomach aches, dried fruits are powdered and eaten orally. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 22 | Curcuma longa Linn | Haldi | Rhizome | Bronchitis, gastritis, and bleeding can all be treated with a fresh rhizome infusion mixed with one glass of water/milk twice a day. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 23 | Curcuma longaL. (185, Zingiberaceae) | Chyrmit | Rhizome | To treat dyspepsia, mashed rhizomes are formed into pills (1–2 g each) administered orally before food. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 24 | Drynariaquircifolia (L) J.Sm | Do’renggangpak | Leaves, Rhizome | On the forehead, a paste of leaves and rhizomes is knotted with cladding. Juice can also be extracted and consumed orally, as well as massaged all over the body daily. | It hasn't been farmed and hasn't been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 25 | DysoxylumbinectiforumRoxb | Bolnasin | Bark | Leaves and barks of Crotalaria tetragonaRoxb, Clerodendrumsquamatum Wall, and Drynariaquircifolia are mashed thoroughly (L). The pounded mixed infusion should be tied with a cloak on the forehead and consumed orally at a rate of 2-3 teaspoonfuls. The concoction can also be used to massage the entire body. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 26 | ErythrinastrictaRoxb | Gonok | Leaves & Roots | For blood sugar, two teaspoonfuls of decoction of leaves combined with one glass of water daily after food can be taken orally. Milk juice derived from the bark can be administered to the affected areas two times a day to relieve pain and to bruise in rheumatism and lumbago. | Cultivated in their garden, but not yet on the IUCN Red List. |
| 27 | Euphorbia neriifolia L | Mandalsu'chi | Leaves, Stems | Leaves of Schimawallichii Kurtz, Solanumanguivi L, and Solanummelongena Linn are pounded for osteoarthritis. The paste combination must be placed to the damaged area of the bones from the outside. Massage the damaged bones with leaf paste if you have bone problems. For UTI, a decoction of the stem with some palm candy can be consumed at a rate of 2-3 teaspoonfuls per day after meals. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 28 | Ficushispida Linn | Sa’kap | Leaves | Scrub the damaged areas of the body with leaves. Externally, a paste produced from leaves can be applied to the affected areas. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 29 | GarciniakydiaRoxb | Denggadoti | Fruits | Fruits can be eaten raw if desired. Fruits can be sun-dried, and in the off-season, dried fruits can be cooked in water and liquidate twice a day after meals orally. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 30 | GmelinaArboreaRoxb | Gambari | Bark, Root, Leave | Bark decoction can be used to massage the body or consumed to treat allergies. For malaria, consume three teaspoonfuls of root juice three times a day. For cough, a two-teaspoon decoction of tender leaves can be taken orally three times a day. | Cultivated in their garden, but not yet on the IUCN Red List. |
| 31 | Hemidesmusindicus Br. | Sokchonbudu | Leaves, Barks | Infusion of leaves and barks can be taken orally at one teaspoonful daily after food for conjunctivitis and as an anthelmintic. In addition, the paste can be worn as a service. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 32 | Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L | Joba/China rose | Leaves | Crushed leaves are applied directly to hair for dandruff and hair conditioner and then washed off after 1-2 hours. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 33 | Hibiscus sabdariffa L | Gal’dagitchak | Leaves | Leaves decoction can be consumed at a rate of 2-3 cups per day. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 34 | Hymenodictyonexcelsum Wall | Wakginde | Leaves | The damaged area of the body is covered in a paste made from leaves. | Rarely observed in the wild (according to the field survey) and has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 35 | Jatrophagossypiifolia L | Bolmandalgitchak | Stem | The stem's fresh latex is removed and blended with water. Orally, 2-3 teaspoonfuls of the mixture can be taken twice a day. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 36 | Kaempferiagalanga L | Wakpatra | Leaves | Leaves are broken on the palm and applied directly to the affected portions of the body for skin problems, including itch and irritation. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 37 | Kaempferia rotunda L | Kaempferia rotunda L | Rhizome | Rhizomes, Stephania japonica (Thunb) Miers, and HedyotisscandensD.Don are crushed together. As mentioned earlier, the mixture can be consumed at a rate of 1-2 teaspoonfuls per day after meals, and it can also be used to massage the body. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 38 | Leucasindica (L) R.Br ex vatke | Domkolos | Laves | To control nose bleeding, a few drops of a leaf infusion are placed in the nostrils. | Although it is found in the wild, it has not yet been evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 39 | LitseamonopetalaRoxb.ex Baker Pers. | Adakakki | Bark | On shattered bones, the bark is utilized as an adhesive plaster. It has the ability to generate blood cells, which aids muscle recovery. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 40 | Lygodiumflexuosum (L.) SW | Ru’at tip | Leaves, Rhizome, Whole plant | For pneumonia, Carica papaya (L.) leaves and roots are crushed and applied to the head as a massage. Cuts and wounds can be treated using a paste produced from fresh leaves. Sprains are treated with the entire plant, which is tied around the waist. Externally, leave pastes are used to treat leech bites and stop bleeding. | Although abundant in the wild, it has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 41 | Mangiferaindica Linn | Te’gatchu | Leaves/ | Dysentery is treated by crushing the leaves and extracting the juice. A tiny bit of milk or honey can be added to this. It should be used twice a day after food, one teaspoonful each time. Drink one glass of decoction of bark twice daily after food for dropsy. | Cultivated, IUCN Red List data insufficient |
| 42 | Melastomamalabathricum (Linn.) | Kakku | Fruits | Crush the fruits and mix them with water. During the early stages of cancer, 12 cups of the mixture can be taken twice a day orally. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 43 | MurrayakoenigiiSpreng | Nolsing | Leaves, Roots | Orally, two teaspoonfuls of infusion of leaves and roots after food can be taken to relieve toothache. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 44 | NelumbonuciferaGaertn | A’pilak | Roots | Two teaspoonfuls of infusion or roots can be taken twice a day after food orally. | It hasn't been farmed and hasn't been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 45 | OroxylumIndicum (Linn.) Vent | Kering | Leaves, Root, Barks | Root-barks are carefully ground and a juice made from them for diarrhea. Until the patient heals, one cup of the extracted juice can be given twice a day orally. Leaves are used as a vegetable to treat UTI. | It hasn't been farmed and hasn't been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 46 | Oxalis corniculata Linn | Me’kampretchongipa | Fruits | Approximately 2-3 fruits can be consumed raw. | It hasn't been farmed and hasn't been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 47 | PandanusodoratissimaL.f | Burungnianaros | Roots | The roots are pounded on a stone and cooked with water until a nice paste is formed. For headaches and rheumatism, the paste can be given orally with 1 cup of water. | Very rare (according to the field survey) and has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 48 | PegianitidaColebr. | Du’chengkrip | Leaves & Barks | After meals, 1 cup of decoction of leaves and barks can be eaten. | According to the field survey, the species is scarce in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 49 | PhyllanthusEmblica Linn | Ambri | Fruit, Barks & Roots | A decoction of bark can be administered orally for blood clothing/internal bleeding. One teaspoonful of fruit juice is mixed with 12 teaspoons of honey and eaten once a day as a cough treatment. Fruits are fermented inside an earthen pot with sugar for around 2-3 months in the case of jaundice, and the juice can be taken regularly after meals. For asthma, however, a root infusion can be taken twice a day after food. Infusion of bark can be given daily after food for menstruation problems and piles. | Although abundant in the wild, it has not yet been assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List |
| 50 | Raphidophoralancifolia Schott | Dotmija’pachongipa | Leaves | Roots are carefully mashed and juice extracted to treat diarrhea and malaria. Depending on the severity of the ailment, three teaspoonfuls of fluid can be taken daily. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 51 | Rhododendron arboreum SM | Bibalgitchak | Flower | Dysentery is treated with flowers disguised as vegetables. | Rarely observed in the wild (according to the field visit) and not yet on the IUCN Red List. |
| 52 | Scheffleravenulosa Harms | Do'reng m | Twigs | Twigs are worn around the neck to help babies stop crying. The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 53 | Schumannianthus dichotomous (Roxb) Gagnep | DikgeHi’r | Rhizome | It's used to treat infections in the urinary tract. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 54 | SolanumIndicum L. | Sabangang | Fruit | Boil the dried fruit and use the decoction to manufacture tablets (about 10 gm each day) for hypertension treatment twice a day. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 55 | Spilanthuspaniculata DC. | Santustem | Flowers | The decoction is used to manufacture tablets used twice a day to treat high blood pressure. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 56 | Stephania japonica (Thunb.) Miers. | Samkuchak | Rhizome | The rhizome is use to treat asthama. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 57 | Stereospernumtetragonum D.C | Bolsil | Bark, Leaves | On the forehead, pounded barks and leaves are knotted with cladding. | The species was discovered in the wild and has not yet been assessed for the IUCN Red List. |
| 58 | Tabernaemontanadivaricata(L.) R. Br. (1146, Apocynaceae) | Santu-jri-iong | Latex | Latex is applied twice a day to avoid cavities. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List |
| 59 | UrenalobataL. (1234, Malvaceae) | That-Thu | Leaves | The leaf decoction is given twice daily before dinner to treat rheumatic pain and physical soreness, and it is also used to control blood pressure and before bedtime. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 60 | Zea mays L | Me'rakku | Roots | Phyllanthusurinaria Linn, Aloe barbadensis Mill, and Asparagus Officinalis Linn are mashed with the roots. The combination must be heated with water before being consumed orally in doses of 2-3 cups each day. | Cultivated but not yet assessed for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
| 61 | ZiziphusmauritianaLamk | Angkil | Bark, Leaves | Tender leaves are crushed with a small amount of salt for dysentery, and the juice is extracted with a clean and fine cloth. After eating, take 2-3 teaspoonfuls of the combination every day. Cough is treated with a decoction of bark. Young leaves of Ficushispida L and leaves of Ficushispida L are pounded good for scorpion and insect stings. The combination can be applied twice a day to the afflicted areas. Drinking a decoction of bark with Piper longum L and Syzygiumgrande (Wight) regularly can help with tuberculosis. Drinking a decoction of bark with added sugar can help with UTI. | Both cultivated and wild, they have not yet been evaluated for inclusion on the IUCN Red List. |
Table3: List of medicinal plants and their uses in the Garo community at Rongram.
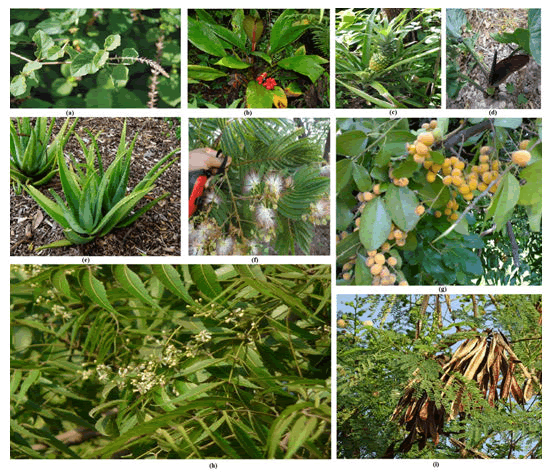
Figure 3: General view of the medicinal plants at Rangram. (a) AchyranthesAspera L, (b) Aglaonemahookerianum Schott, (c) Ananus cosmoses L, (d) Arum dioscoridisSibth. & Sm., (e) Aloe barbadensis Mill, (f) Albizzia chinensisRoxb., (g) Artocarpus lakuchaRoxb., (h) Azadirachtaindica A. Juss, (i) Albizzia lebbeckBenth.
Figure 4: Family Wise distribution of medicinal plants. Figure 2: Distribution of plant parts used Plant parts.
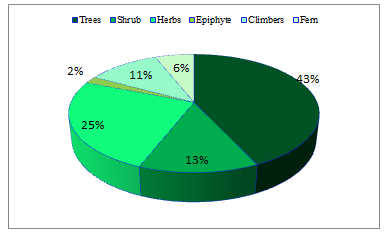
Medicinal plants are used to treat a variety of conditions in a variety of methods. Many are immediately supplied orally, according to the findings. Some are used as a decoction of leaves and roots; others are formed into a paste; the juice of some plants is extracted and used to treat illnesses; others are dried and powdered into powder, and cooked with oil and used as an ointment. Trees accounted for the majority of medicinal plants (43 %), followed by shrubs (13%), herbs (25%), climbers (2%), pteridophytes (8%), and epiphytes (6%). (seeFigure 3).
The uses of ethnomedicine medicine, literacy rates, and distance from metropolitan centers all have a relationship. In the study area the use of ethnoveterinary medicine was found to be related to distance. There was a definite positive correlation between utilization and distance from metropolitan centers (Pearson correlation coefficient, r value is 0.91, at = 0.05 and p is 0.01). Compared to the standard t value at 5df, the standard error for this correlation coefficient is 0.590, and the estimated t-test is 0.0001. Because the examined villages are located outside of Tura, the people of the Garo community rely heavily on ethnomedicine for their initial treatment. Folk healers work in the primary health care sector, reaching out to people in need of life-saving treatment in locations where communication is difficult [5].
Traditional wisdom associated with the ethnomedicinal plants and its uses
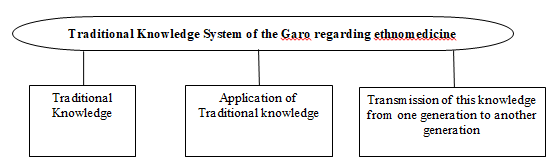
In the framework of indigenous knowledge, innovation, and community traditions, "Traditional Knowledge" (TK) is frequently employed reciprocally with "traditional knowledge," conservation of the environment, sustainable use of biodiversity, and other traditions. TK is essential for ensuring food security and maintaining health for millions of people. It is passed down from one generation to the next through cultural practices, songs, stories, local languages, customs, cultural values, local languages, customs, contemporary practices, healing arts, etc. Traditionally based knowledge system is the mother of all sciences and invention because indigenous people were intrinsically connected to their surrounding environment, which was not something they could obtain from the environment but was instead a part of their being. However, there is a separate issue with traditional ecological knowledge: Not only is it relevant to conservation on its own, but it could also have the ability to aid species conservation through information owned by a group of individuals about an ecosystem. Such information is frequently modified for localities and locations, which helps to shape the day-to-day lives of the majority of people throughout the country and internationally. It is defined as an essential aspect of people's cultural identities(Bain, 2019)(Berkes et al., 1995).It has been observed that among theOjhas of Rongram, all the traditional knowledge and wisdom related to ethnomedicine ultimately flow from practice (see Figure 4). It is preserved, passed, and improved almost entirely in applying it in practice, and therefore, is highly sensitive to changing relationships between people and their ecological resource base. The knowledge regarding ethnomedicine is highly skillful. TheOjhasbelieve that Mother Nature has especially given this skill to some people and are specialized for this work due to the blessings of Mother Nature. According to oneOjhaof Chibokgre, "I get the ethnomedicinal knowledge from my maternal uncle. He was a specialized healer of the village. He had some special talent. He knew to cure several diseases". According to anotherOjhaof Robagre village, "Grandfather or grandmother transmits his/her knowledge to his/her son or daughter, and they transmit their knowledge to son or daughter. The young generation learns how to make medicine from the plants and treat the disease from their father or grandfather. But it is not like that in an Ojha's family where the father or mother is a specialized healer; his or her son or daughter should be a healer. Any member of the community can get the knowledge regarding medicinal plants". From the specialized healers, the interested person learns how to collect the plant from its habitat. They also teach how to diagnose sick people [6].
Diagnosis and treatment of disease
Fieldwork at the study area has explored diverse techniques of examination and diagnosis of diseases by theOjhas. The Ojhas categorized diseases based on various criteria.In identifying illness, there are precise processes for diagnosing diseases and specific ritual actions.Ojhasemploy multiple forms of divination to diagnose and treat different conditions, particularly those that are thought to be caused by supernatural influences. They also identify each health concern by taking down the patient's medical history and performing a physical examination. Patients are frequently questioned about the symptoms they have noticed and the length of time they have had the health issue. A practitioner studied changes in eye and skin color, tongue color, and body temperature before recommending a treatment. Internal diseases were usually treated with oral preparations, while wounds and skin infections were treated with recipes applied to the affected areas and mantras chanted [7].
Preparation of ethnomedicine
Both material and non-material components are used in Garo ethnomedicine. Plant parts or organs and their products are generally included in the material elements (see Image4). Animal organs, minerals, and other natural components are also present. Charms, magic, incantations, religious phrases, and amulets are non-material components that make up significant religious and spiritual healing objects. Because the central premise of Garo ethnomedicine is to treat the whole person rather than isolated sections and to conceive of him concerning his emotional sphere and physical environment, theOjhasalso employed non-biological materials such as mustard oil and palm candy. For the most part, single plants or plant parts were utilized to make medicine, though the Ojhas also used poly-herbal formulations for various diseases. The most popular preparation technique was extraction in hot or cold water, and oral administration was preferred over topical or other modes of administration. The dosage of a certain recipe varies depending on the healer, the severity of the sickness, and the patient's age. The doses for liquid preparations were estimated in terms of a full, half, or one-fourth cup, depending on the patient's age and physical condition, and the severity of the sickness, and there was no standardized measuring process for the herbal recipes provided as a result [8,9].
Conclusion
Deforestation, environmental degradation, and habitat loss are posing a severe threat to medicinal plants in the area and knowledge of their usage, which is progressively vanishing. Plant biodiversity has also been discovered to be in grave danger due to the widespread commercial harvest of plant materials from the forest. As a result, there is a necessity to curb harmful and overexploitation of plant resources and take steps to safeguard the area's woodland and preserve these medicinal plants, their environment, and traditional wisdom for future generations. Plant conservation and long-term use, as well as scientific collecting of plant parts, are critical. Residents can play a crucial role in this regard. Local communities can only be sustained if genetic resources are appropriately managed and conservation plans are carefully implemented. Conservation measures such as medicinal plant planting in home gardens or on the outskirts of forests, prohibition of the unsustainable harvesting of plant resources from forests, forest protection, and so on can help in the conservation of medicinal plants in and around the villages of West Garo Hills. Infrequent harvests of small amounts of biomass may not affect the indiscriminate harvesting of medicinal plants in and around the villages of West Garo Hills. For the researcher, conservation is an essential aspect of the development of the local environment. However, farmers prioritize cultivation owing to a lack of information and their reliance on forest products for their subsistence. As a result, biodiversity conservation and indigenous peoples' ethnobioculture are critical (Lalramnghinglova, 2003). There is also a requirement to increase awareness about the need to pass on knowledge and protecting medicinal plant species. The use of spontaneous and wild-collected plants should be reduced as much as possible, and cultivation should gradually replace them. To maintain the conservation of medicinal plant biodiversity, rural people should be encouraged to grow their folk therapeutic gardens or herb gardens in their communities. Prioritize research on developing appropriate technologies for medicinal plant propagation, culture, processing, chemical characterization, and marketing, as well as valuable and endangered species. As part of the extension, local people should be taught how to propagate, conserve, and harvest medicinal plants. They should be trained and given the proper guidelines to ensure that wild vegetation continues to regenerate. Traditional healers have become a vulnerable category as tribal traditions have eroded. Due to shifting agriculture and the large-scale devastation of medicinal plants' natural habitats, the genetic diversity of medicinal plants has also decreased. Overexploitation of medical resources by unskilled labor in an improper way, as well as poor natural or artificial regeneration, has resulted in the virtual extinction of many essential species. The ethnomedicinal practice is deeply rooted with Garo’s own culture. Since the thirties of the 20th century Christianity started to take root in Garo Hills. It has brought about a noticeable change among the Garos. It has been found that with the introduction to Christianity in the studied region the Ojhas and their practices are fading away. During the poll, it was also observed that the younger generation has no understanding of medicinal plants due to their preference for the allopathic medical system. Older individuals, especially those over 55, are familiar with these plants and utilize them to treat common ailments such as colds, coughs, fevers, and headaches. Because they prefer allopathic drugs, the younger generation is less concerned about their use. The tradition of traditional healer and their associated knowledge system of herbal and natural medicine certainly requires to be preserved urgently. If we are unable to take any step urgently about this traditional wisdom then in near future we will lose it. This will be not only a loss of them but also a great loss of human civilization.
References
- Bain, W. K (2019) Bamboo Craft and Associated Knowledge System of Lepcha Community of North Sikkim: An Endangered Cultural Heritage. Journal of Kolkata Society for Asian Studies, 3(1 & 2), 35.
- Berkes, F., Carl, F., & Madhav, G (1995) Traditional Ecological Knowledge, Biodiversity. 281–299.
- Chowdhury, S. K. (2000) From ethnobotany (Vol. 2). Manasi Press, Kolkata, India).
- Hostettmann, K. A., Marston, K., & Ndjoko, J. L (2000) The potential of African medicinal plants as a source of drugs. Curr. Org. Chem., 4, 973–1010.
- kayang, h., kharbuli, b., myrboh, b., & syiem, d. medicinal plants of khasi hills of meghalaya, india. Acta Horticulturae, 675, 75–80. (2005).
- Pratibha, M (2013) A Glimpse of the Garo tangible medicine: The Ruga-Garo picture. Indian Journal of History of Science, 48(4), 603–623.
- Rates, S. M. K.Plants as a source of drugs. Toxicon, 39, 603–613. (World Health Organization. WHO. (2002). Traditional Medicine Strategy. (2001).
- UNESCO (1996) Conservation, Biodiversity and International Law. Alexander Gillespie.324-325.
- Lalramnghinglova, H. & Jha, L.K (1997) Ethnomedicine from Mizoram – North East India. Ethnobotany 9: 105 – 111.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences