Comparative Genome Wide Identification, Gene Structure and Phylogeny Analysis of POU5F1 Transcription Gene in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus
Mahwish Amin*
Department of Molecular Biology, Government College University Faisalabad, Faisalabad, Pakistan
- *Corresponding Author:
- Mahwish Amin
Department of Molecular Biology,
Government College University Faisalabad,
Faisalabad,
Pakistan,
Tel: 923247185617;
E-mail: mahwishamin4111@gmail.com
Received Date: April 29, 2021; Accepted Date: May 13, 2021; Published Date: May 20, 2021
Citation: Amin M (2021) Comparative Genome Wide Identification, Gene Structure and Phylogeny Analysis of POU5F1 Transcription Gene in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus. J Mol Biol Biotech Vol. 6 No.3: 04.
Abstract
House mouse (Mus musculus) is a model organism and has role in understanding and studying human diseases. Mus musculus and human have many conserved domains. POU domain is one of those conserved domains and in this recent study, POU5F1 gene, part of POU domain is studying. POU5F1 is a POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1. It has role in pluripotency development in embryo, embryonic and adult stem cell development, in protein binding, miRNA binding, chromatin DNA binding, RNA polymerase 2 cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding and involve in reprogramming of cells. In this study, the phylogenetic relation of Mus musculus with other subfamily members is found to use them as model alternate to Mus musculus. Initially the comparative genome wide analysis of POU5F1 gene was performed in Mus musculus specie, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis nilotius. This study focused on the identification of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus (common house mouse) among Mus caroli (Ryukyu mouse), Onychomys torridus (Southern grasshopper mouse), and Arvicanthis niloticus (African grass rat) based on the bioinformatics techniques and tools to explore evolutionary relationship. For the identification genome sequence retrieved from NCBI, for conserved domain analysis, PROSITE-Expasy, SMART Protein and Pfam were used. Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis was performed by Clustal Omega and MEGA-X. The results showed that in Mus musculus POU5F1 gene is present on chromosome number 17 and has 6 exons, In Arvicanthis niloticus POU5F1 gene is present on chromosome number 20 and has 5 exons, Mus caroli POU5F1 gene is placed on chromosome number 17, and has 6 exon, and Onychomys torridus POU5F1 gene has 5 exons with unknown chromosome number. Finally, our results provide important genomic suggestions for upcoming studies of biochemical, physiological and phylogenetic understanding on POU5F1 gene among other species.
Keywords
POU5F1, Mus musculus, Multiple sequence alignment, Phylogenetic analysis, Oct-4, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus, Arvicanthis nilotius
Introduction
Mus musculus is the specie which has largest contribution in modern research. It could bread anywhere in the world as compared to previous fancy mice which could bread only in Europe and Asia. Mus musculus is a wild type and had commensalism to humans, therefore could be used in study of human diseases. It considered as the prime mammalian laboratory model [1]. The Mus musculus genome sequence is much related to human genome sequence and about 14% smaller than human genome with function homology.
Most of genes in the mouse and human are conserved [2]. Out of that conserved genes, One POU gene family is decided for study. The Mus caroli is also a species of rodents and having habitat China, Cambodia, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam. The Onychmys torridus is also rodent family member and habitat in New Mexico, California and United States. The Arvicanthis niloticus has use as animal model for Type 2 Diabetes mellitus
POU domain is a structural motif of transcription factors which are composed of the POU-specific domain and the POU homeodomain. POU family has role in pluripotency development in embryo, embryonic and adult stem cell development, in protein binding, miRNA binding, chromatin DNA binding, RNA polymerase 2 cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding and involve in reprogramming of cell’s neurogenesis, brain formation and animal development. POU5F1 is the member of POU domain family. In mammals including humans, POU5F1 transcription factor belong to one of the largest gene families that play vital role in control of pluripotency. The pluripotent cells include primordial germ cells, embryonic germ cell and inner cell mass [3].
The genome wide analysis of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus will help in future to analyse the undifferentiated cells at embryo level in humans. In this recent study, initially the genome wide analysis of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus species was performed and based on the NCBI retrieved genome sequence. This study focused on the identification of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus and perform phylogenetic analysis among Mus caroli (Ryukyu mouse), Onychomys torridus (Southern grasshopper mouse) and Arvicanthis niloticus (African grass rat) to explore evolutionary relationship.
Materials and Methods
Identification of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus
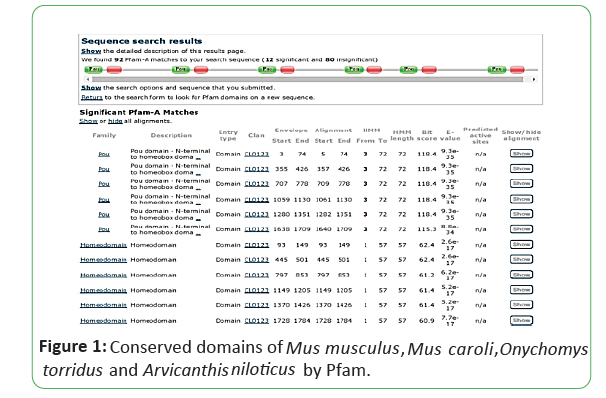
Nucleotide sequences of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus were retrieved from NCBI in FASTA format (NC_000083.7, NC_047677.1, NC_034586.1, NW_02341287.0). Homologous sequences were then obtained from BLASTN. The variants which have E-value less than 0 were considered for the homology analysis. All the variants were checked for sequence homology by the graphic summery and alignment. Conserved domains of the nucleotide sequences were found by Pfam.
Conserved domains analysis
Conserved domains are recurring units in the molecular evolution that can be determined by sequence analysis. It informs about pattern or motif to see its similarity in other polypeptide sequences.
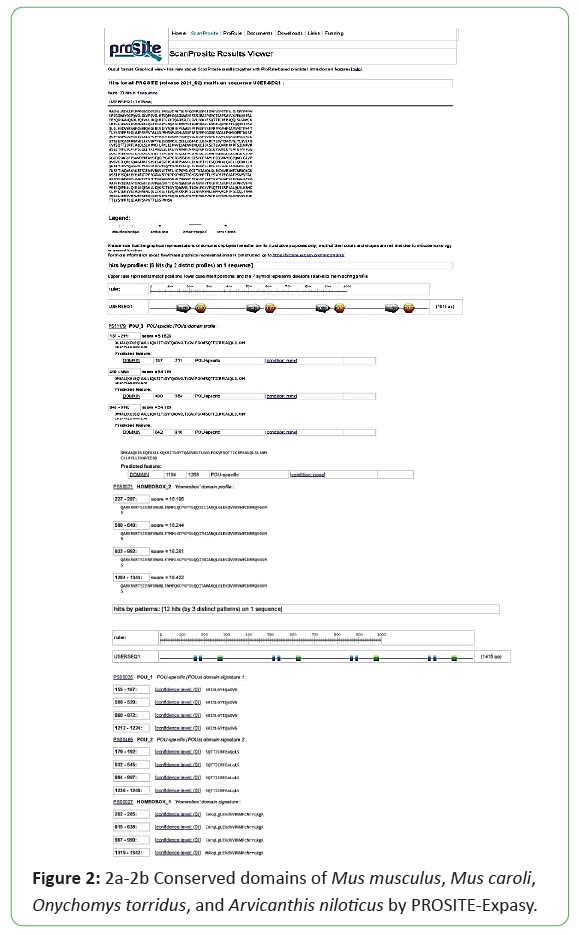
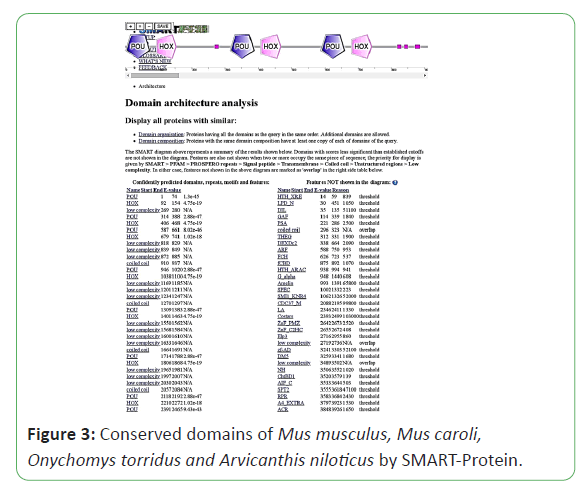
The protein sequence of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus was retrieved in FASTA format by NCBI (NP_001239381.1, NP_038661.2) Mus caroli (XP_021005284.1, XP_021005285.1), Onychomys torridus (XP_036032305.1), and Arvicanthis niloticus (XP_034379773.1). Conserved domains in the protein sequence were determined through PROSITE-Expasy, SMART Protein and Pfam [4-6]. Genome information related to cDNA sequence, length of protein, ORF (Open Reading Frame), chromosome location was also retrieved from NCBI. The NCBI BLAST retrieved sequence of Mus musculus was used as query sequence to obtain nearly related matches and precise results. For the confirmation of presence of signature POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus were tested by SMART Protein database and Pfam, PROSITE-Expasy [4-6].
Multiple sequence alignment
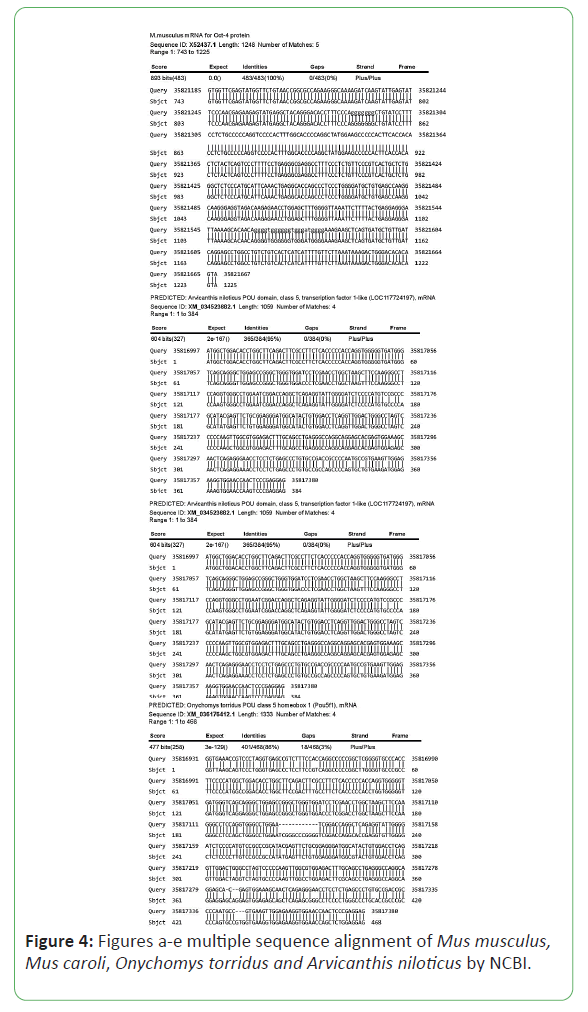
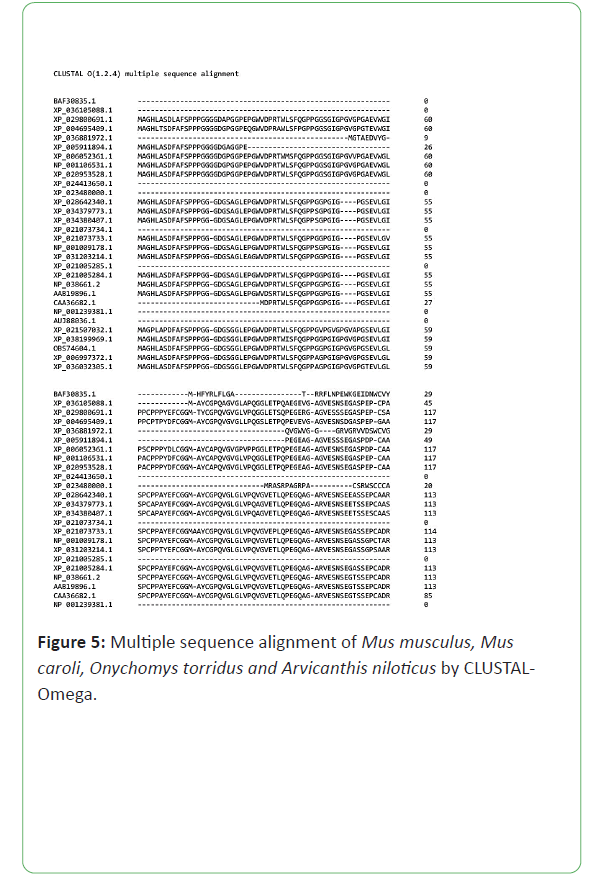
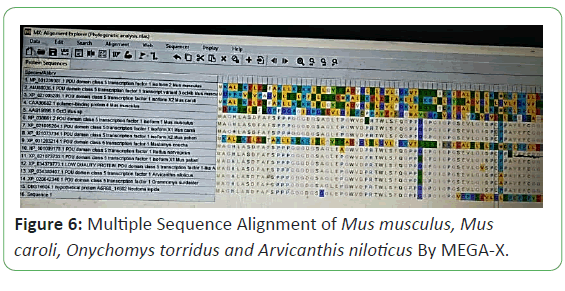
Clustal Omega tool, MEGA-X and NCBI were used to see the related genes or proteins to find the evolutionary relationship between genes and to identify functionally or structurally related genes in other species. Sequences of Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus, and Arvicanthis niloticus were used. BLAST was used to obtain multiple sequences, followed by sequence alignment by ClusterOmega and MEGA-X respectively [7,8]. The evolutionary relationship of POU5F1 gene was found in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus, and Arvicanthis niloticus. First, multiple sequence alignment was performed by MEGA. X by using CLUSTAL W, and another database Cluster Omega that was used online.
Gene structure analysis
For the analysis of gene structure in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus. Gene Structure Display Server was used [9]. It informs about the gene features like exons, intron and conserved elements. It can be used for both genomic and cDNA sequence phylogenetic tree construction. For the construction of gene structure, cDNA sequence and genomic DNA sequence in FASTA format were put in Gene Structure Display Server database and the result showed in the form of gene structure.
Phylogenetic analysis and phylogenetic tree construction
The phylogenetic tree shows the evolutionary relationship between the related organisms and also inform about differences between them. Phylogenetic analysis was performed by using MEGA-X software. To see how many times the branches repeat in phylogenetic tree bootstrap kept 1000 replicates and pairwise deletion and poison correction was used to construct phylogenetic tree. During phylogenetic tree construction Maximum Likelihood method was used. Phylogenetic tree was also generated by database Cluster Omega, MEGA-X and IQ-tree [7,10]. Then using three databases, rooted phylogenetic tree was built with Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomystorridus, Arvicanthisniloticus and 13 other subfamily members.
Results
Identification of POU5F1 gene in Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus
The POU5F1 protein sequence of Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomystorridus, and Arvicanthisniloticus was retrieved from NCBI. The complete information is available in Table 1.
| Proposed names | Gene symbol | Protein accession # | RNA accession# | Exons | Chr | ORF length | Amino acid length | Start of genomic location | Conserved domains in protein sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mus musculs POU domain | Pou5f1 | NP_001239381.1 | NM_001252452.1 | 6 | 17 B1;17 18.69cM | 666 | 221 | 35816929 | smart 00352 pfam00046 |
| Mus musculs POU domain | Pou5f1 | NP_038661.2 | NM_013633.3 | 6 | 17 B1:17 18.69cM | 1059 | 352 | 35816929 | Smart00352 Pfam00046 |
| Arvicanthis niloticus POU domain | LOC117724197 | XP_034379773.1 | XM_034523882.1 | 5 | 20 | 1059 | 352 | 50621362 | Smart00352 Pfam00046 |
| Mus caroli POU domain | Pou5f1 | XP_021005284.1 | XM_021149625.1 | 6 | 17 | 1059 | 352 | 32277972 | Smart00352 Pfam00046 |
| Mus caroli POU domain | Pou5f1 | XP_021005285.1 | XM_021149626.1 | 6 | 17 | 666 | 221 | 32277972 | Smart00352 Pfam00046 |
| Onychomys torridus POU domain | Pou5f1 | XP_036032305.1 | XM_036176412.1 | 5 | Unknown | 1080 | 359 | 2412441 | Smart00352 Pfam00046 |
Table 1: S1 Proposed nomenclature and important features of Pou5f1 genes.
Conserved domain analysis
Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomystorridus, and Arvicanthisniloticus have same two conserved domains smart00352 and Pfam00046. Mus musculus and Mus caroli have two isoforms, Onychomystorridus, and Arvicanthisniloticus have single isoform. The ORF is also obtained online by ORF finder, Mus musculus and Mus caroli have two ORF values 1059 and 666. Arvicanthisniloticus has single ORF that is 1059 and Onychomystorridus also has single ORF with value 1080. The Pfams, SMART Protein and PROSITE-Expasy results are attached below (Figures 1-3).
Multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment was generated by NCBI and CLUSTAL Omega. They are aligned pair-wise. Multiple sequences are a phylogeny-aware alignment and that information use in the generation of phylogenetic tree (Figures 4-6) [11].
Phylogenetic analysis and phylogenetic tree construction
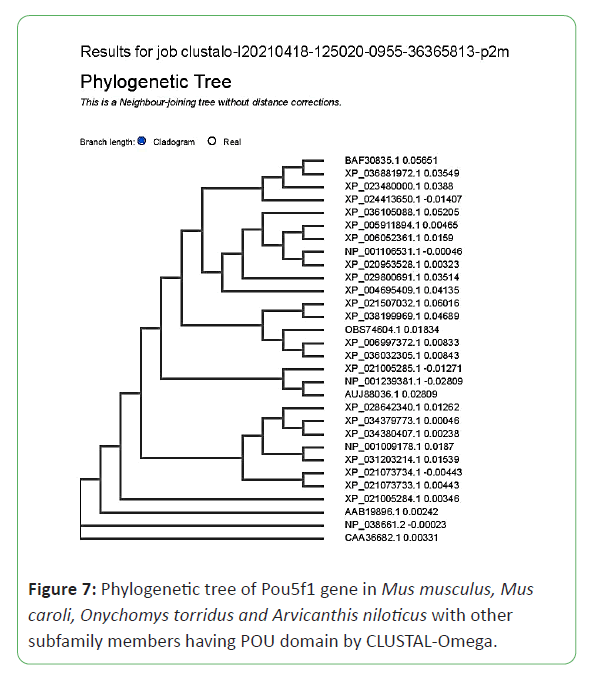
The characterization of the evolutionary relationship for POU5F1 gene among Mus musculus, Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus was performed by generating the rooted tree of four species by the maximum likelihood (ML) method. The figure showed that 31 subfamily members have homology gene (Figures 7 and 8).
The phylogenetic analysis results showed that CAA36682.1 octamer-binding protein 4 Mus musculus, NP 038661.2 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform 1 Mus musculus, AAB19896.1 Oct3 Mus sp., NP 001239381.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform 2 Mus musculus, AUJ88036.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 transcript variant 3 oct4b Mus musculus, XP 021005284.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X1 Mus caroli XP, 021005285.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X2 Mus caroli , XP 021073734.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X2 Mus pahari, XP 021073733.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X1 Mus pahari , XP 028642340.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Grammomys surdaster, XP 034379773.1 LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1-like Arvicanthis niloticus, XP 034380407.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Arvicanthis niloticus, XP 031203214.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Mastomys coucha, NP 001009178.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Rattus norvegicus, XP 021507032.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Merionesung uiculatus, XP 038199969.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Arvicola amphibius, OBS74604.1 hypothetical protein A6R68 14882 Neotoma lepida, XP 006997372.1 PREDICTED: POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Peromyscus maniculatus bairdii, XP 036032305.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Onychomystorridus, XP 029800691.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Suricata suricatta, XP 005911894.1 PREDICTED: LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Bos mutus, XP 006052361.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Bubalus bubalis, NP 001106531.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 Sus scrofa, XP 020953528.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X1 Sus scrofa, XP 004695409.1 PREDICTED: POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X1 Condylura cristata, XP 036105088.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X2 Molossus molossus, XP 024413650.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X3 Desmodus rotundus, XP 023480000.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1 isoform X2 Equus caballus, XP 036881972.1 POU domain class 5 transcription factor 1-like Manis javanica, BAF30835.1 octamer-binding transcription factor-3B Macaca fascicularis have POU domain homology and they have phylogenetic relationship with each other.
It signifies that out of these 31 subfamily members, anyone can be used for further pluripotency research work due to their phylogenetic relationship. The phylogenetic trees are presented below.
Gene structure analysis of POU5F1 gene
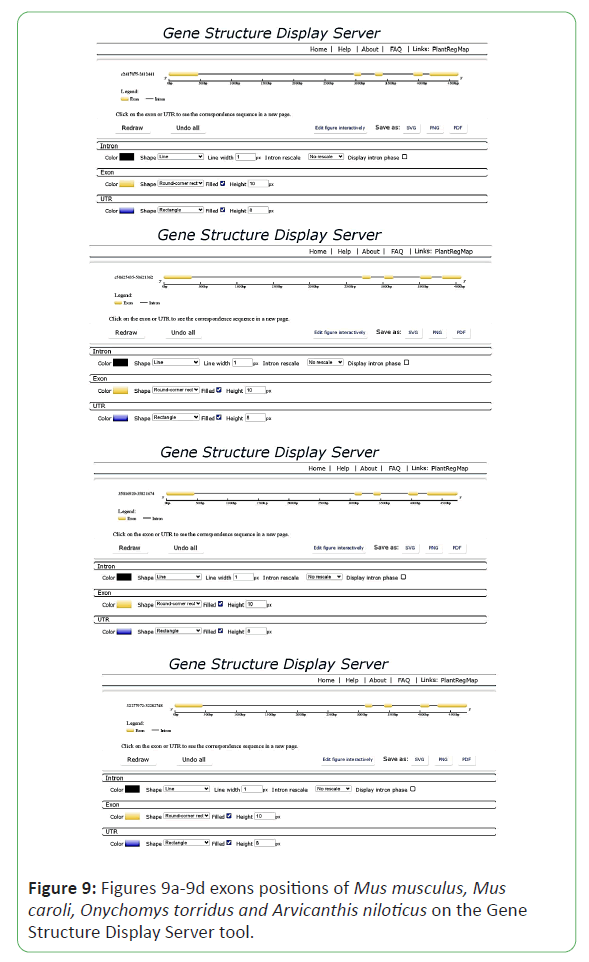
The gene structure of POU5F1 gene was obtained online by Gene Structure Display Server. It provides the information about the intron and exon position and number in evolutionary times. The Gene Structure Display Server showed that the genome range of 35816929-35821674 of Mus musculus shows 6 exons and 5 introns, the genome range of Arvicanthis niloticus c50625435-50621362 show 5 exons and 4 introns, the genome range of Mus caroli 32277972-32282748 show 6 exons and 5 introns and the genome range of Onychomys torridus c2417075-2412441 show 5 exons and 4 introns, the positions are showed in the result diagram below (Figures 9a-9d).
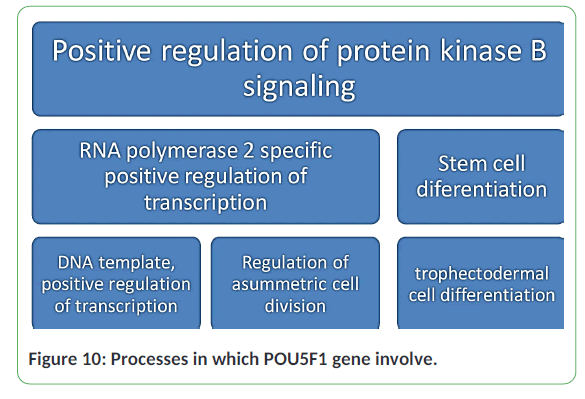
The POU5F1 gene is present in chromatin, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleolus, nucleoplasm, nucleus and transcription regulator complex. The POU5F1 gene was studied to see its phylogenetic relation with other subfamilies. In comparison to other subfamily members, most of them have same motifs and domains which show that they are closely related to each other in evolutionary time and have less than 0 E values. That conserved domains are involved in multiple processes like positive regulation of protein kinase B signalling, positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase 2, DNA template positive regulation of transcription, regulation of asymmetric cell division, Stem cell differentiation, and trophectodermal cell differentiation (Figure 10) [12-16].
Discussion
The genome identification of POU5F1 gene showed that in Mus musculus POU5F1 gene is present on chromosome number 17 and has 6 exons and 2 isoforms. The isoform 1 has 352 amino acids and maximum ORF length of 1059. The isoform 2 has 221 amino acids, with ORF length of 666. In Arvicanthis niloticus POU5F1 gene is present on chromosome number 20 and has 5 exons, maximum ORF length of 1059, and 352 amino acid. In Mus caroli POU5F1 gene is placed on chromosome number 17, and has 6 exon and 2 isoforms. The isoform 1 has 352 amino acids and maximum ORF of 1059. Its isoform 2 has 221 amino acids, and maximum ORF length of 666. In Onychomys torridus POU5F1 gene has 5 exons with unknown chromosome number, with 359 amino acids and 1080 maximum ORF length. All the species have same conserved domains which are smart 00352 and pfam 00046. It signifies that out of these subfamily members, anyone can be used for further pluripotency research work due to their phylogenetic relationship. The phylogenetic tree which was built with 31 subfamily members showed that they have common ancestors.
Conclusion
In the present study, genome wide identification, conserved domain and phylogenetic analysis of POU5F1 gene were conducted in Mus musculus. Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus. This study revealed a high similarity in exon-intron structure of POU gene family in Mus musculus. Mus caroli, Onychomys torridus and Arvicanthis niloticus. This study supports the close phylogenetic relationship between M. caroli, M. musculus, A. niloticus and O. torridus. This identified gene can be a rich informational resource to specify diseases at embryo level in humans.
References
- Holsinger K E. (2013) Brenner's encyclopedia of genetics. Cytogenetics 268:270.
- Maloy S R, Hughes K. (2013) Brenner's encyclopedia of genetics. Academic Press.
- Parvin M S, Okuyama N, Inoue F, Islam M E, Kawakami A, et al. (2008) Autoregulatory loop and retinoic acid repression regulate pou2/pou5f1 gene expression in the zebrafish embryonic brain. Dev Dyn 237(5):1373-1388.
- Sigrist C J A, Castro E, Cerutti L, Cuche B A, Hulo N, et al. (2012) New and continuing developments at PROSITE. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D344-7.
- Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting C P. (1998) SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(11):5857-5864.
- Finn R D, Bateman A, Clements J, Coggill P, Eberhardt R Y, et al. (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database issue): D222-D230.
- Sievers F, Higgins D G. (2014) Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol Biol 1079:105-116.
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Koichiro Tamura. (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6): 1547-1549.
- Guo A Y, Zhu Q H, Chen X, Luo J C. (2007) GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi chuan 29(8):1023-1026.
- Trifinopoulos J, Nguyen L T, Haeseler A V, Minh B Q. (2016) W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W232-W235.
- Russell D J. (2014) Multiple sequence alignment methods. Springer 1079.
- Campbell P A, Rudnicki M A. (2013) Oct4 interaction with Hmgb2 regulates Akt signaling and pluripotency. Stem Cells 31(6):1107-1120.
- Rosner M H, Vigano M A, Ozato K, Timmons P M, Poirier F, et al. (1990) A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature 345(6277): 686-692.
- Okamoto K, Okazawa H, Okuda A, Sakai M, Muramatsu M, et al. (1990) A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell 60(3):461-472.
- Plachta N, Bollenbach T, Pease S, Fraser S E, Pantazis P. (2011) Oct4 kinetics predict cell lineage patterning in the early mammalian embryo. Nat Cell Biol 13(2):117-123.
- Niwa H, Toyooka Y, Shimosato D, Strumpf D, Takahashi K, et al. (2005) Interaction between Oct3/4 and Cdx2 determines trophectoderm differentiation. Cell 123(5):917-929.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences